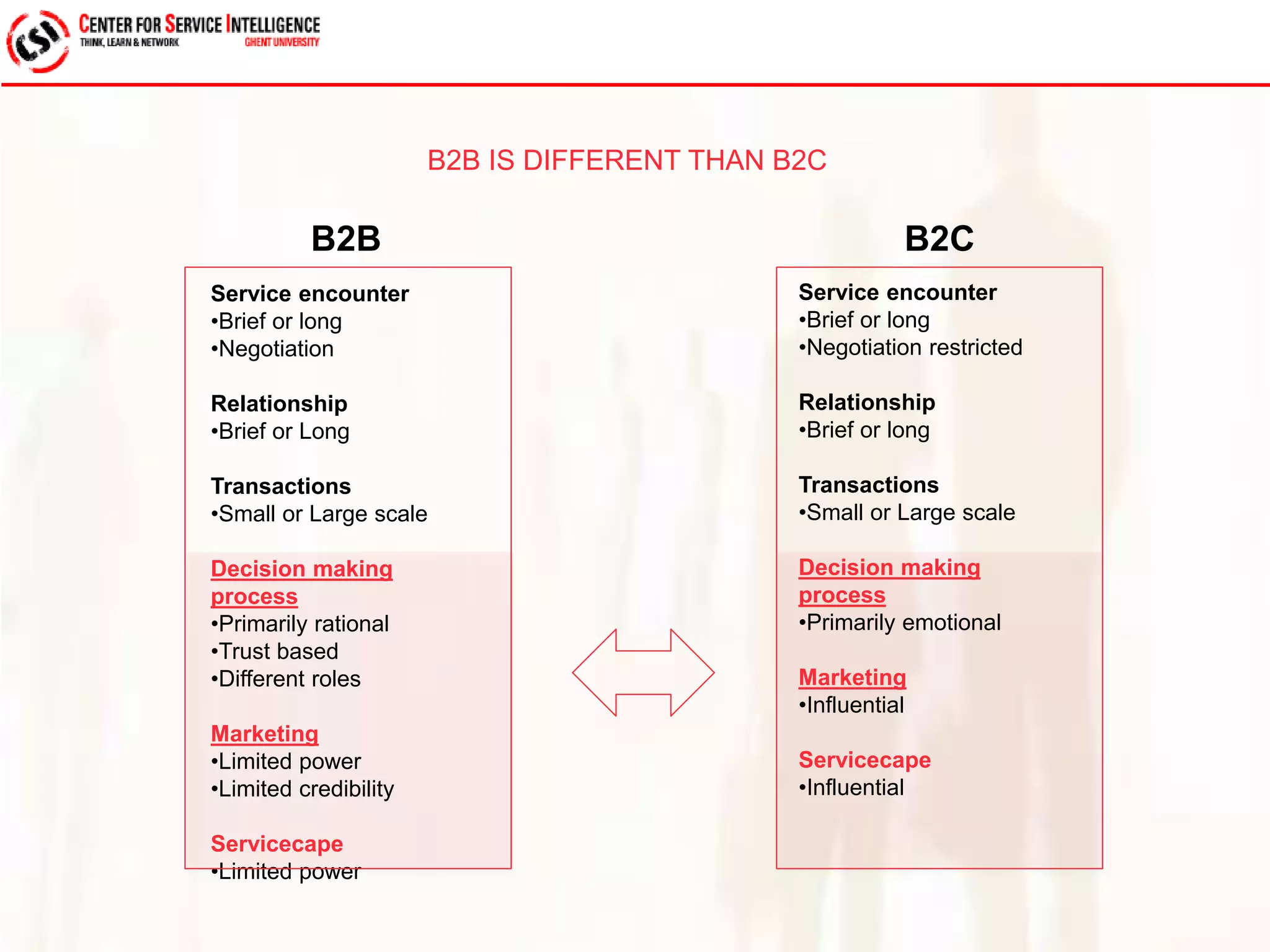
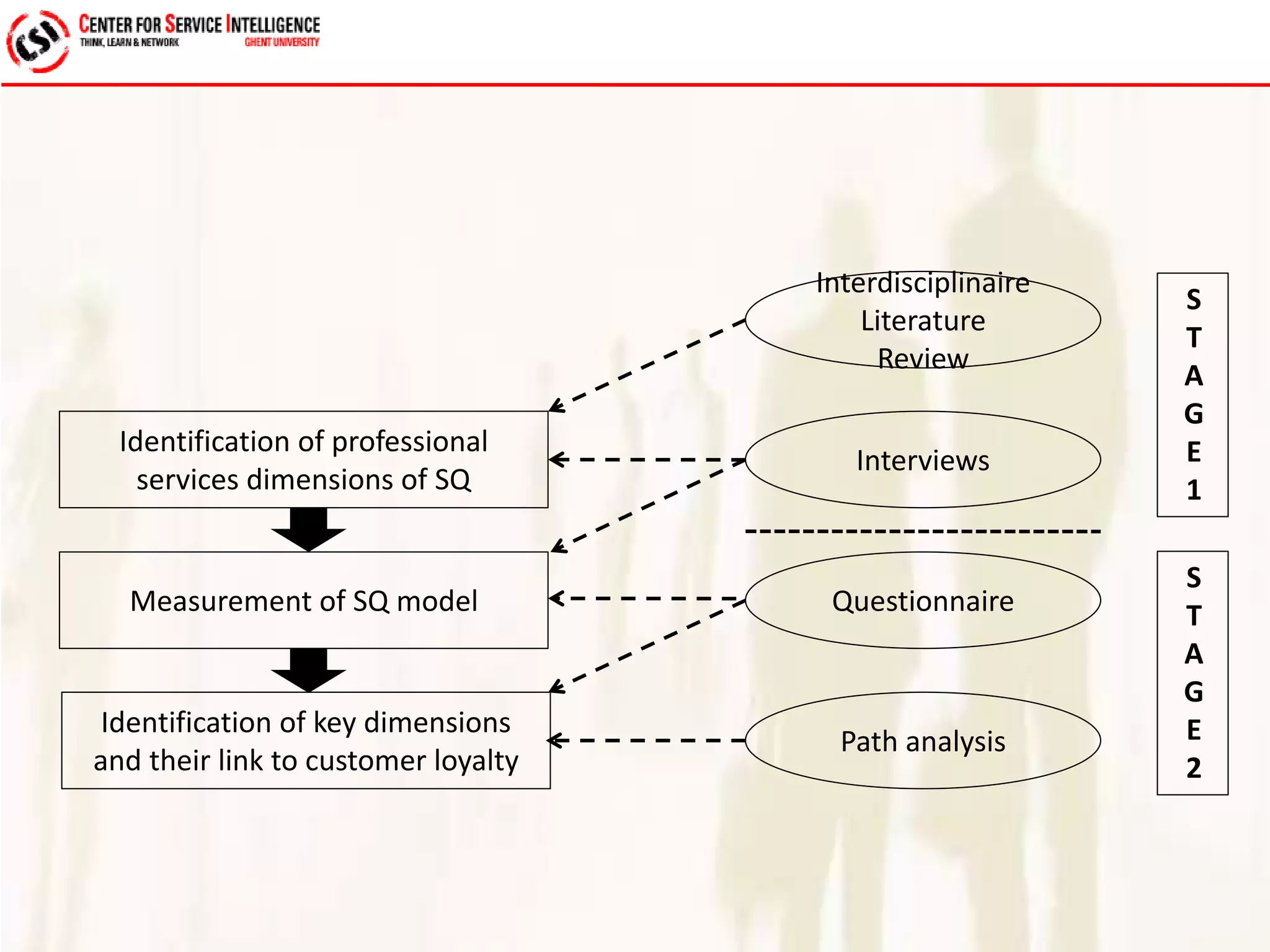
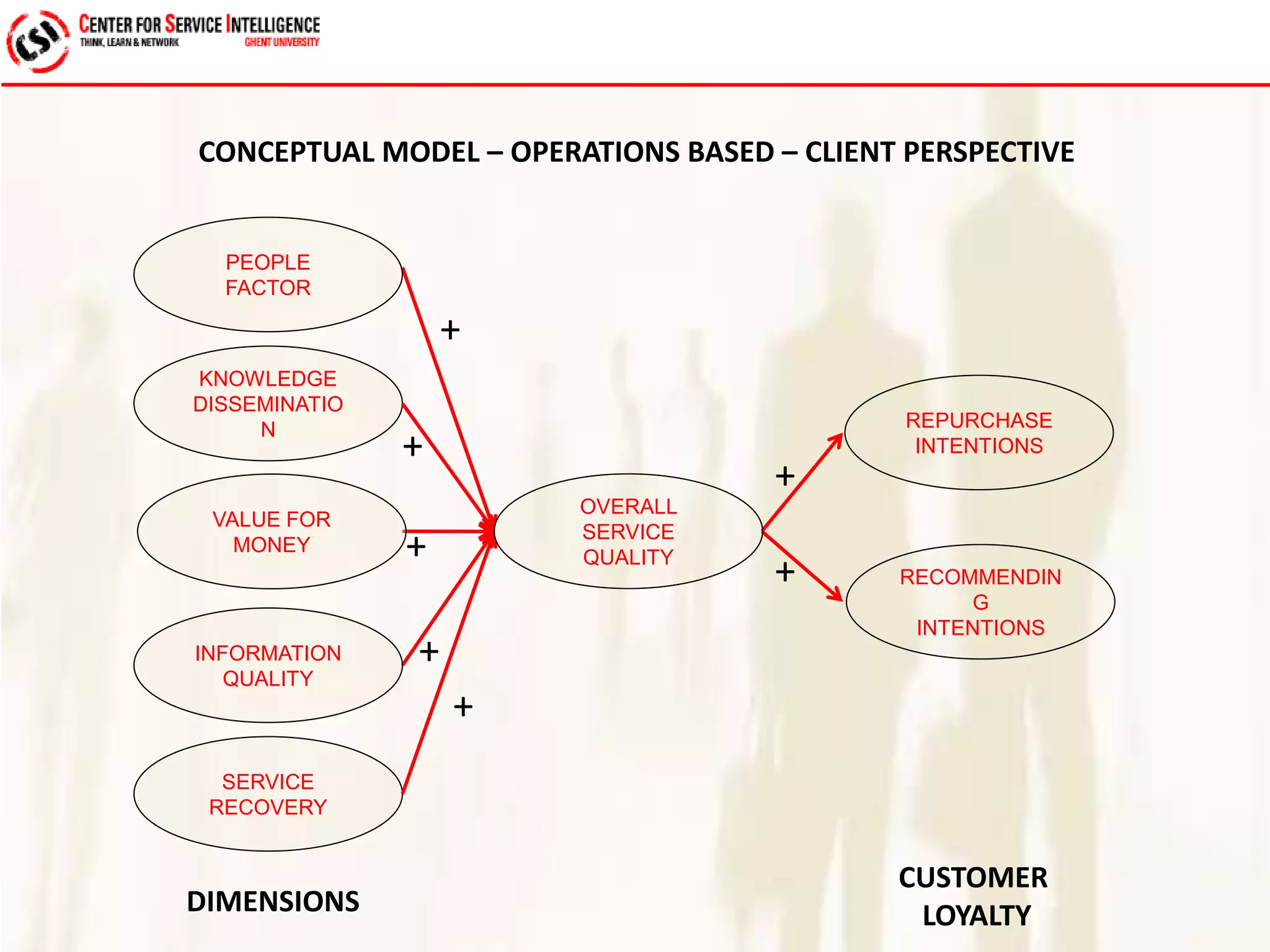
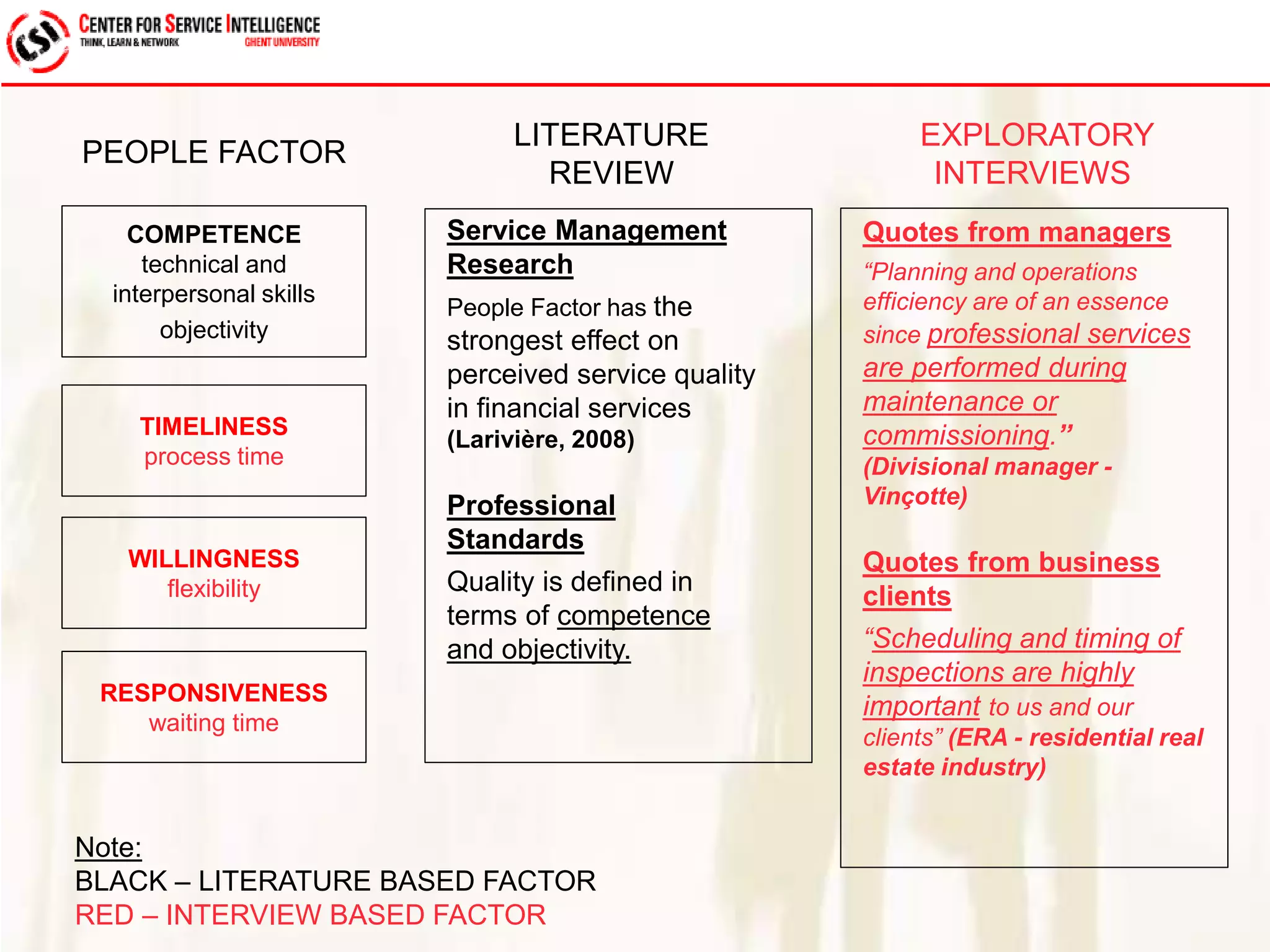
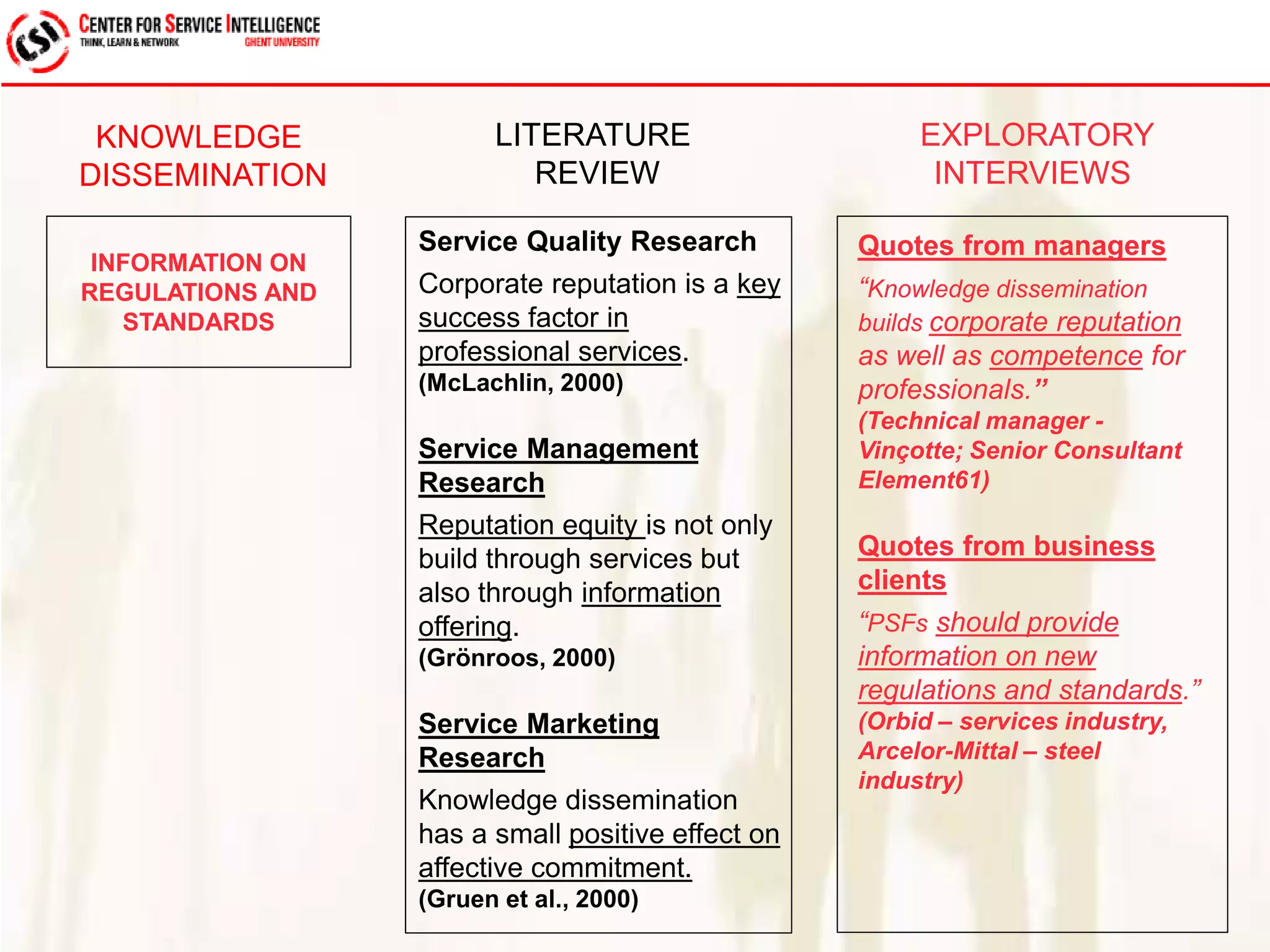
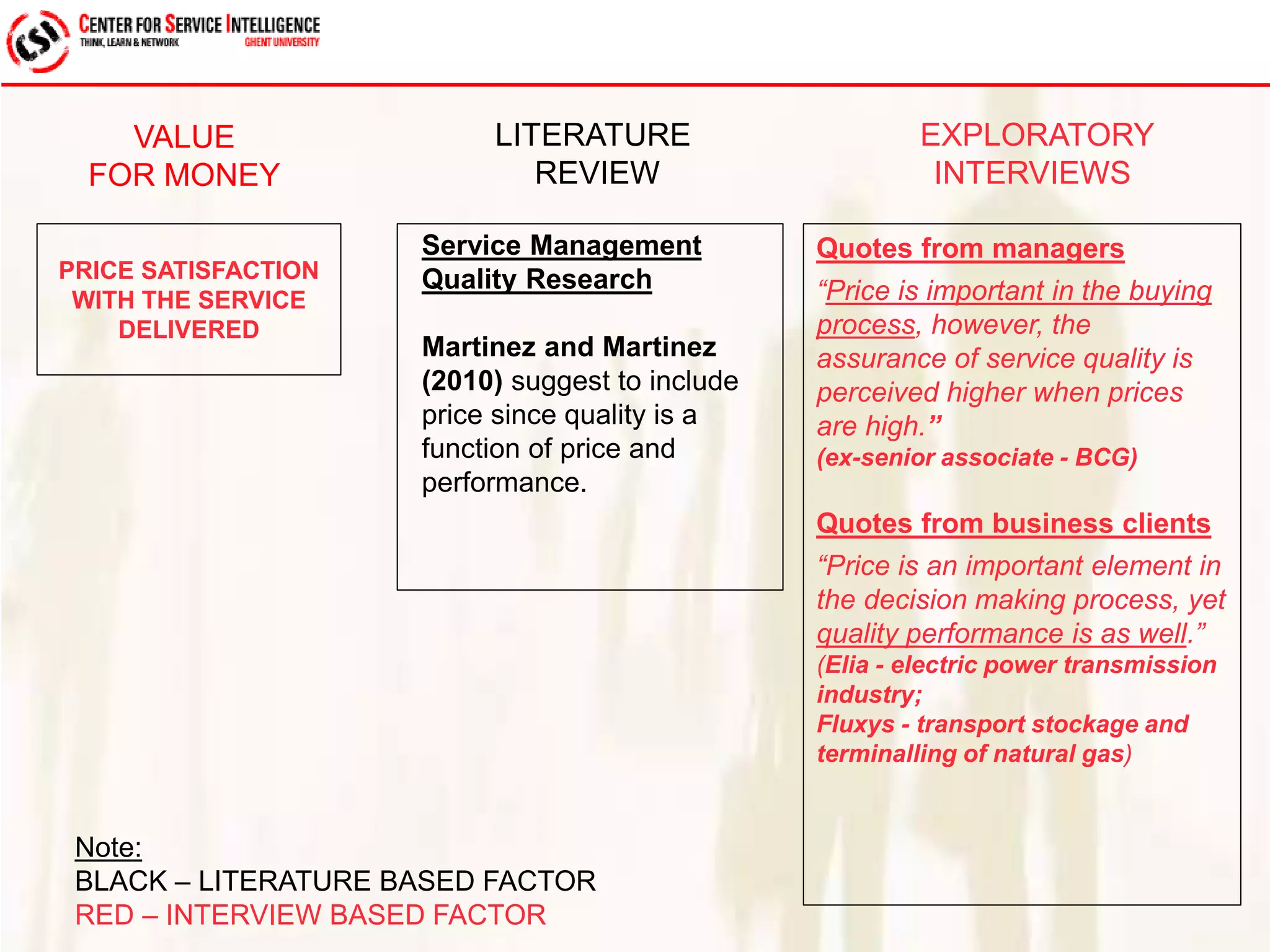
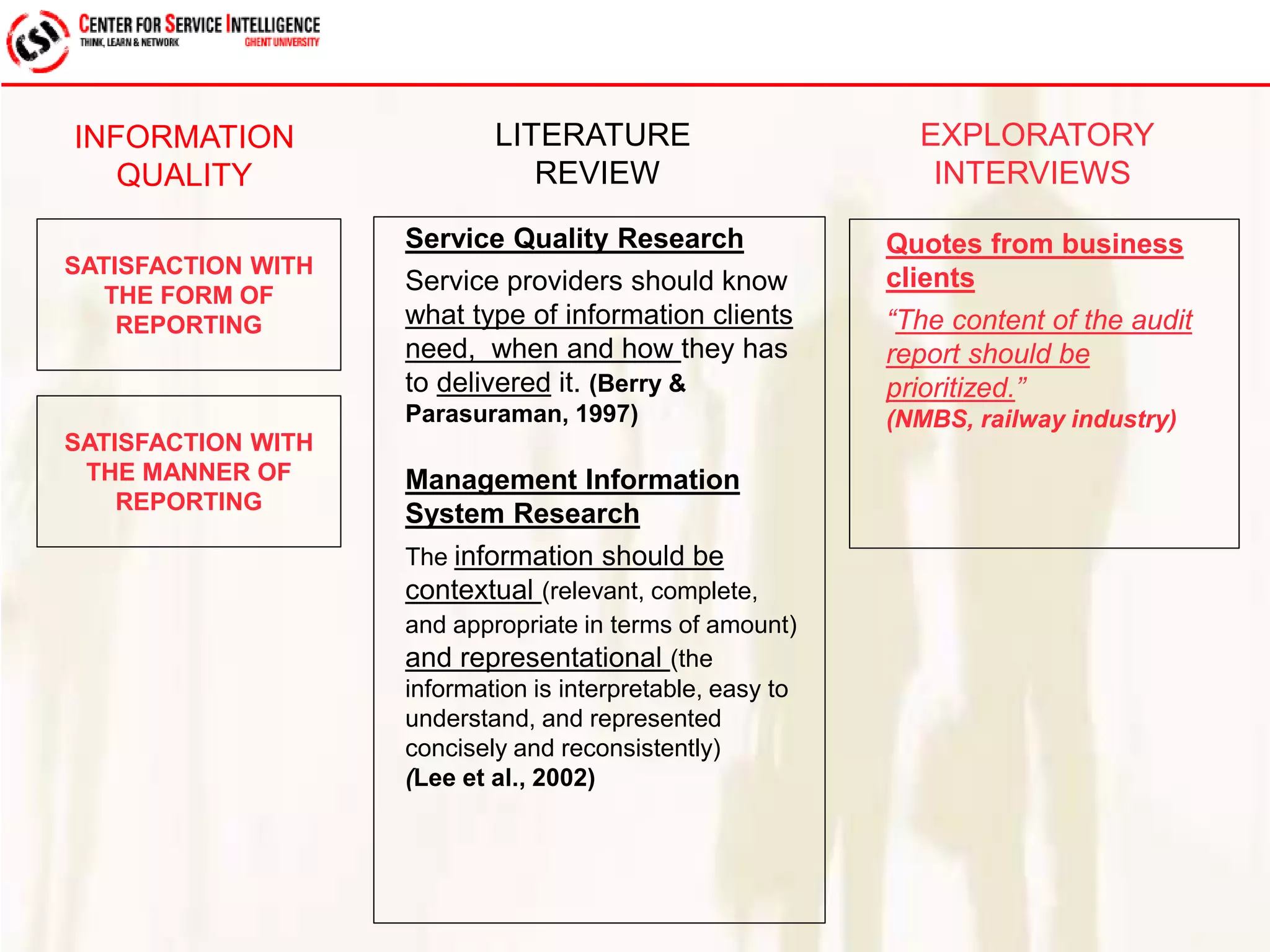
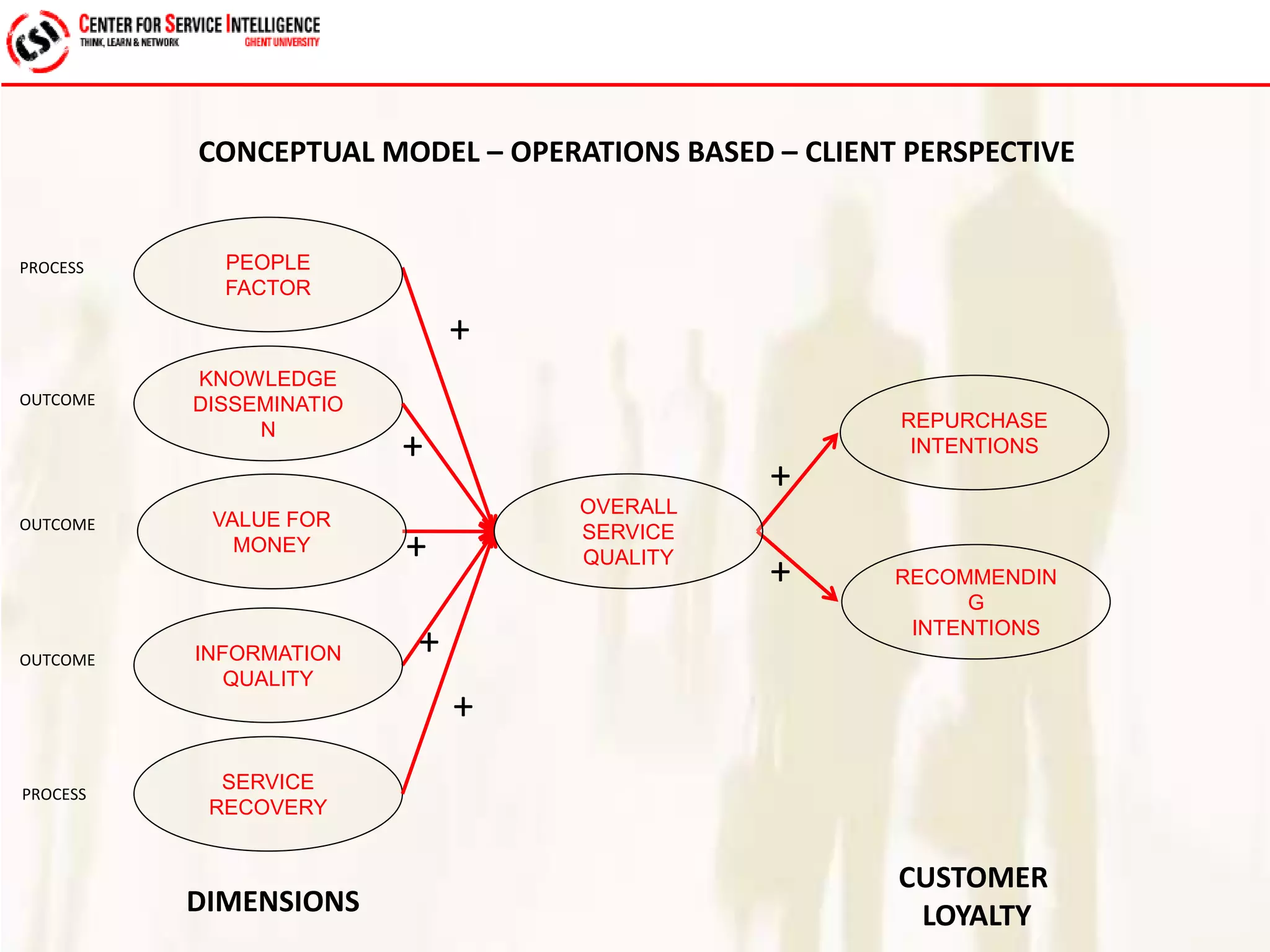
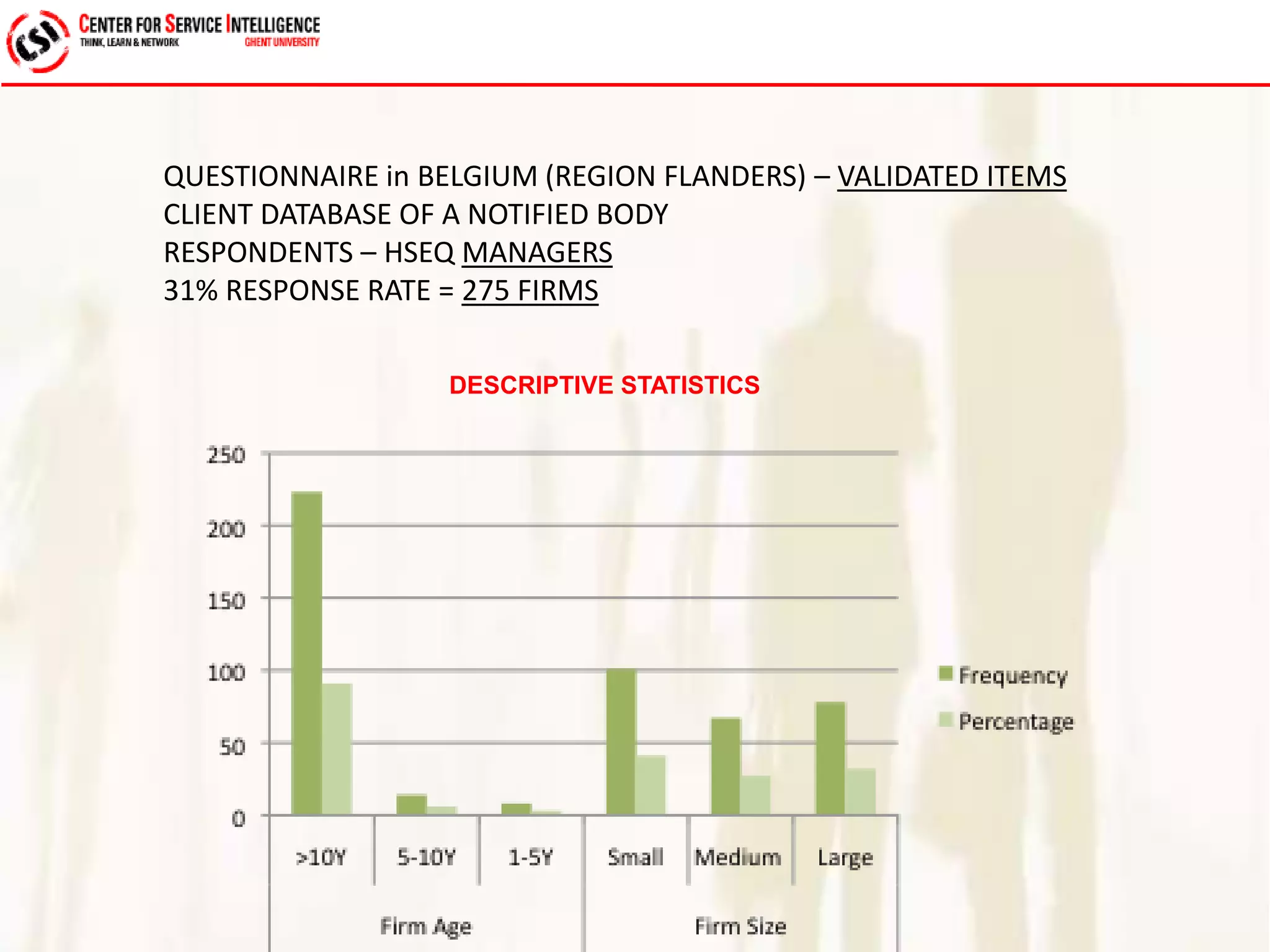
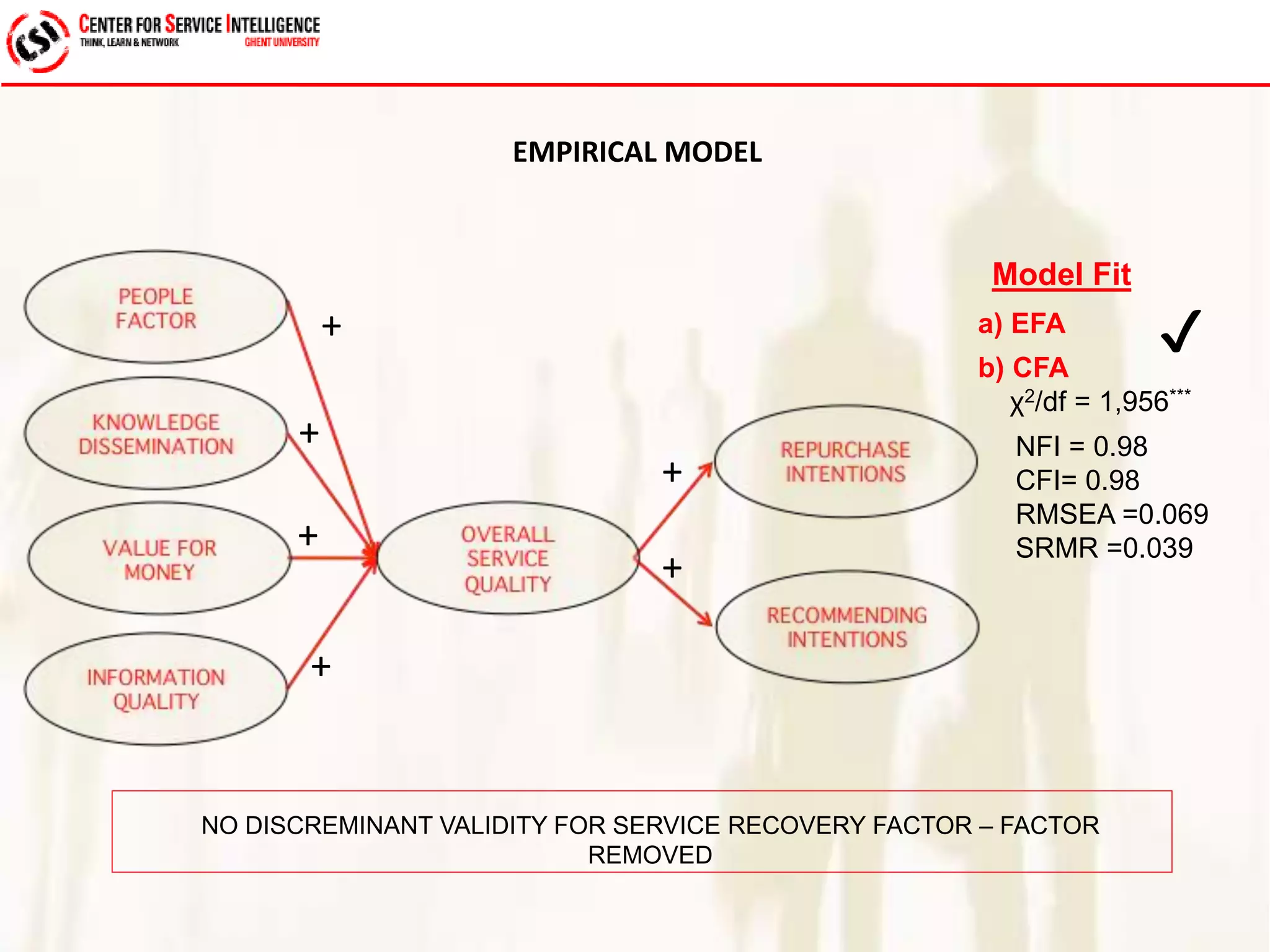
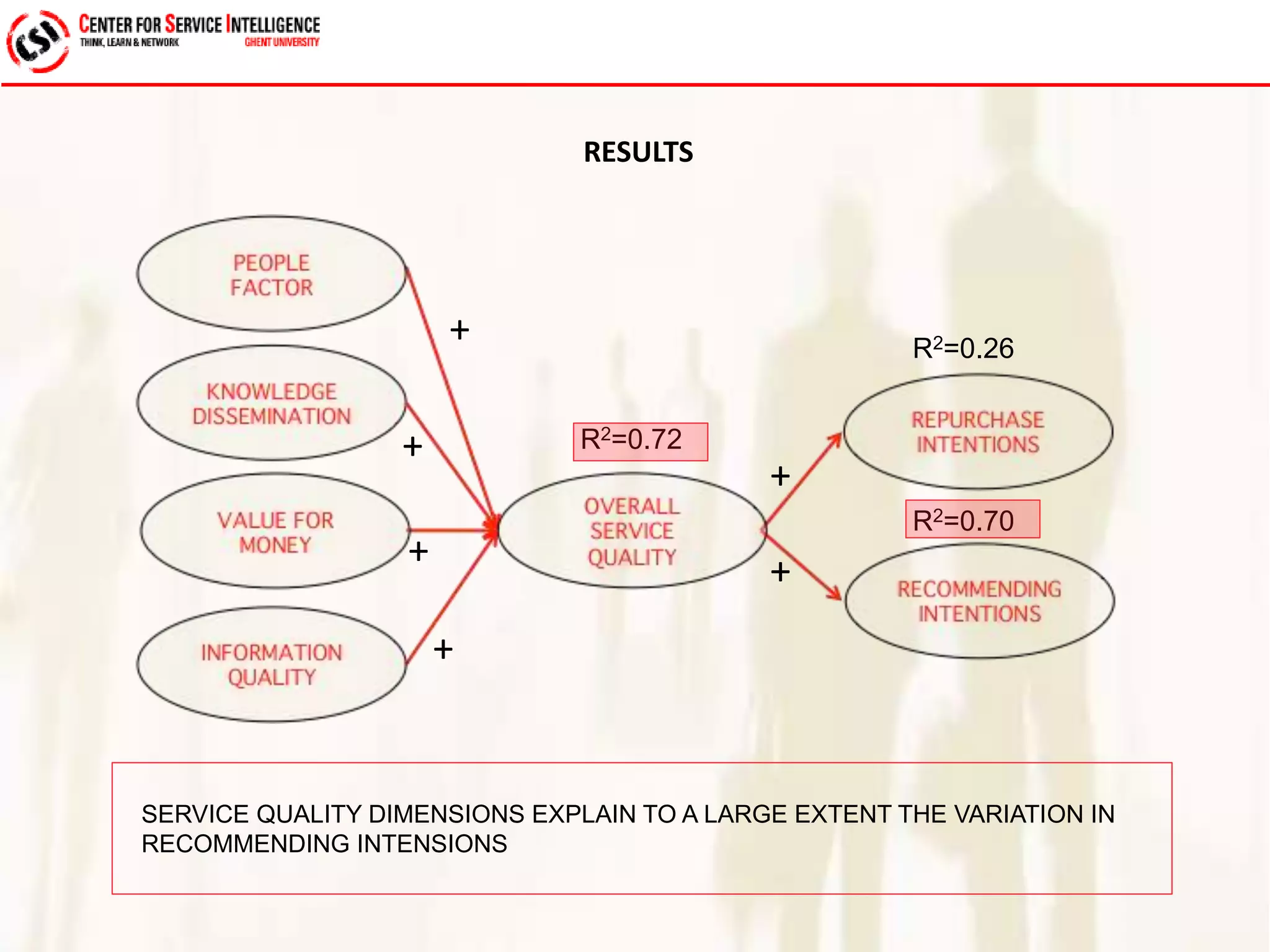
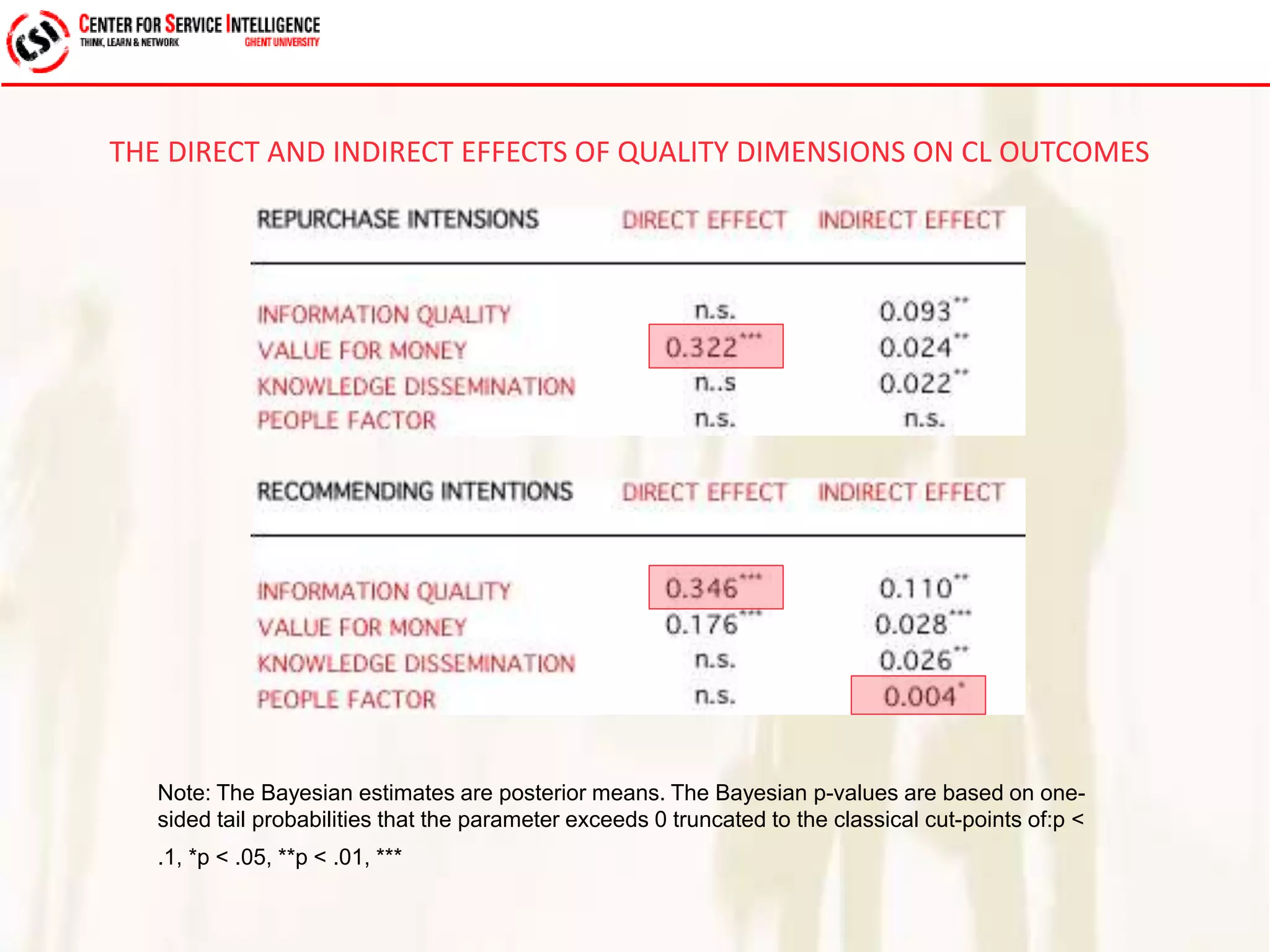
The study explores service quality dimensions that most effectively influence customer loyalty in B2B professional service firms, highlighting differences between B2B and B2C contexts. Key findings suggest that the 'people factor' significantly impacts perceived service quality, while 'value for money' and 'information quality' are crucial for enhancing customer loyalty behaviors. A holistic model from an operations-based client perspective indicates that the outcomes of services are more important than the processes involved.