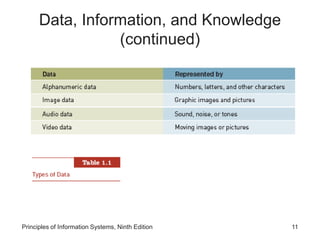
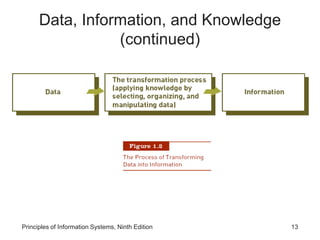
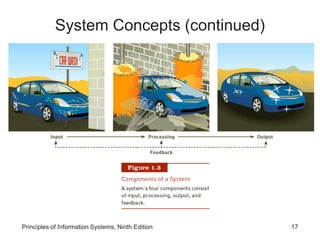
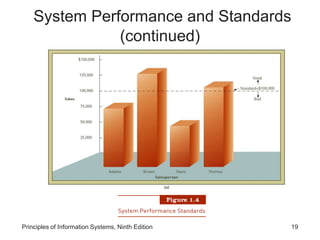
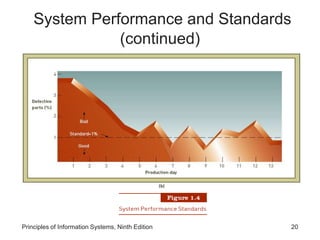
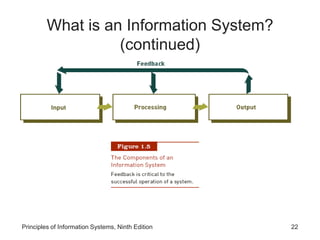
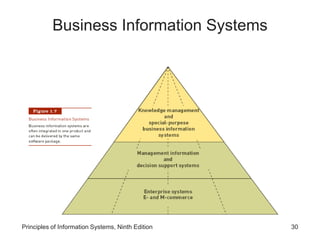
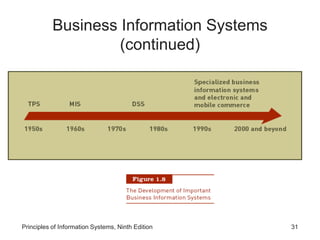
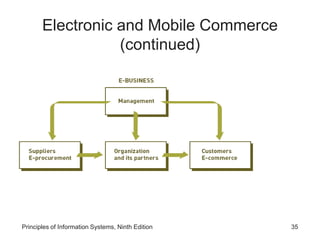
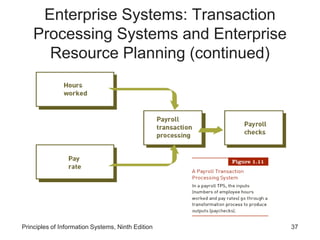
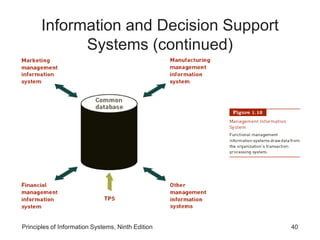
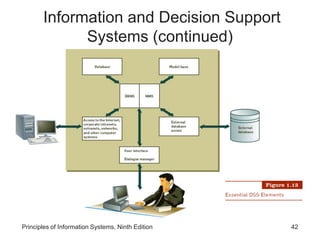
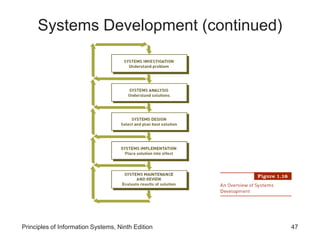
The document introduces concepts related to information systems including data, information, system components, types of business information systems, and the systems development process. It discusses how information systems can help organizations by processing data into valuable information that supports decision-making, identifies the components of computer-based information systems, and describes different types of systems like transaction processing systems and enterprise resource planning systems. The document also covers topics like electronic commerce, knowledge management, security and privacy issues, and the role of information systems in business functions and industries.