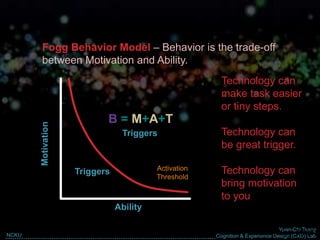
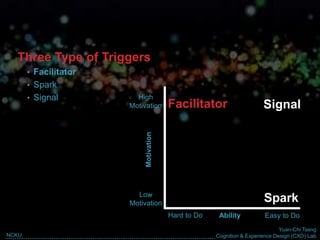
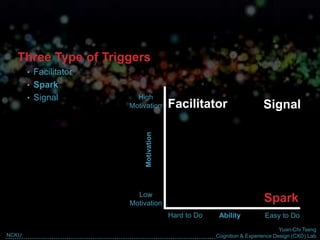
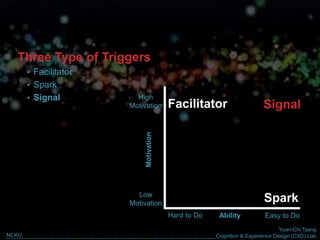
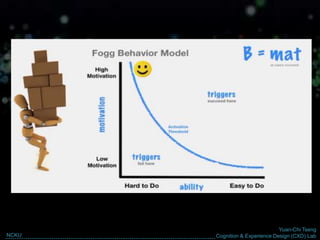
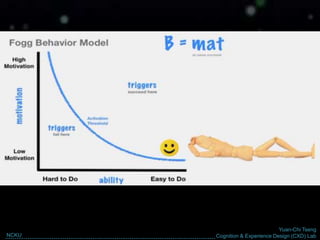
The document discusses behavior change and motivation from the perspectives of different disciplines like psychology, engineering, philosophy, and design. It notes the limitations of each perspective in isolation and argues they can work together better. It also discusses theories of decision making from behavioral economics and models of motivation like Fogg's Behavior Model. The document advocates for technology-supported approaches to behavior change through experience design that leverages human motivations like sensation/pleasure, anticipation/hope, and social cohesion/acceptance.





















































































![Yuan-Chi Tseng
Cognition & Experience Design (CXD) LabNCKU
Format for a “Tiny Habit”
After I ________________,
I will _________________.
[existing habit]
[new tiny behavior]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015-151229074827/85/_1041217_14_-_-100-320.jpg)