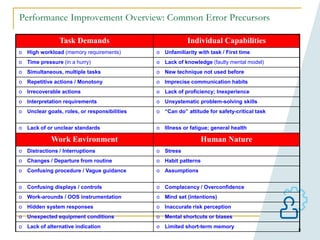
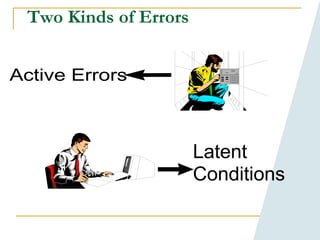
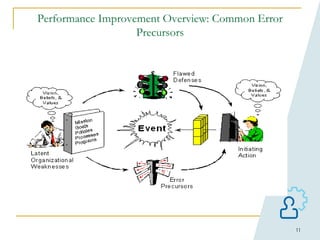
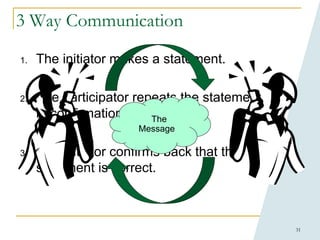
This document provides an overview of human performance improvement and error prevention tools. It describes 8 fundamental tools: tailboards, S.T.A.R (self-checking), 3-way communication, 2-minute rule, stop when unsure, questioning attitude, phonetic alphabet, and procedure use and adherence. The tools are designed to anticipate, prevent, and catch errors by promoting work preparation, performance, feedback, and defense in depth through techniques like pre-job briefings, self-verification, clear communication, situational awareness, and adherence to approved procedures. Mastering these tools can help reduce mistakes and improve safety.