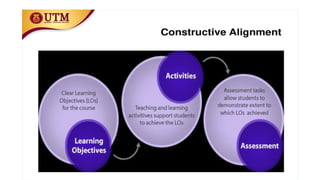
The document discusses constructive alignment in geography education, emphasizing the importance of engaging learners through relevant activities that meet clearly defined learning objectives. It outlines how teaching strategies, methods, and assessments must align with these objectives to promote deep learning and comprehension. The example provided illustrates how teaching practices and assessment tasks can effectively enhance learner understanding of geographic concepts like slope.