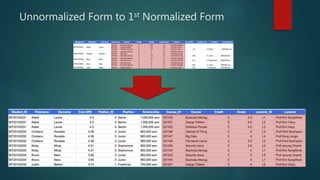
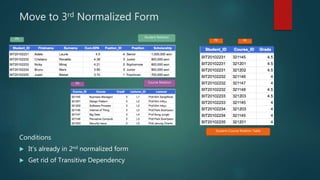
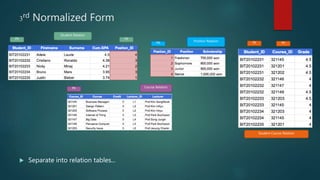
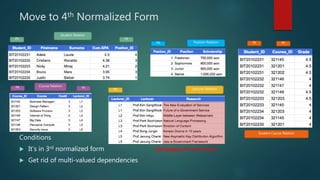
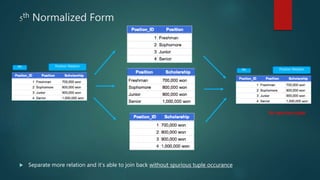
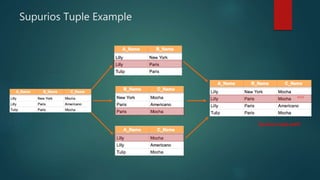
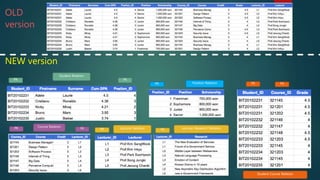
This document discusses database normalization through five forms. It explains why normalization is important to minimize data redundancy and update anomalies. The five normalization forms are described as removing repeating groups (1st), partial dependencies (2nd), transitive dependencies (3rd), remaining anomalies from functional dependencies (4th), and multi-value dependencies (5th). Examples are provided to illustrate transforming an unnormalized database design into normalized forms through separating relations and removing dependencies between fields.