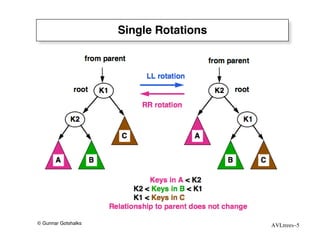
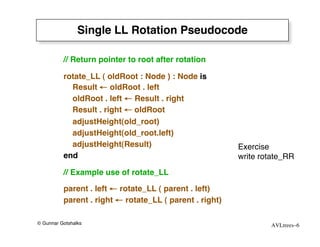
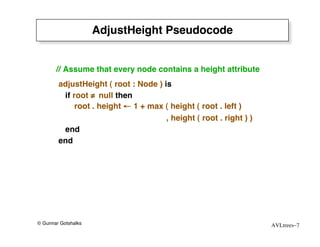
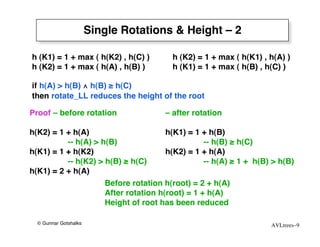
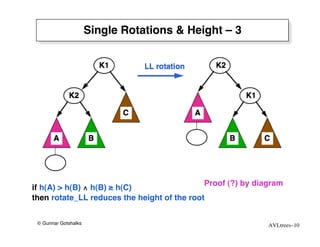
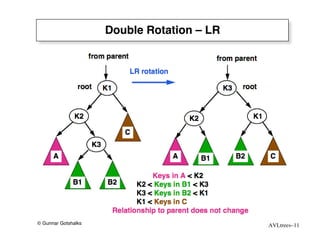
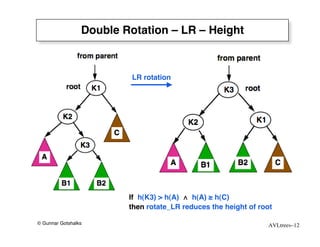
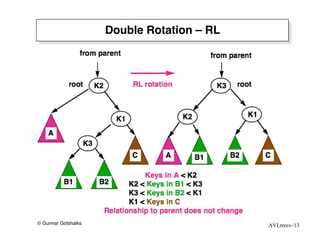
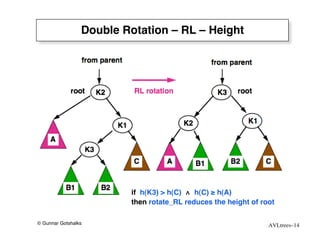
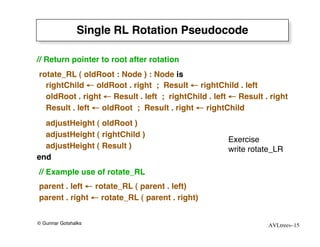
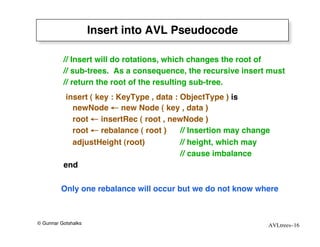
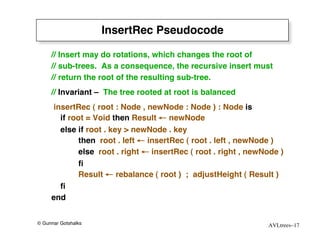
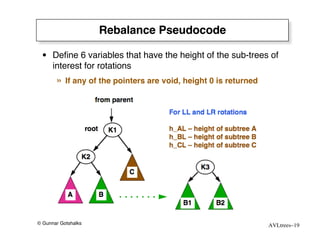
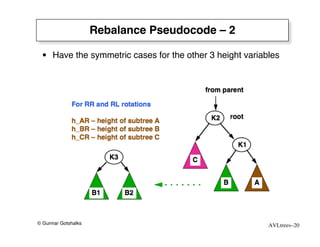
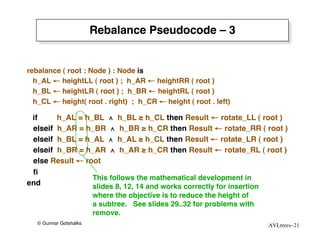
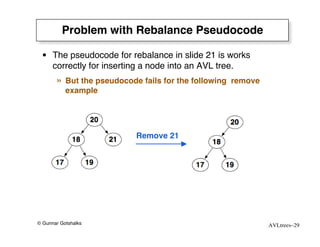
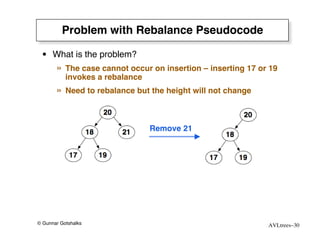
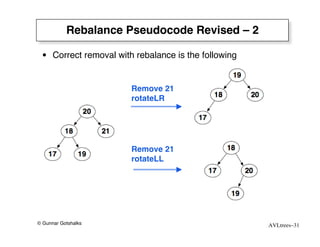
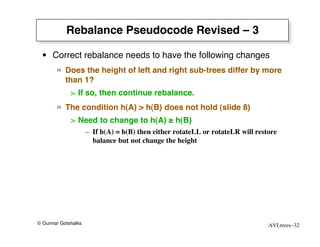
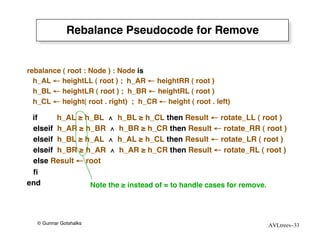
The document discusses AVL trees, which are self-balancing binary search trees. AVL trees ensure that insertions and deletions perform in O(log n) time by enforcing that the heights of any two subtrees of a node differ by at most one. They use rotations to rebalance the tree after insertions or deletions. Single and double rotations are used to move nodes and restore the balance property. Maintaining the balance factor during insertions, deletions, and rotations requires adjusting the heights of nodes as they are moved.