This document provides an introduction and overview of PHP. It discusses that PHP is a server-side scripting language used for web development that can be embedded into HTML. It then covers PHP syntax including using <?php ?> tags, variables, data types, operators, conditional statements, loops, functions, and regular expressions. The document also provides examples of common PHP functions for arrays, calendars, dates, math, mail, MySQLi, strings, and errors.











![PHP Constants
<?php
define("GREETING", "Welcome to india.com!");
echo GREETING;
?>
<?php
define("cars", ["Alfa Romeo", "BMW", "Toyota"]);
echo cars[0];
?>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-200316063722/75/Php-12-2048.jpg)







![PHP Date function
Function Description
getdate() Returns date/time
information of a
timestamp or the
current local
date/time
print_r(getdate());
Array ( [seconds] => 50 [minutes] => 16 [hours] => 9 [mday] => 17
[wday] => 1 [mon] => 2 [year] => 2020 [yday] => 47 [weekday] =>
Monday [month] => February [0] => 1581931010 )
time() Returns the current
time as a Unix
timestamp
echo($t);
echo(date("Y-m-d",$t));
1581931163
2020-02-17
date_diff() Returns the
difference between
two dates
$date1=date_create("2013-03-15");
$date2=date_create("2013-12-12");
$diff=date_diff($date1,$date2);
echo $diff->format("%R%a days");
date_date_
set()
Sets a new date $date=date_create();
date_date_set($date,2020,10,30);
echo date_format($date,"Y/m/d");](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-200316063722/75/Php-22-2048.jpg)





![Regular Expression
REGULAR EXPRESSION MATCHES
rit The string “rit”
^rit The string which starts with “rit”
rit$ The string which have “rit” at the end.
^rit$ The string where “rit” is alone on a string.
[abc] a, b, or c
[a-z] Any lowercase letter
[^A-Z] Any letter which is NOT a uppercase letter
(gif|png) Either “gif” or “png”
[a-z]+ One or more lowercase letters
^[a-zA-Z0-9]{1, }$ Any word with at least one number or one letter
([ax])([by]) ab, ay, xb, xy
[^A-Za-z0-9] Any symbol other than a letter or other than number
([A-Z]{3}|[0-9]{5}) Matches three letters or five numbers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-200316063722/75/Php-31-2048.jpg)
![Operators in Regular Expression
OPERATOR DESCRIPTION
^ It denotes the start of string.
$ It denotes the end of string.
. It denotes almost any single character.
() It denotes a group of expressions.
[]
It finds a range of characters for example [xyz] means x, y or
z .
[^]
It finds the items which are not in range for example [^abc]
means NOT a, b or c.
– (dash)
It finds for character range within the given item range for
example [a-z] means a through z.
| (pipe) It is the logical OR for example x | y means x OR y.
? It denotes zero or one of preceding character or item range.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-200316063722/75/Php-32-2048.jpg)



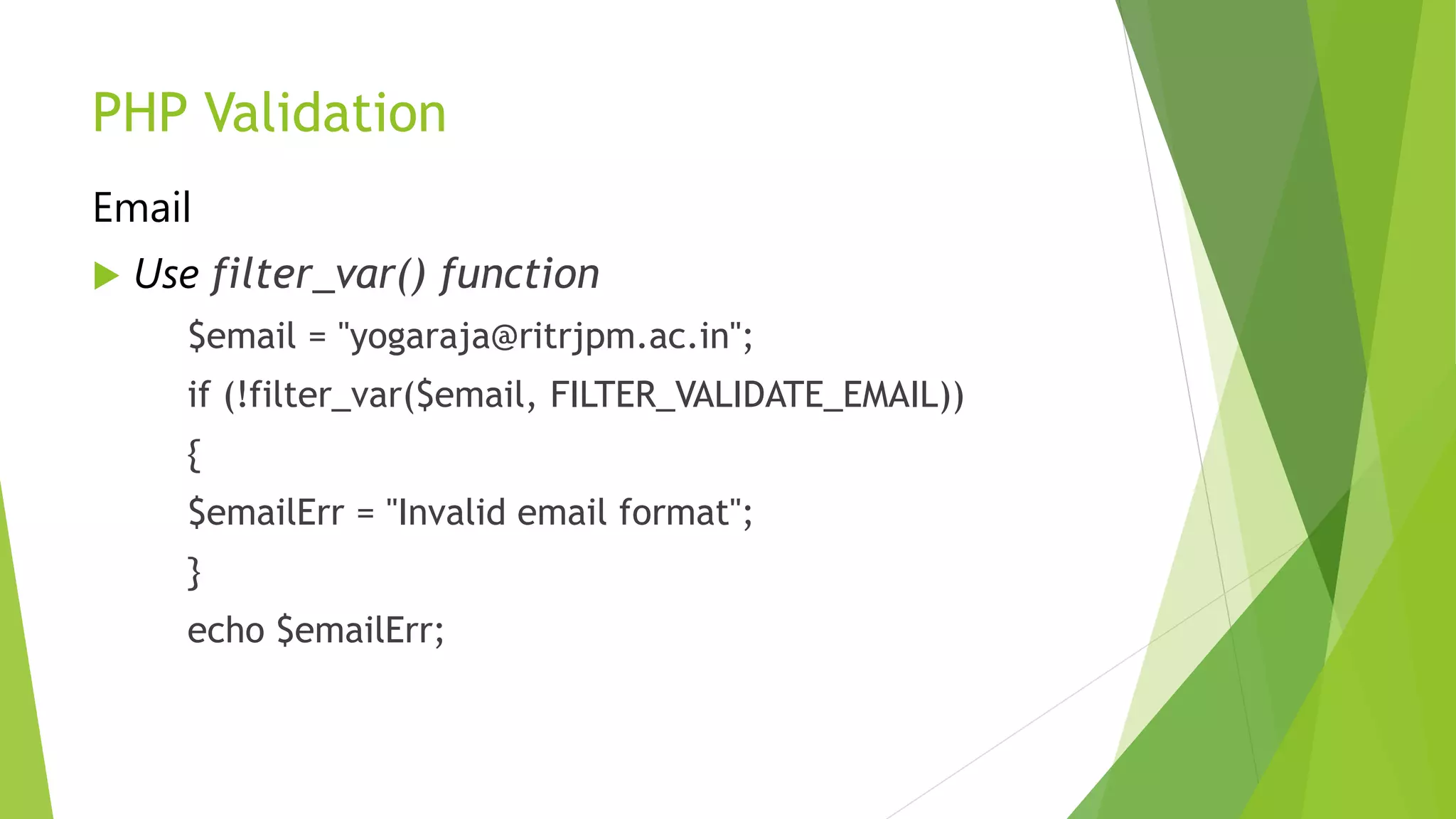
![PHP Validation
Name
Use preg_match() function
if (!preg_match("/^[a-zA-Z ]*$/",$name))
{
$nameErr = "Only letters and white space allowed";
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-200316063722/75/Php-38-2048.jpg)



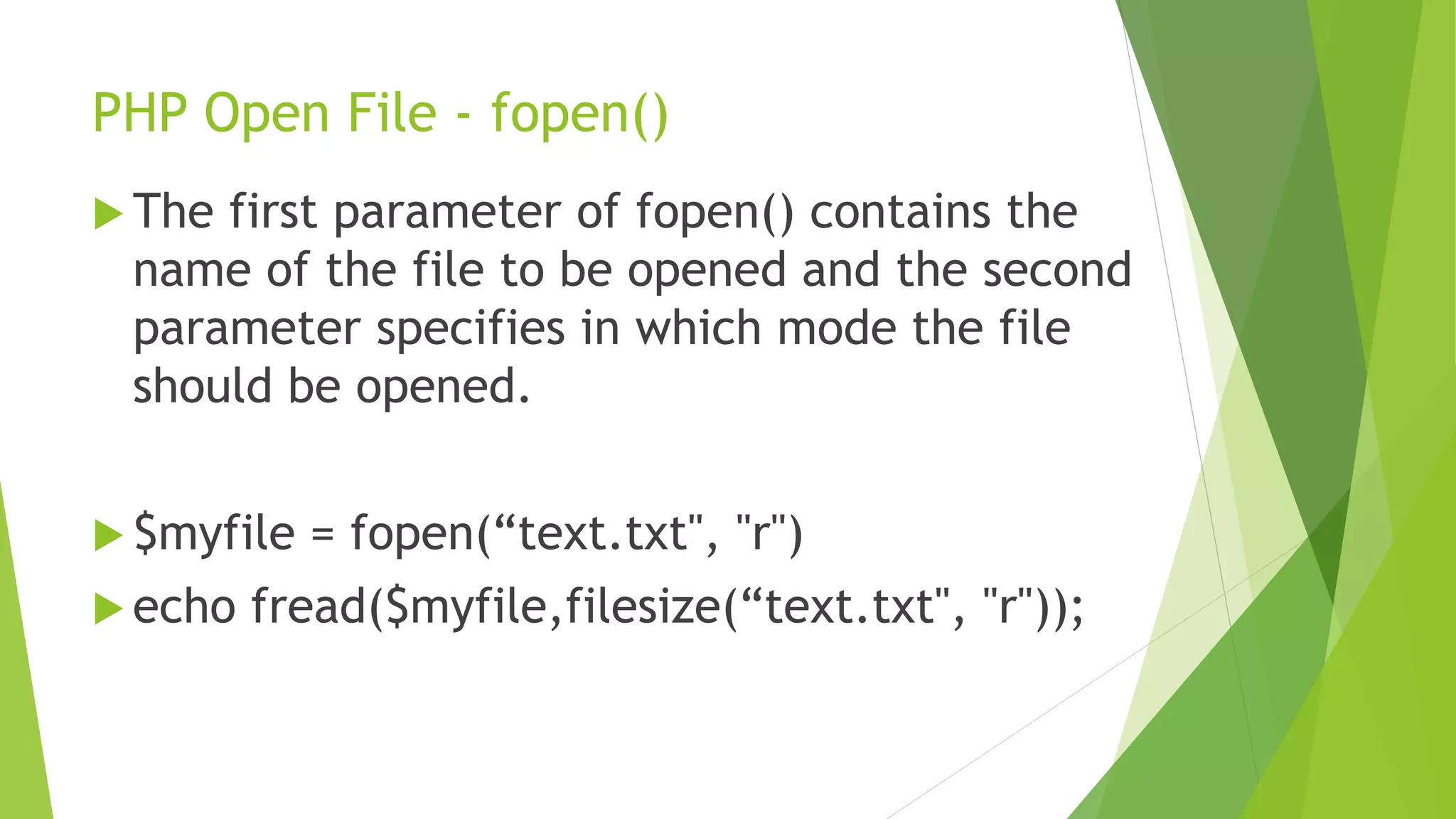







![PHP Cookies
Retrieve Cookies
<?php
if(!isset($_COOKIE[$cookie_name])) {
echo "Cookie is not set!";
} else {
echo "Cookie '" . $cookie_name . "' is set!<br>";
echo "Value is: " . $_COOKIE[$cookie_name];
}
?>
The value of the cookie is automatically URLencoded when sending the cookie, and
automatically decoded when received (to prevent URLencoding, use setrawcookie()
instead).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-200316063722/75/Php-51-2048.jpg)





![PHP Sessions
<?php
session_start();
?>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<?php
$_SESSION["favcolor"] = "green";
?>
</body>
</html>
Note: The session_start()
function must be the very
first thing in your document.
Before any HTML tags.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-200316063722/75/Php-57-2048.jpg)

![PHP Sessions
Reading Session Values
<?php
session_start();
?>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<?php
echo "Favorite color is " . $_SESSION["favcolor"] . ".<br>";?>
</body>
</html>
To show all the session
variable values for a
user session
<?php
print_r($_SESSION);
?>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-200316063722/75/Php-59-2048.jpg)


