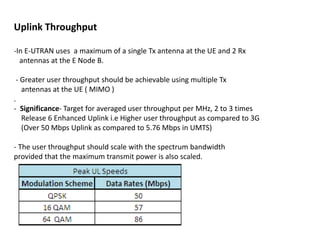
Drive Test Parameters document summarizes key LTE network parameters measured by user equipment (UE) including:
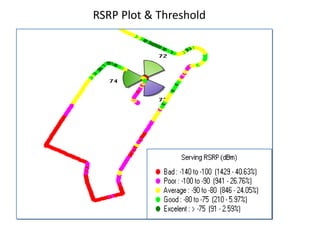
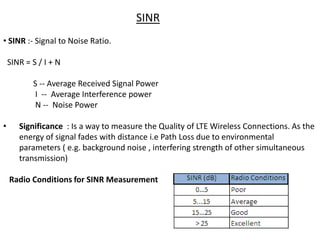
1) RSRP, RSRQ, SINR - measurements of downlink signal strength and quality used for handover decisions and determining optimum network settings.
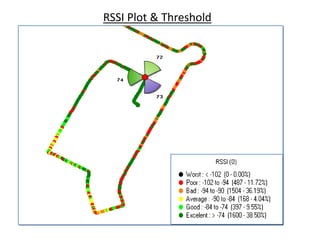
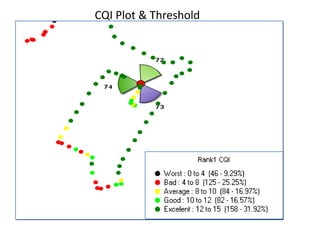
2) RSSI, CQI, BLER - additional signal quality metrics where CQI indicates channel quality and BLER measures error rate.
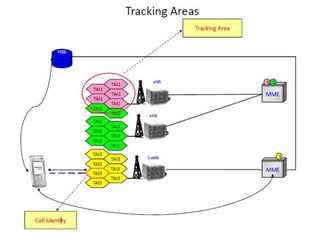
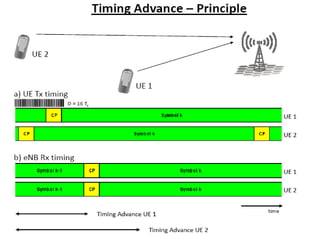
3) PCI, Tracking Area Code - identifiers to locate cell and tracking area within the network. Timing Advance is also discussed to synchronize uplink transmissions.