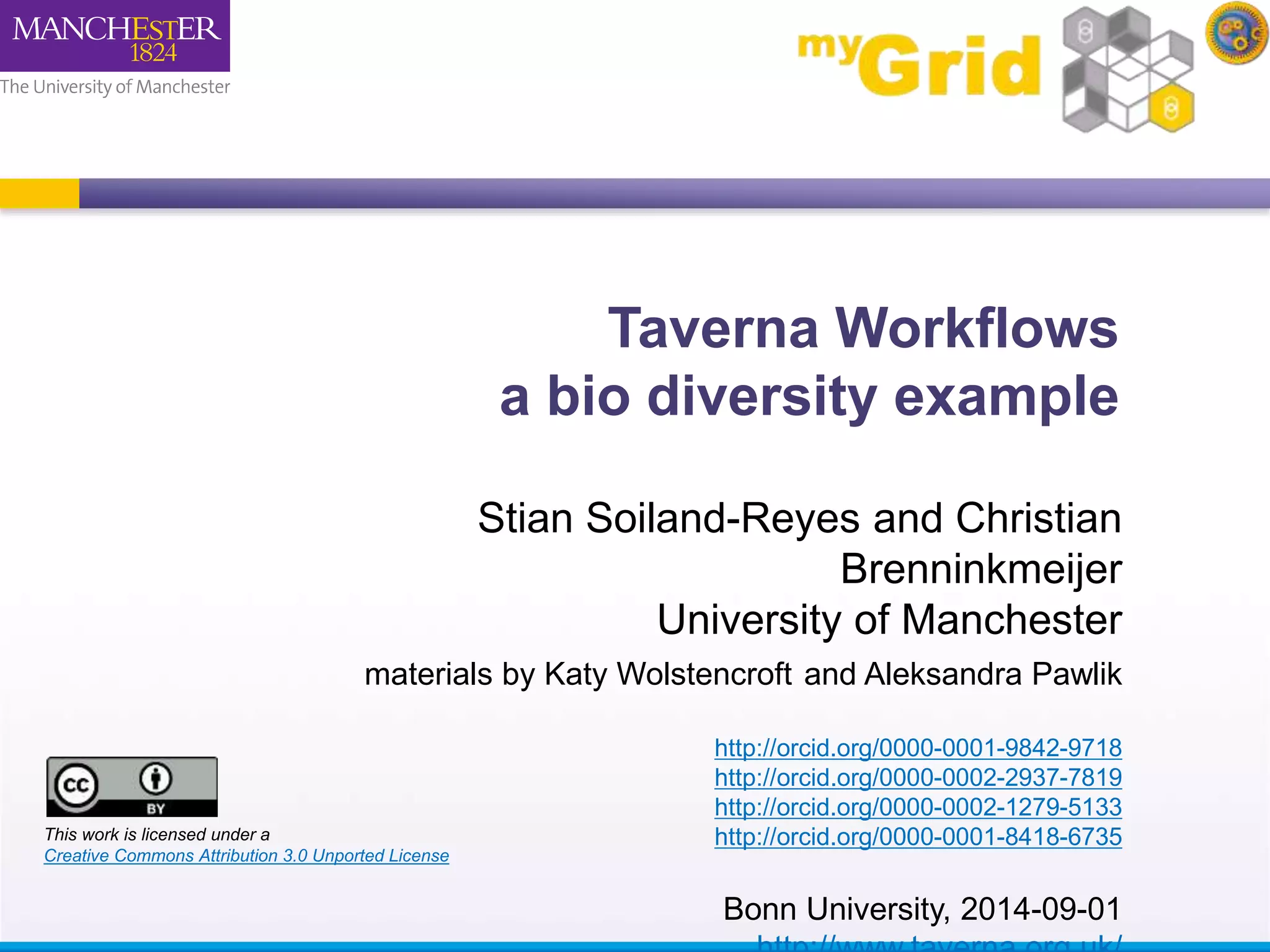
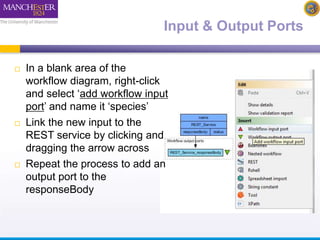
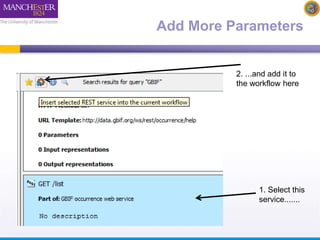
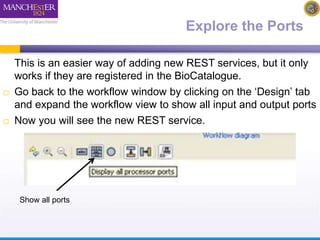
This document describes a workflow built in Taverna that searches for occurrences of species using the GBIF API. The workflow takes in a species name and searches the GBIF occurrence service. It was later updated to also take in latitude and longitude coordinates to filter the results geographically. The results are returned in XML, so another workflow is demonstrated that plots the results on a Google Earth map for easier visualization. Testing with different species names showed that accounting for synonyms is important for comprehensive results.