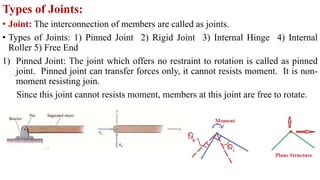
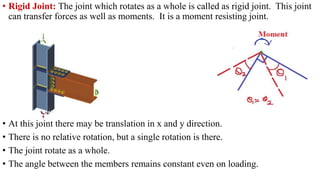
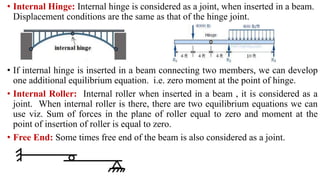
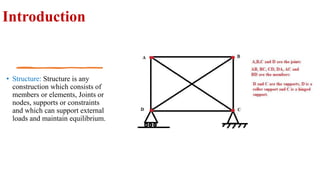
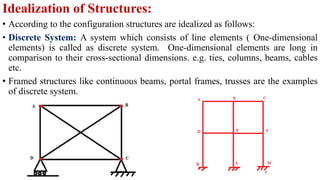
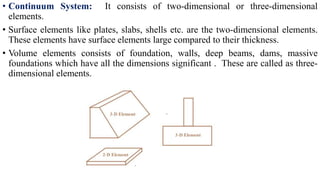
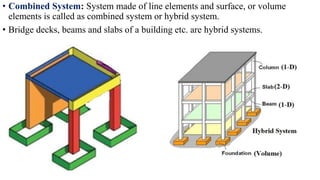
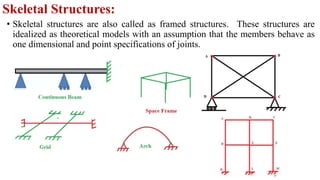
The document discusses different types of structures including discrete systems made of line elements like beams and columns, continuum systems with surface or volume elements like plates and shells, and hybrid systems combining different element types. It also defines structure as any construction consisting of members, joints, supports that can resist loads, and describes skeletal structures as framed structures idealized as theoretical models with point joints.