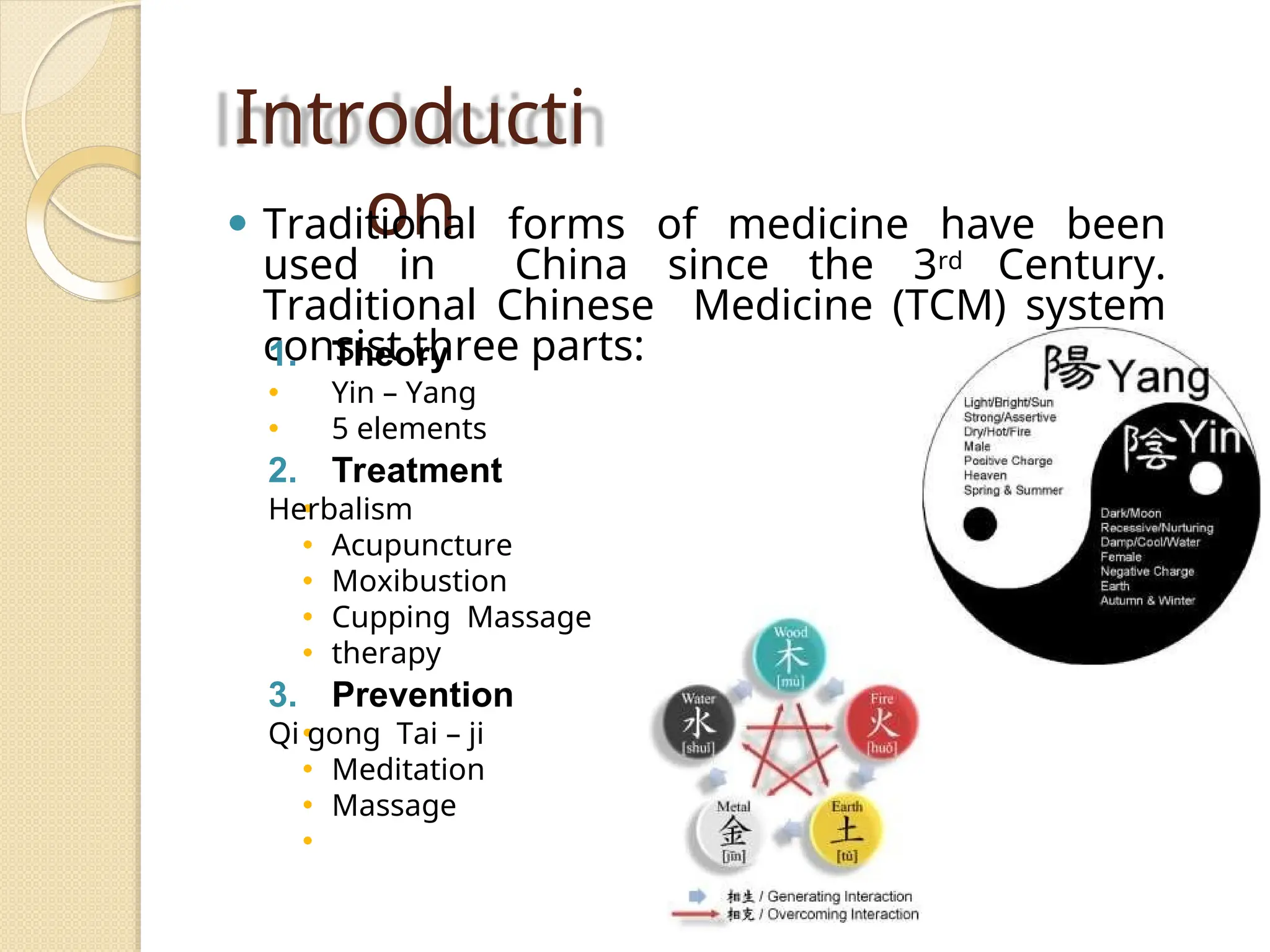
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) is an ancient healing system that utilizes herbal medicines, acupuncture, and mind-body practices to maintain health and prevent disease, based on concepts like yin-yang balance and qi flow. TCM includes various practices such as acupuncture, moxibustion, cupping, Chinese herbalism, and qigong, each with distinct techniques and purposes. While generally safe, TCM practices may have risks, including potential contamination in herbal products and complications from improperly administered acupuncture.