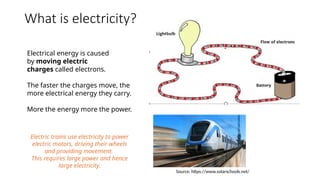
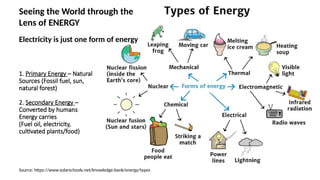
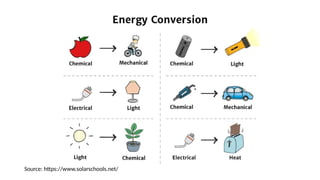
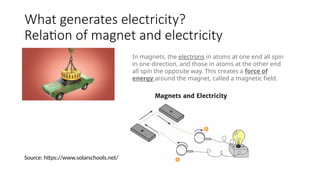
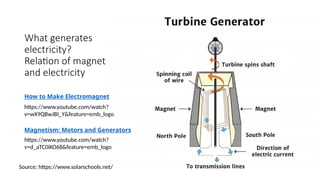
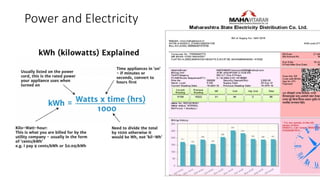
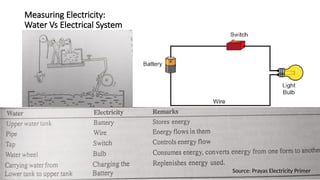
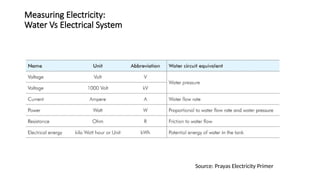
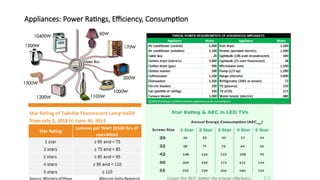
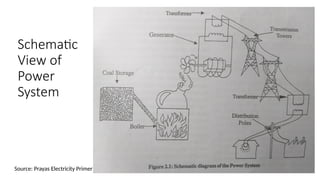
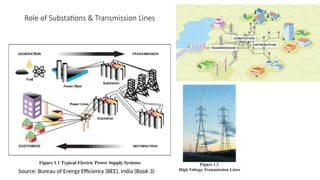
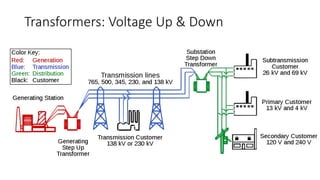
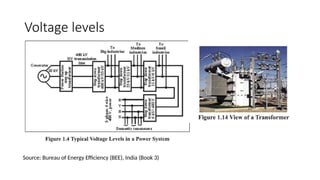
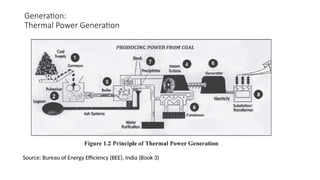
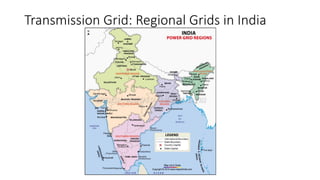
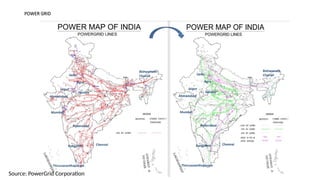
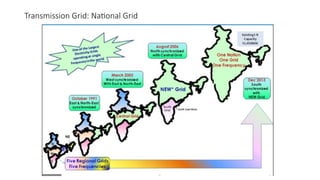
The document explains the technical aspects of power systems, covering the definitions and generation of electricity, its types, and measurement methods. It highlights the relationship between magnetism and electricity, the cost comparison of human and electric power, and the structure of power grids. Furthermore, it details power ratings, the role of substations, and the components of electricity generation and consumption.