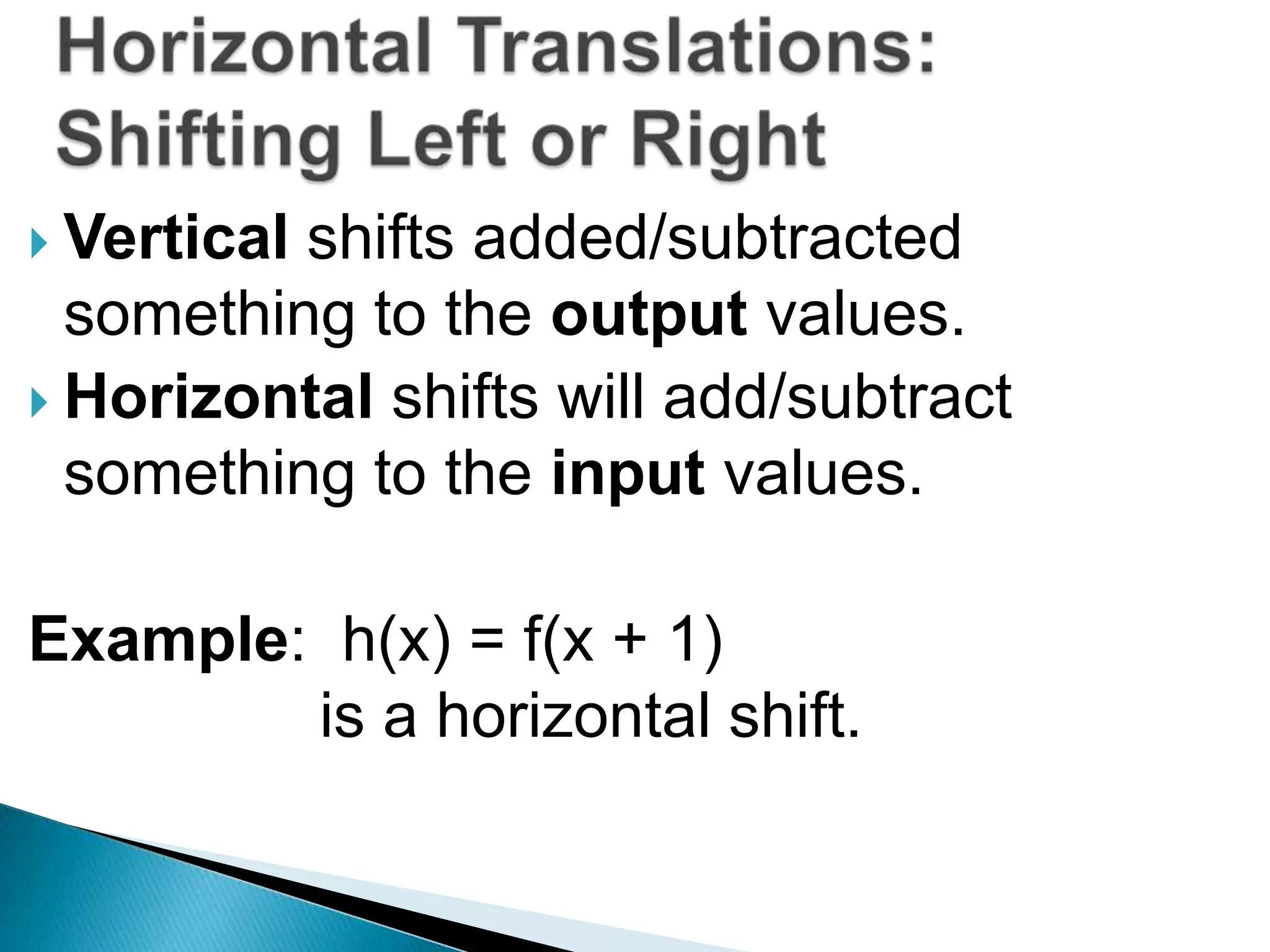
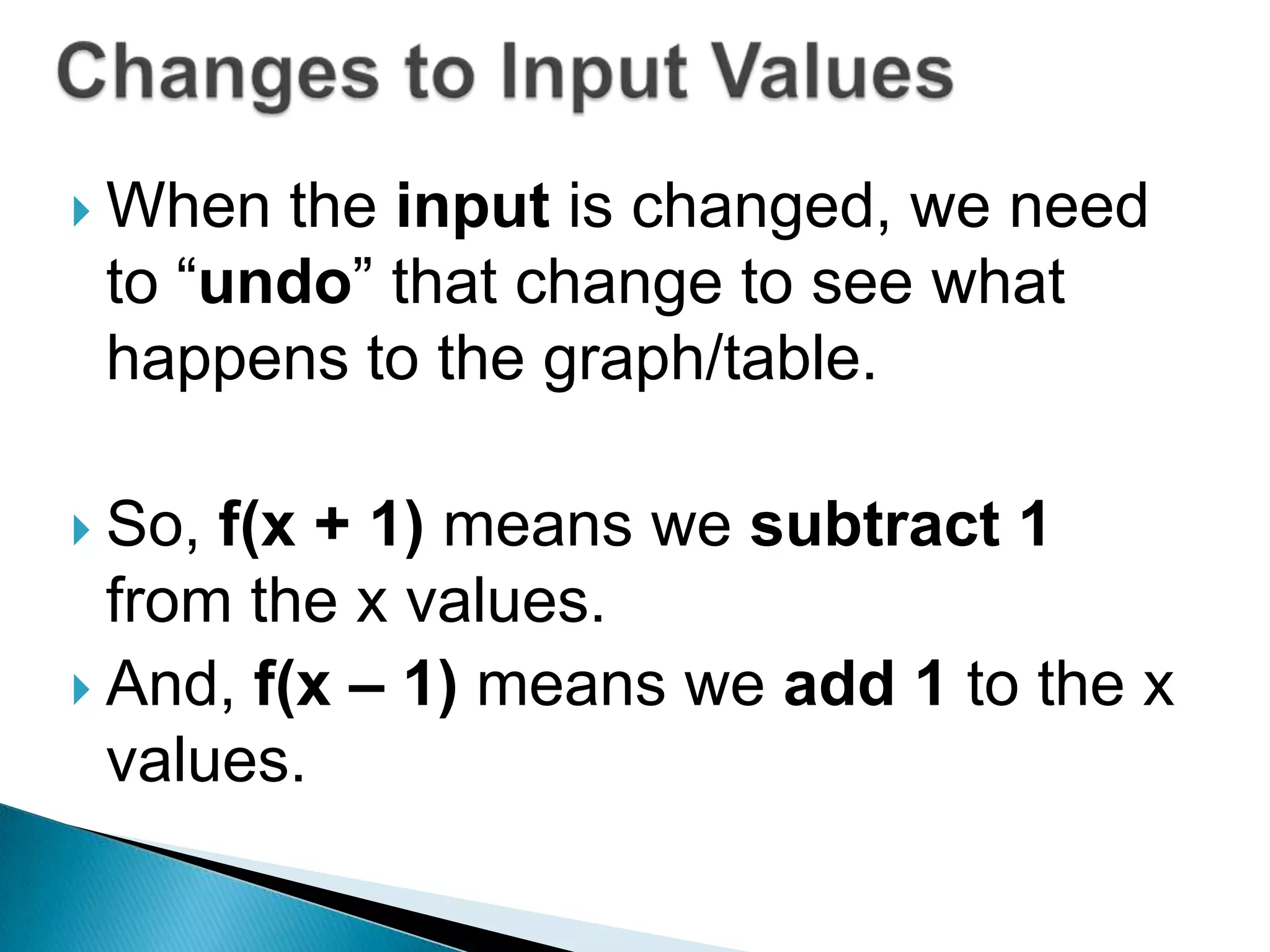
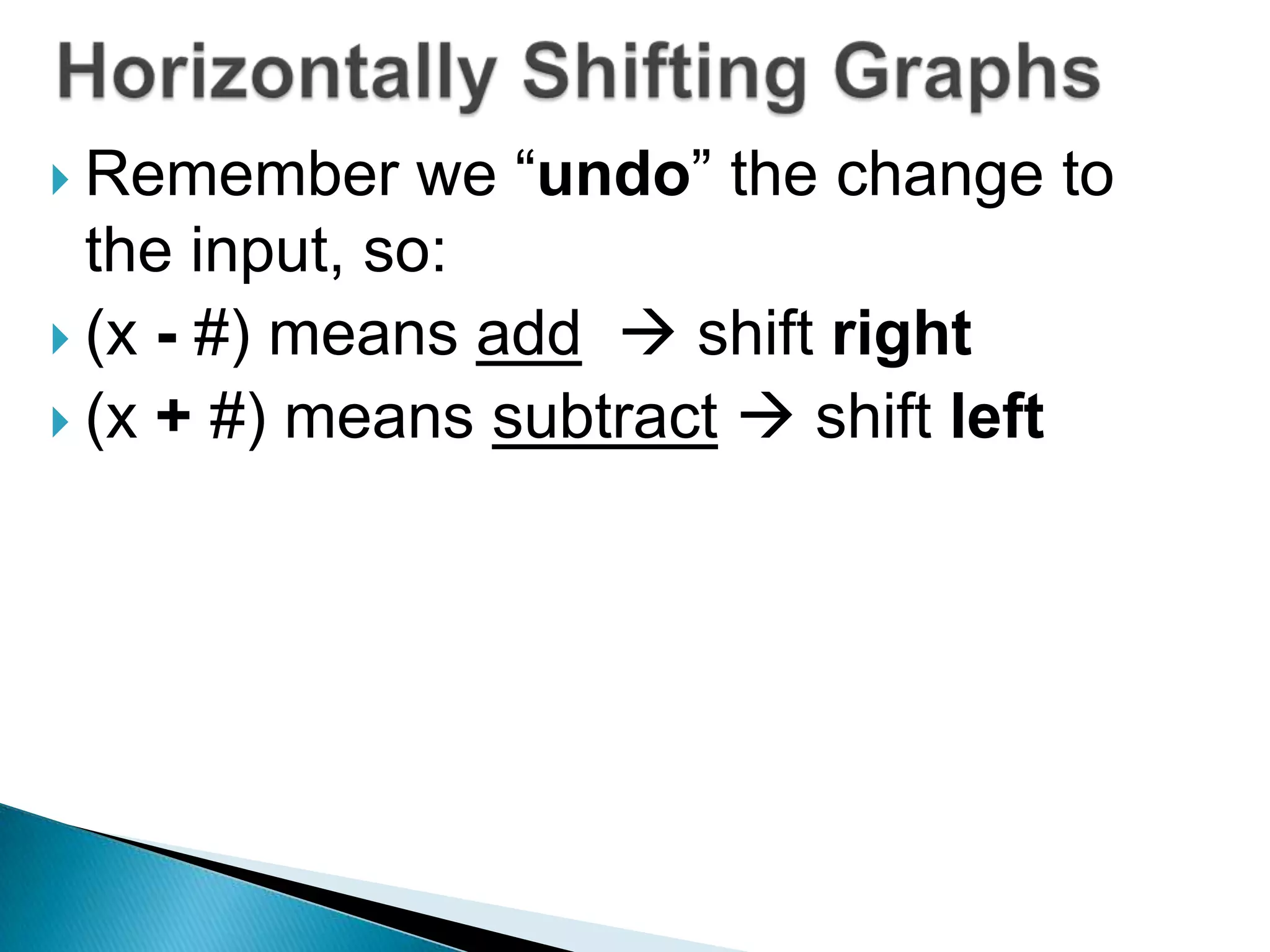
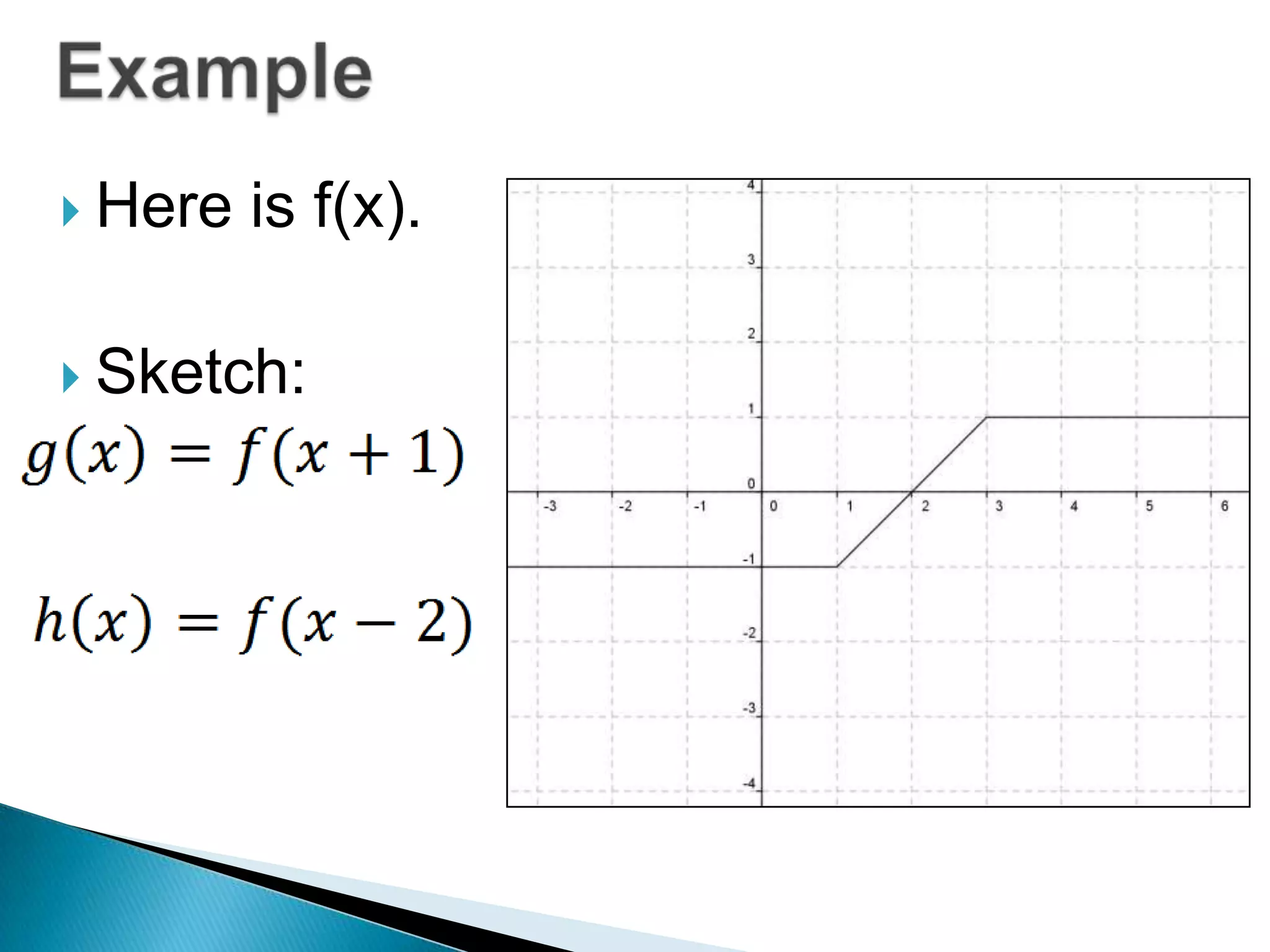
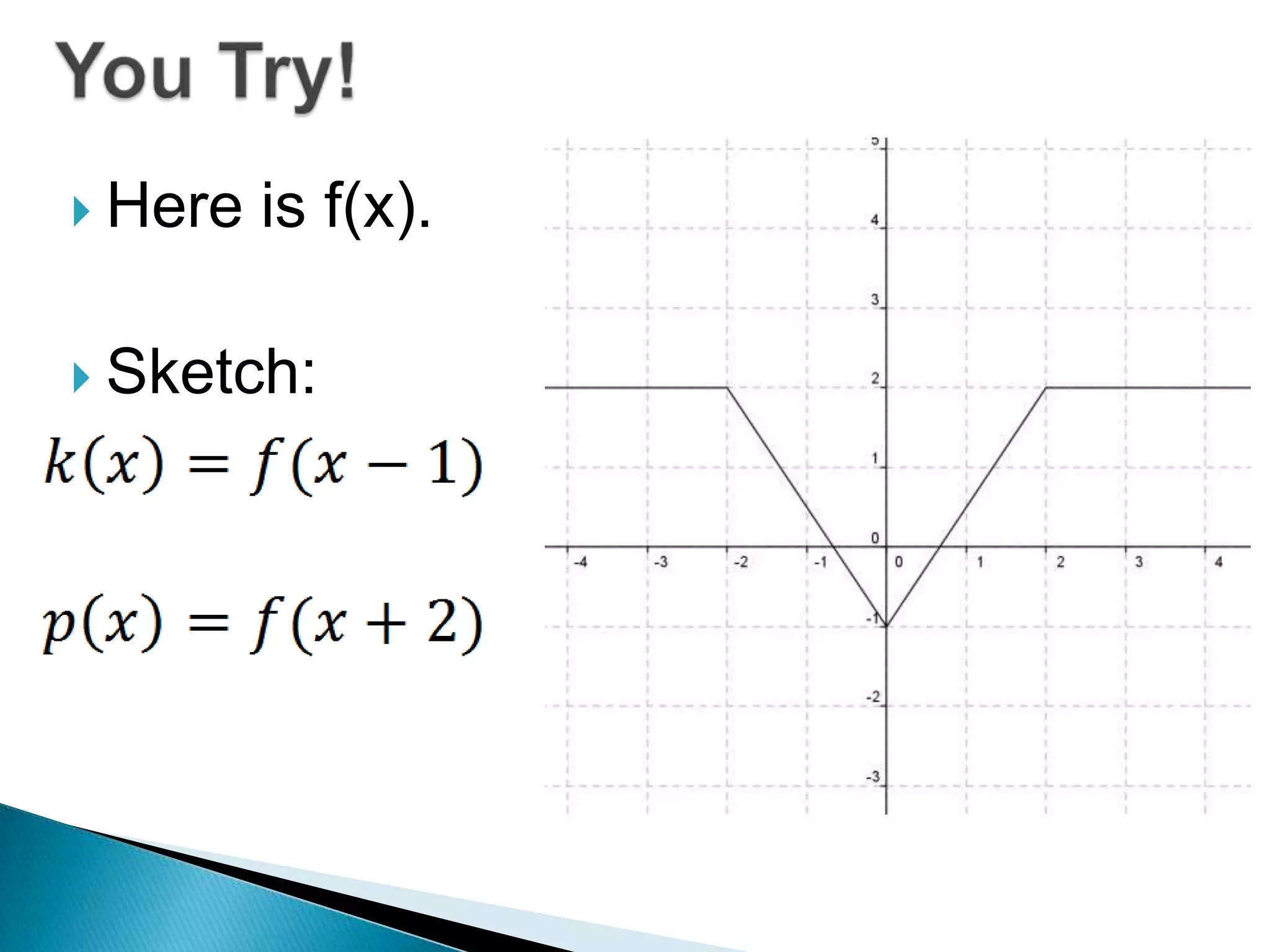
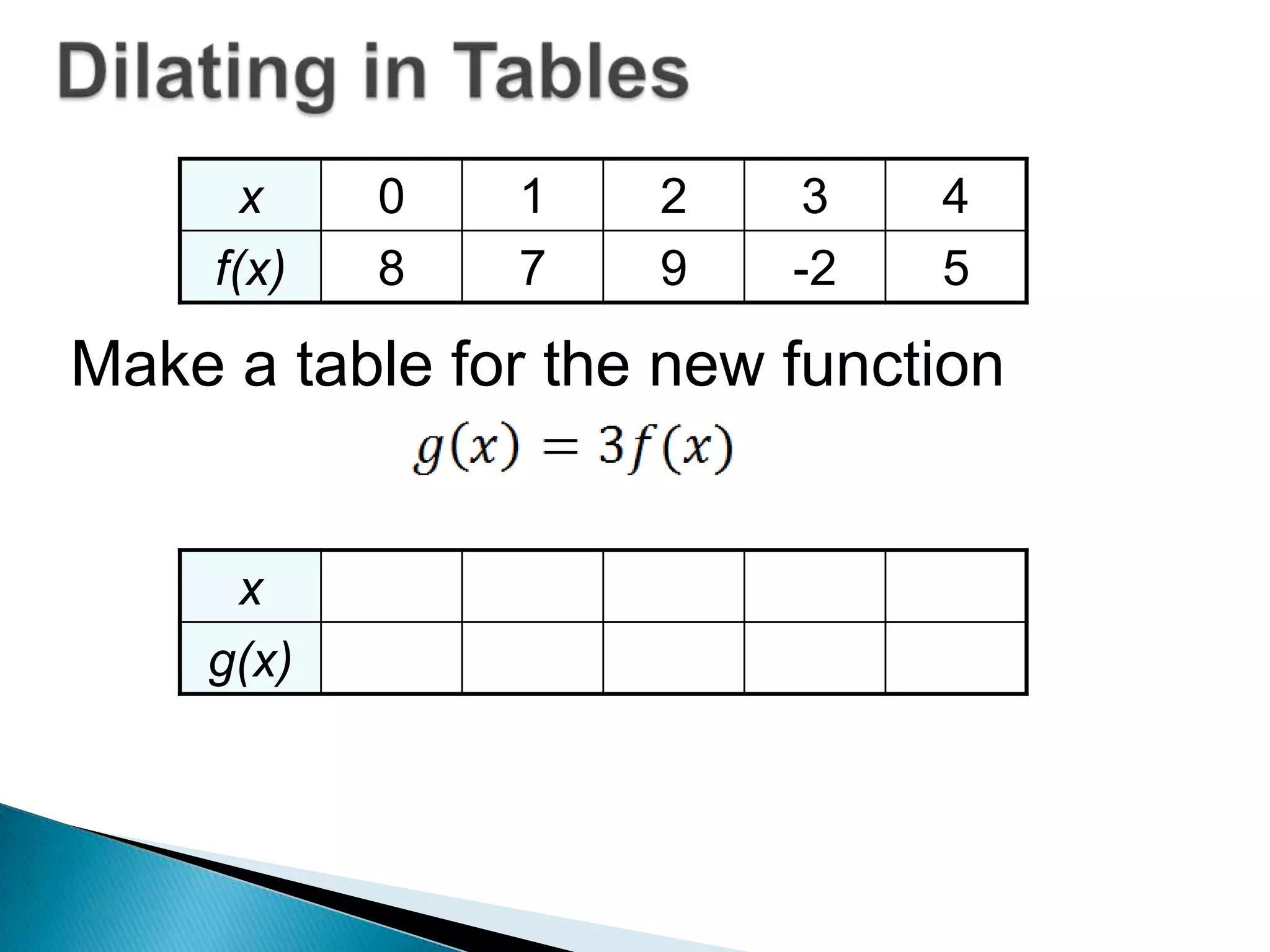
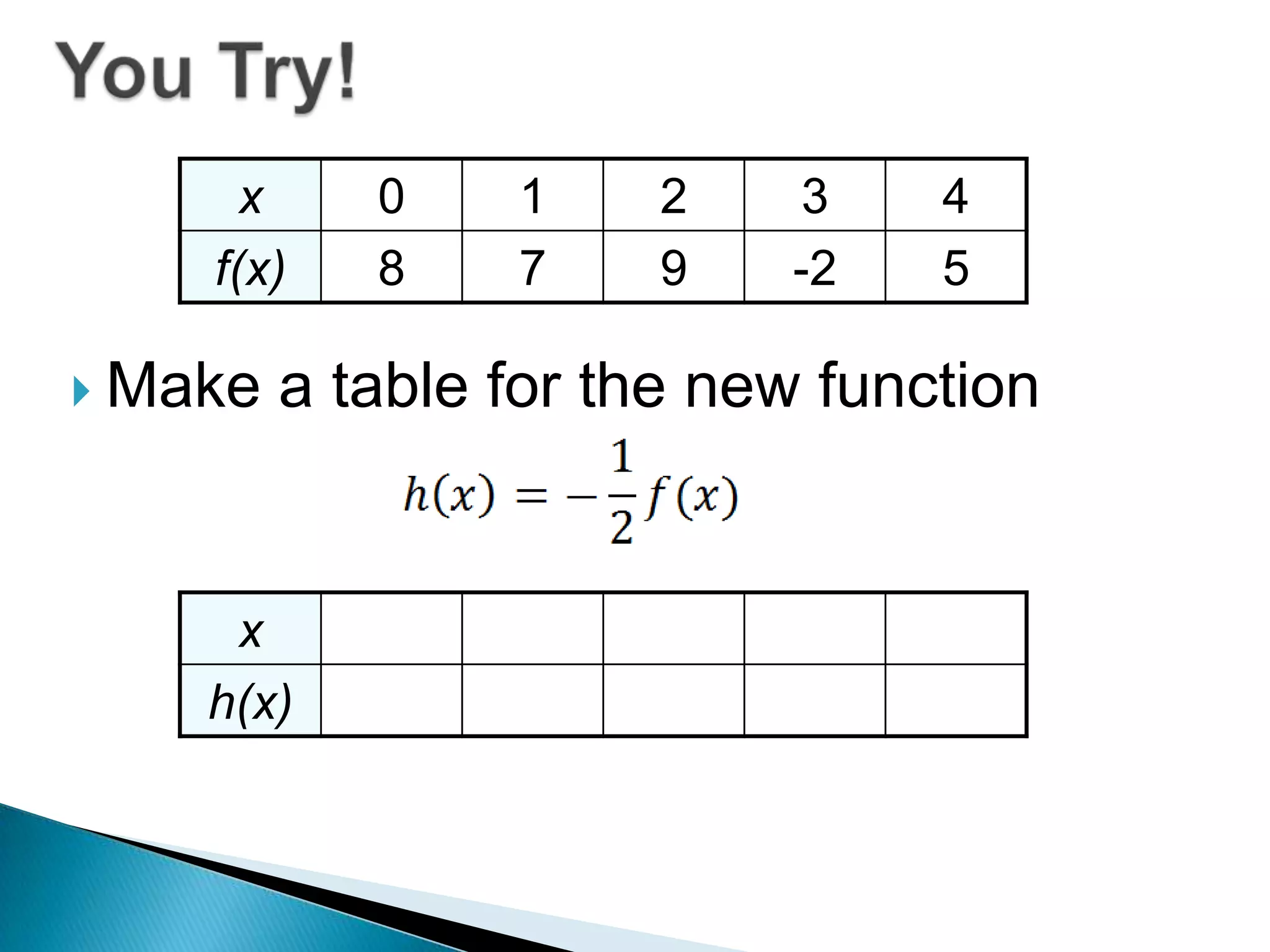
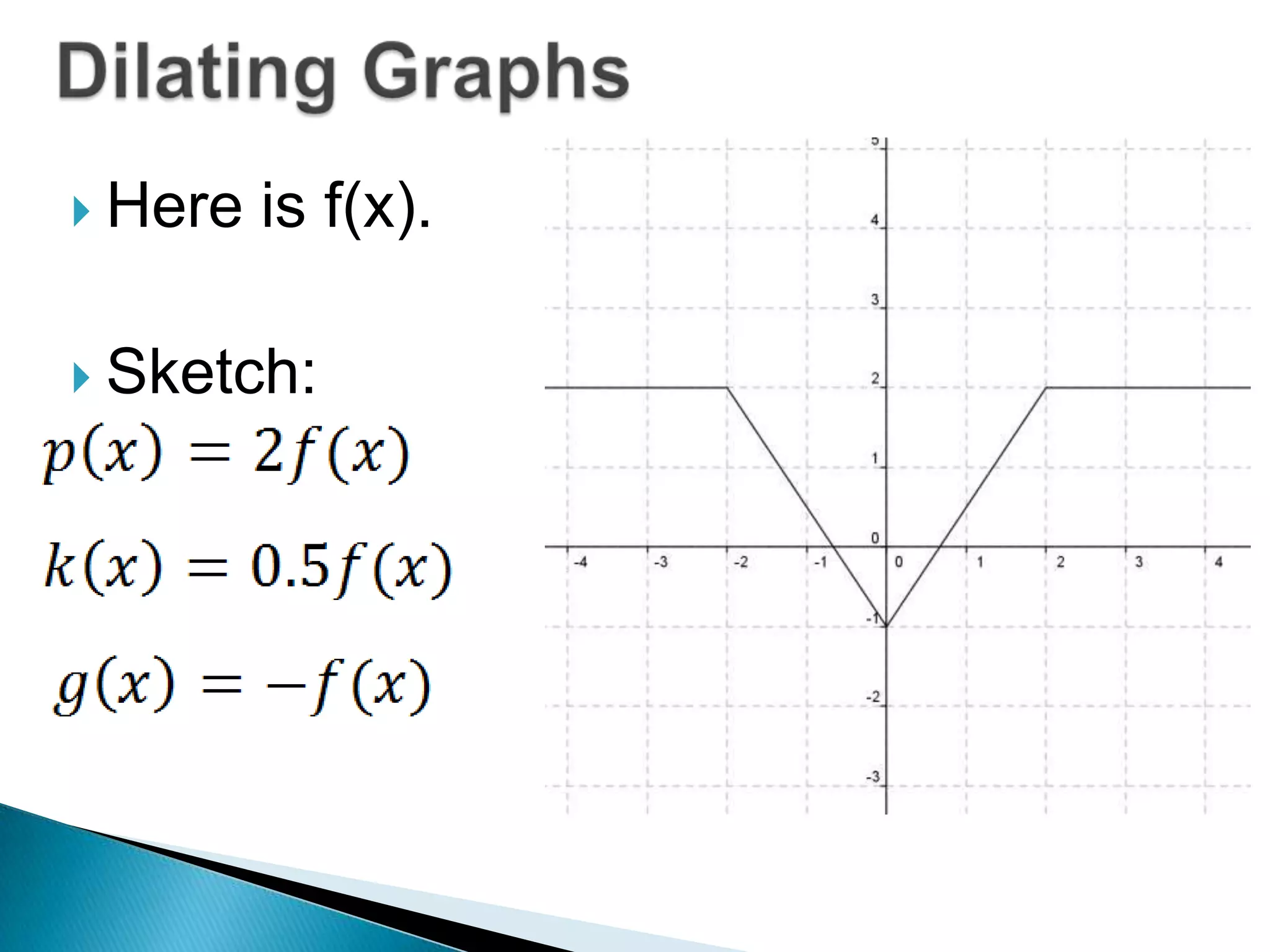
- The document discusses function transformations including translations, dilations, rotations, and reflections. It focuses on translations, which shift the graph up/down or left/right, and dilations, which shrink or stretch the graph.
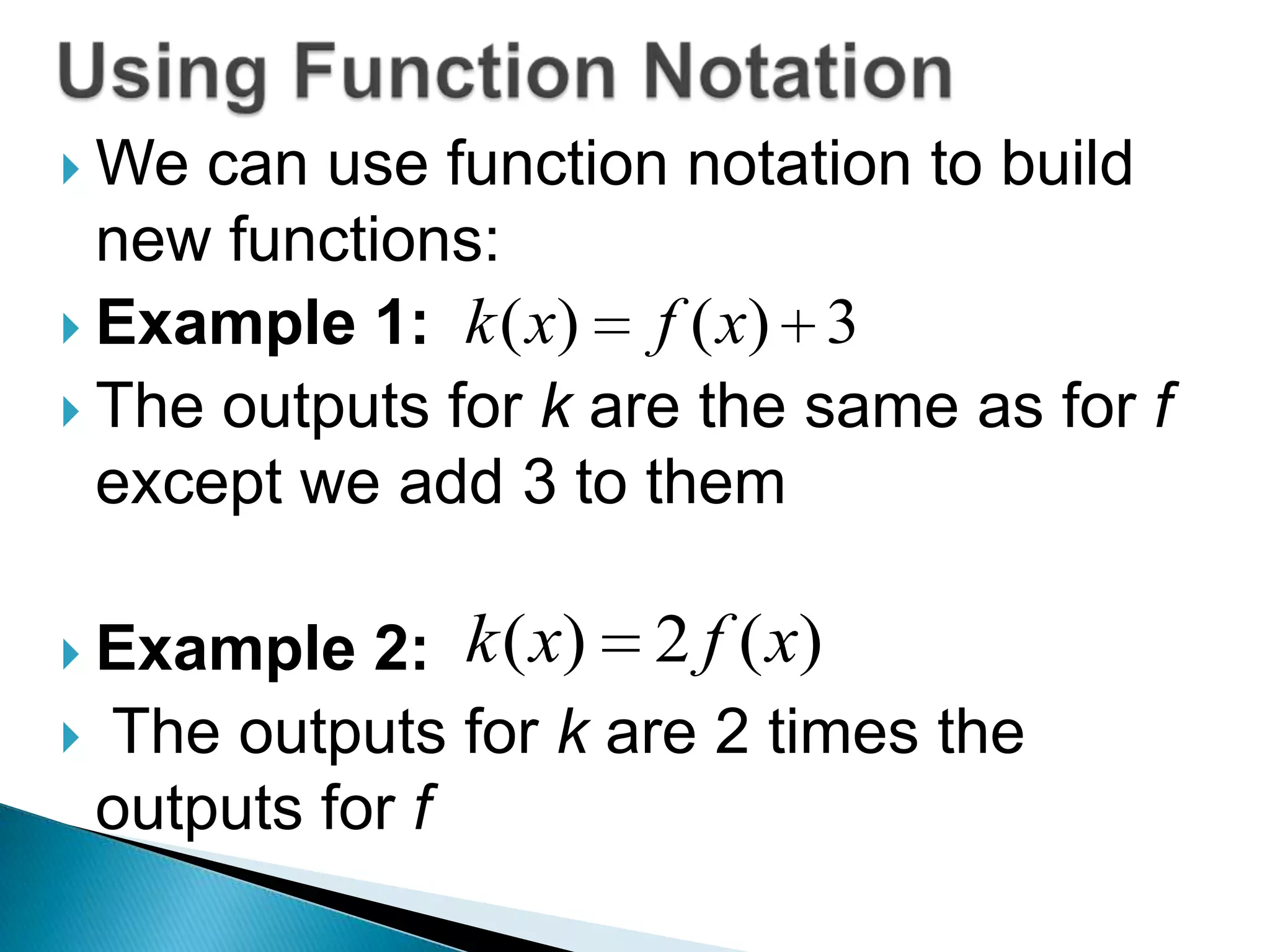
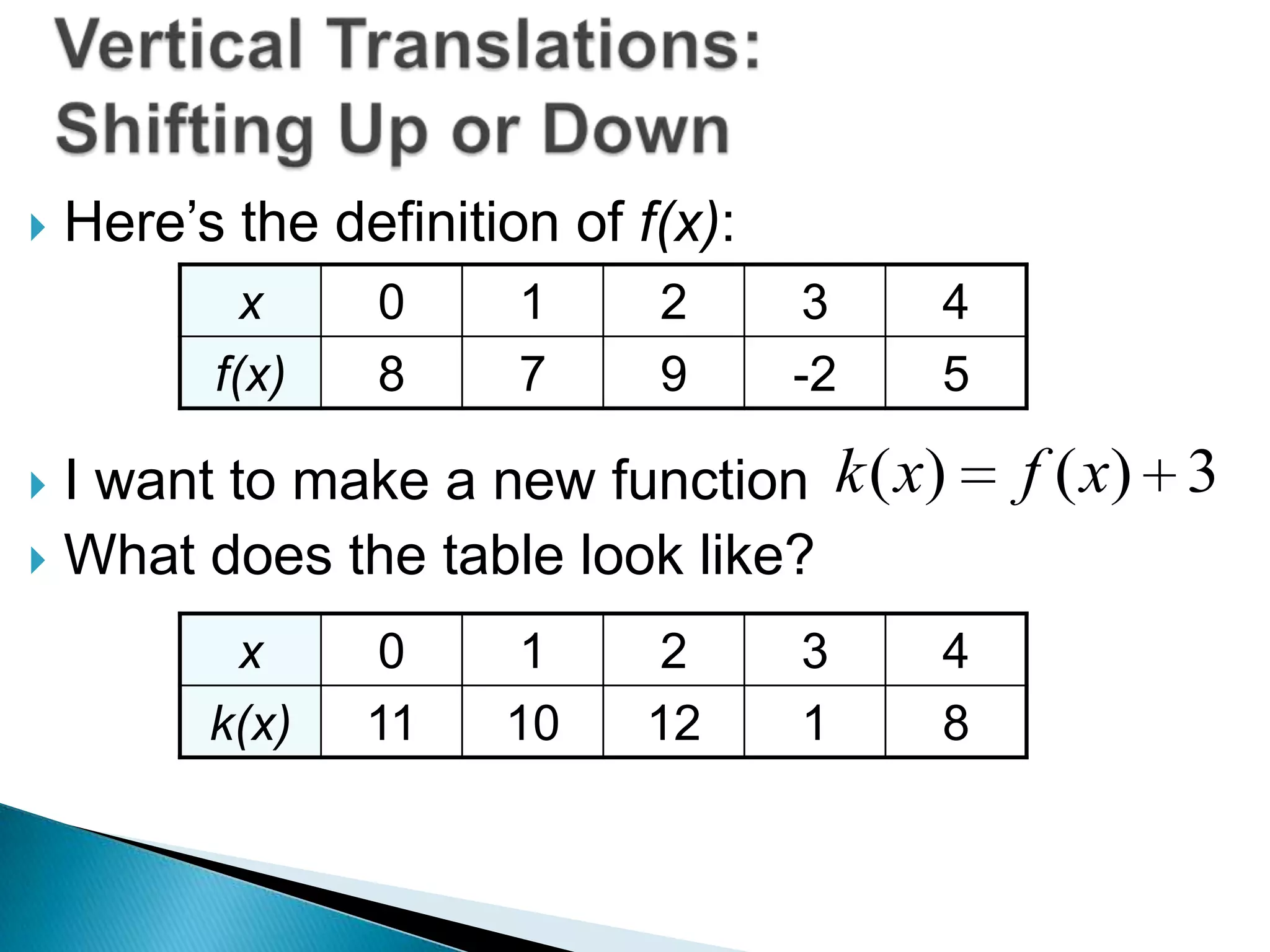
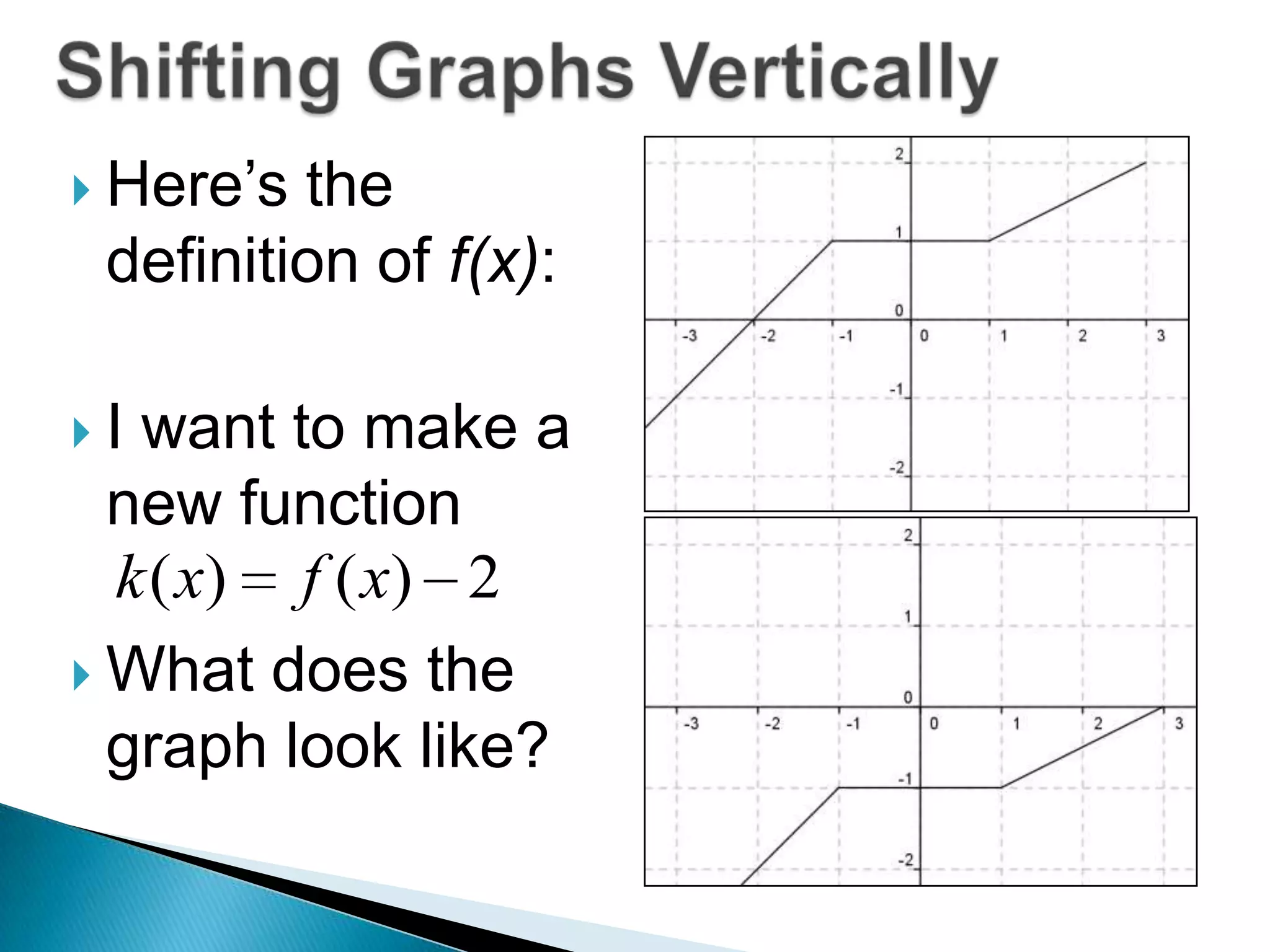
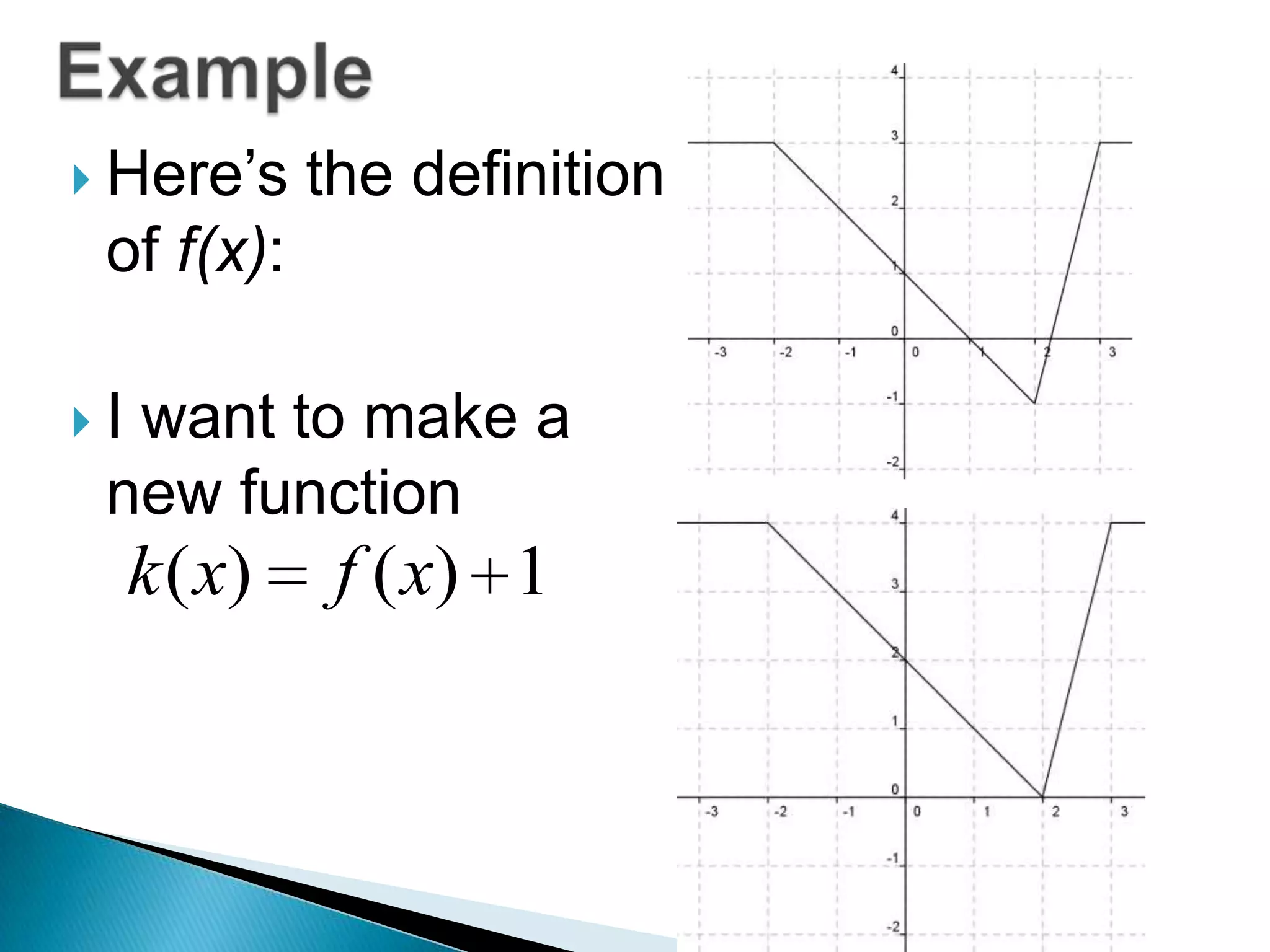
- Examples show how to write functions for translations like k(x)=f(x)+3 which shifts the graph up 3 units, and dilations like h(x)=2f(x) which stretches the graph vertically by a factor of 2.
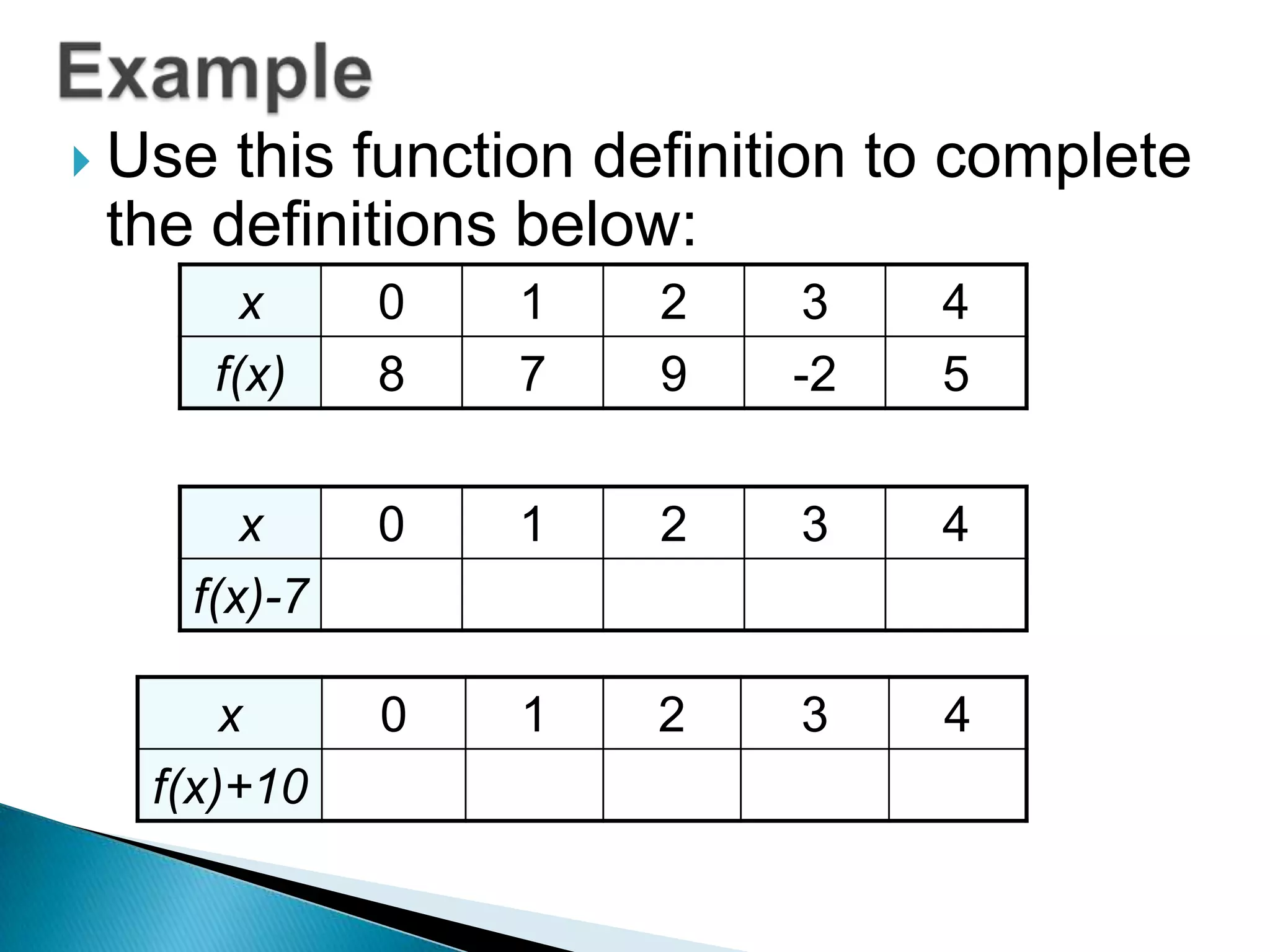
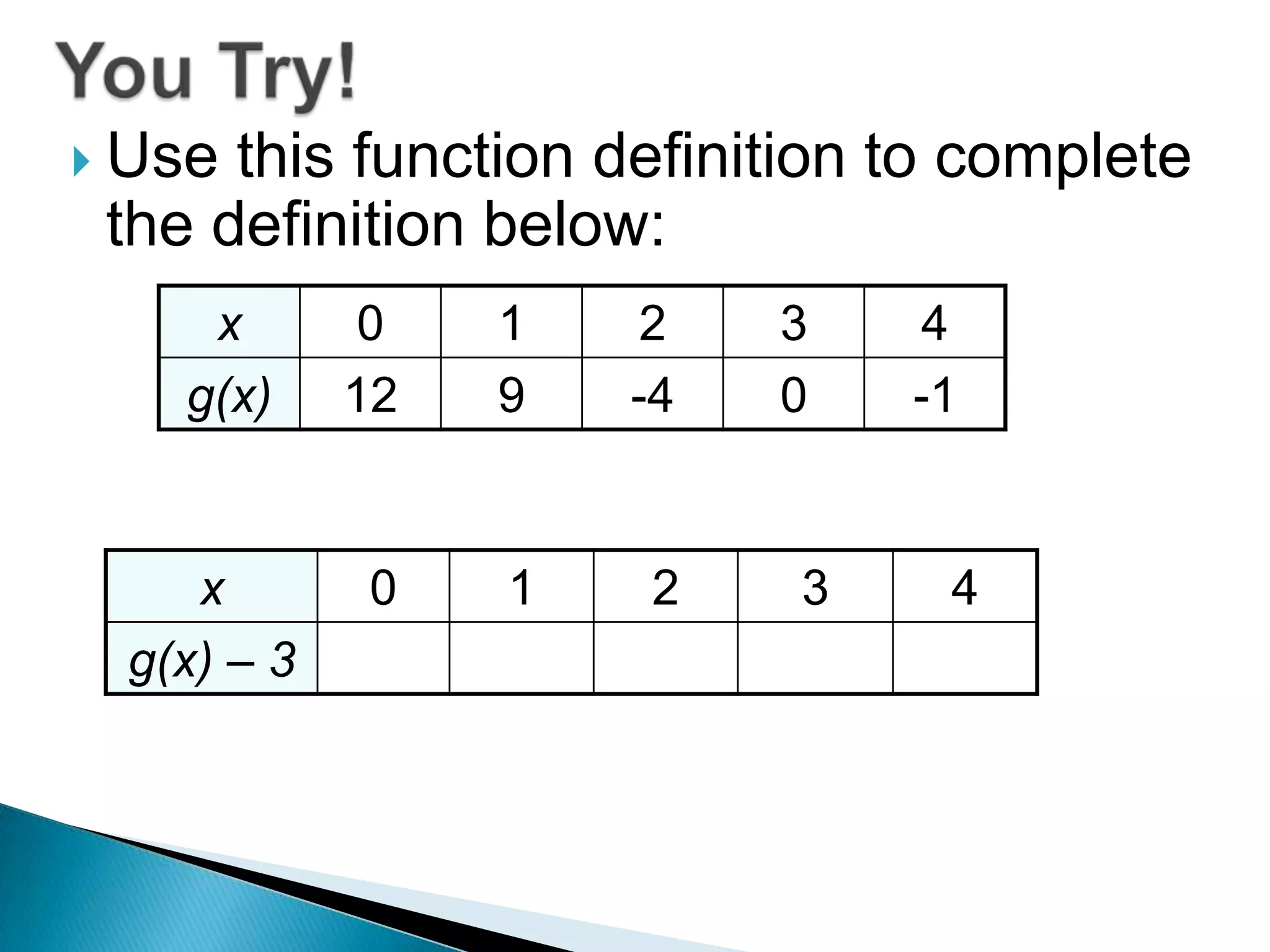
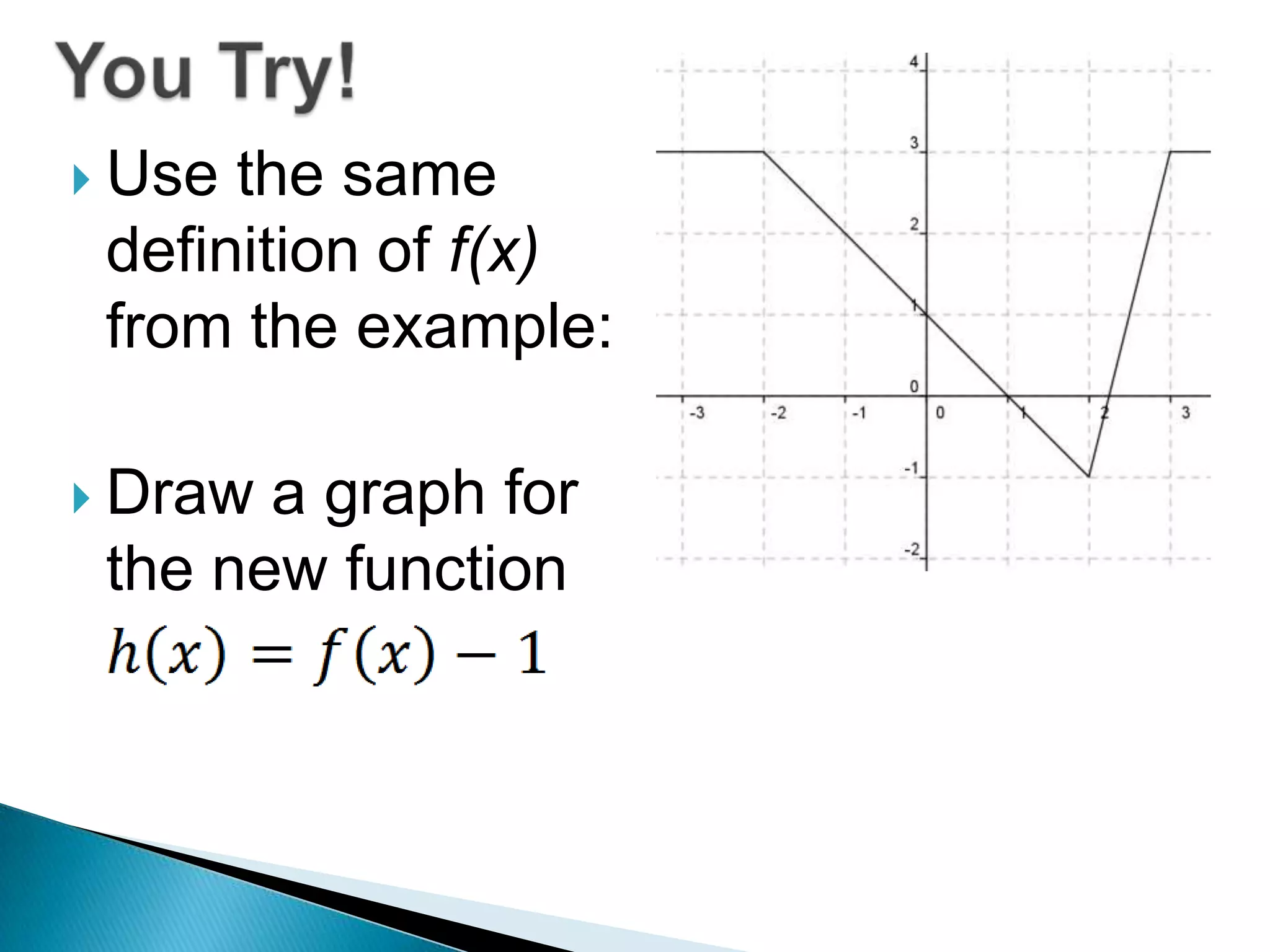
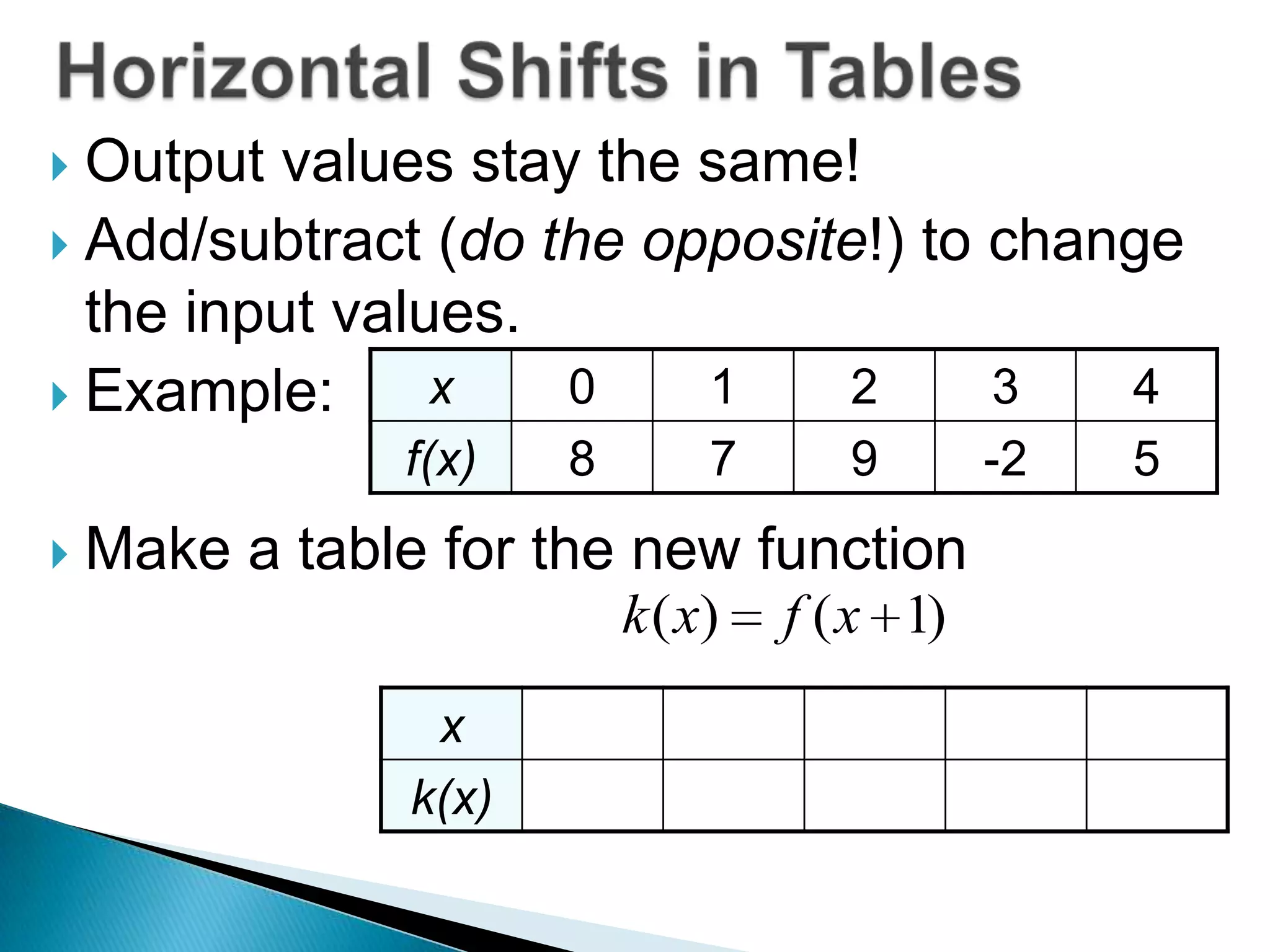
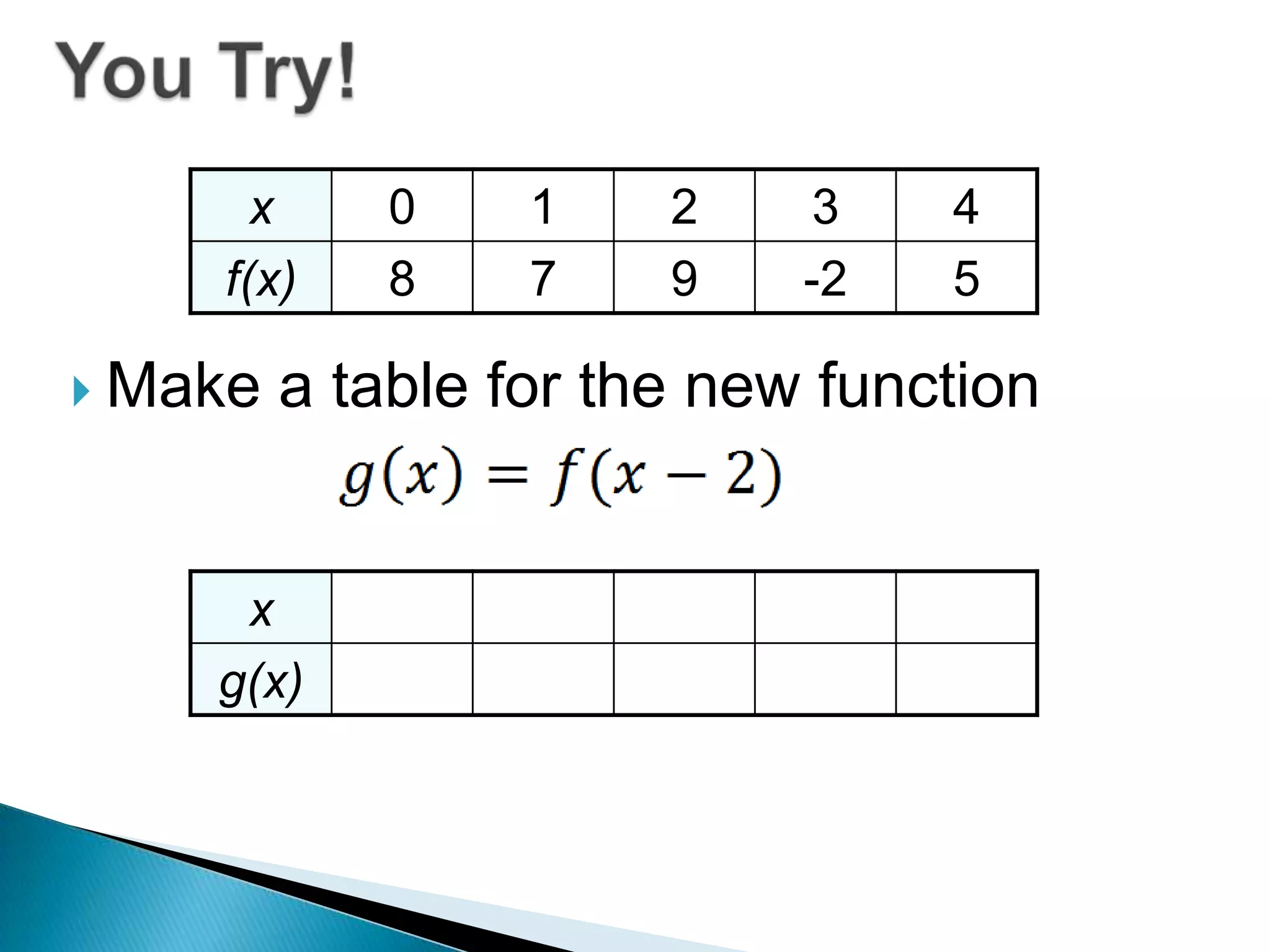
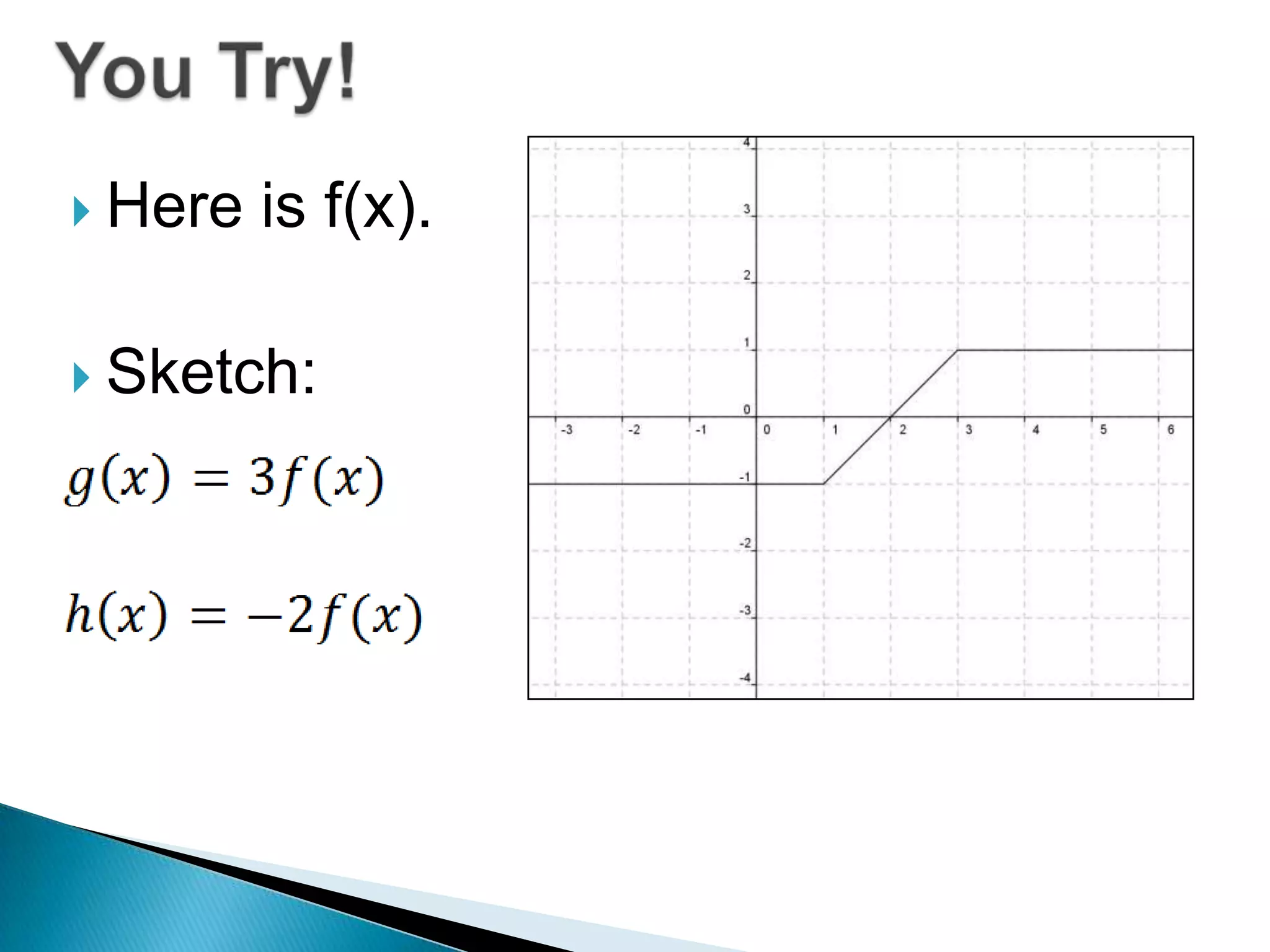
- Questions provide the definition of a function f(x) and ask the reader to write the tables or sketch the graphs for new functions using transformations of f(x).