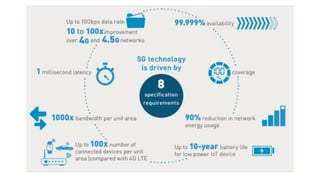
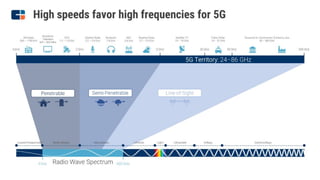
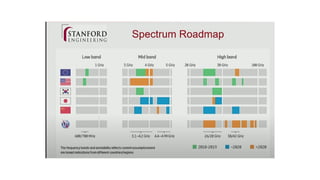
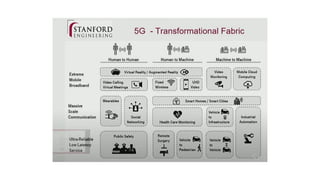
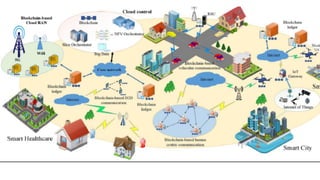
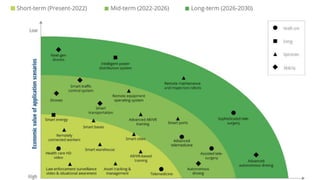
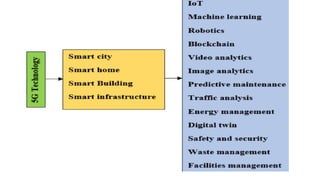
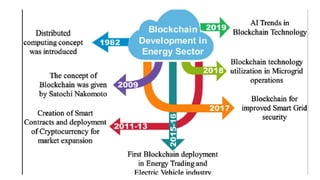
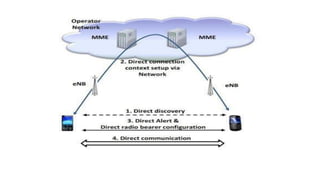
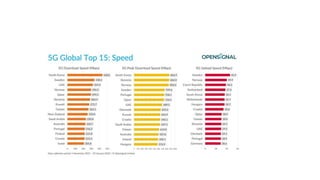
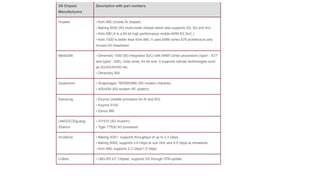
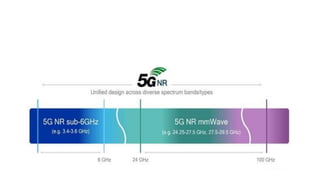
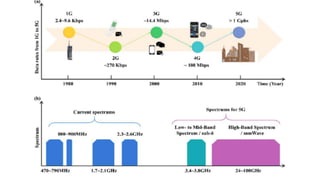
The document discusses the evolution of mobile network generations from 1G to 5G. 1G allowed mobile voice calls, 2G added text messaging and roaming, 3G provided improved mobile internet, 3.5G brought true mobile internet access enabling apps, 4G provided high-speed internet on IP networks, and 5G expands broadband wireless beyond mobile to connect many devices with low latency. Key aspects of 5G networks that improve on 4G include higher peak speeds, ability to connect more devices simultaneously, and support of new applications like connected vehicles and remote surgery through telemedicine.