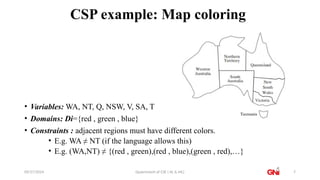
The document outlines a course on Artificial Intelligence, focusing on Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) and their applications, particularly in fields like scheduling and assignment. It defines CSPs, explains their structure, and discusses algorithms related to them, including backtracking and local search techniques. Key topics also include different variable types, constraints, and examples, such as map coloring.











![09/27/2024 Dpaertment of CSE ( AL & ML) 14
Commutative
• CSPs are commutative.
• The order of any given set of actions has no effect on the outcome.
• Example: choose colors for Australian territories one at a time
• [WA=red then NT=green] same as [NT=green then WA=red]
• All CSP search algorithms consider a single variable assignment
at a time there are d
⇒ n leaves.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/22pcoam11session10csp-240927194211-d0d3e5c5/85/22PCOAM11-Unit-2-Session-10-CSP-map-coloring-pptx-14-320.jpg)
