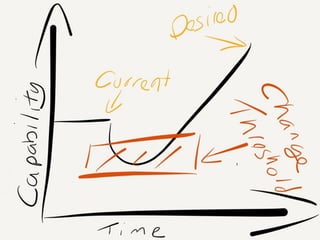
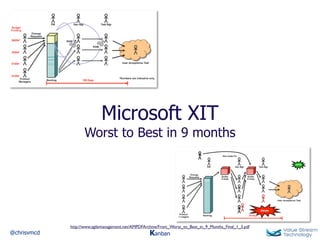
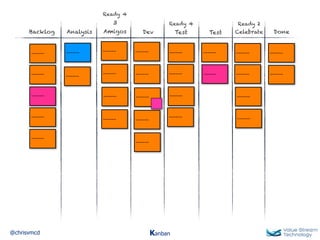
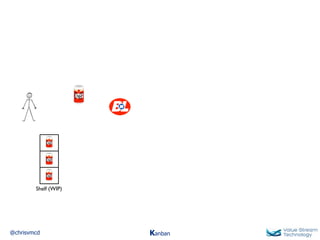
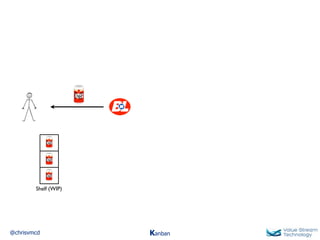
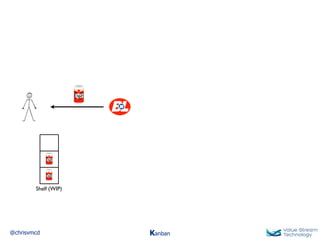
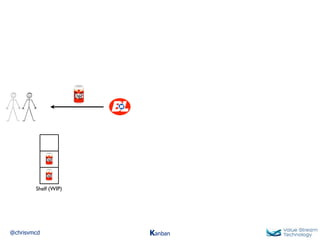
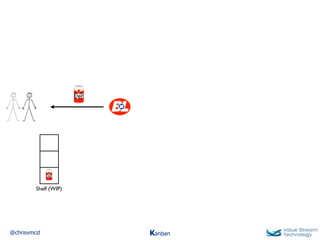
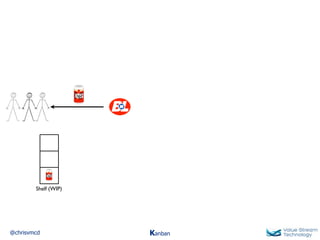
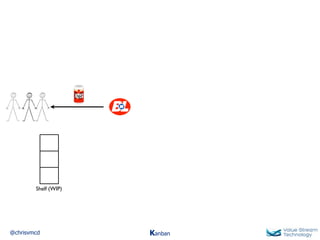
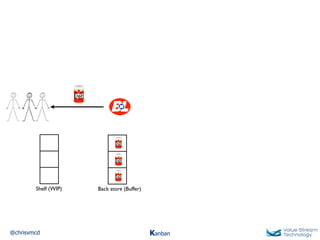
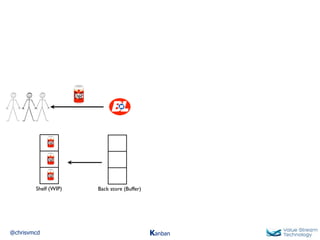
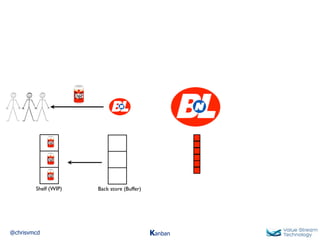
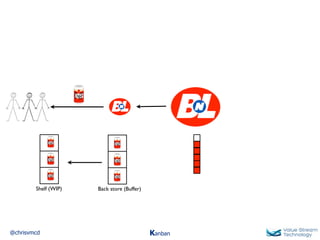
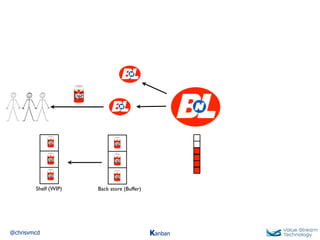
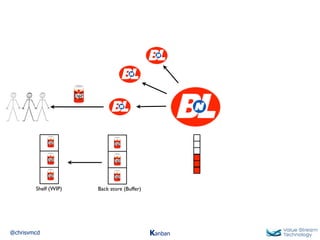
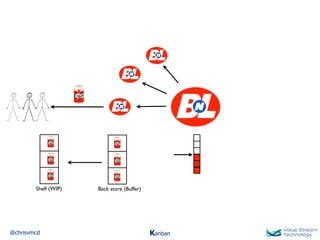
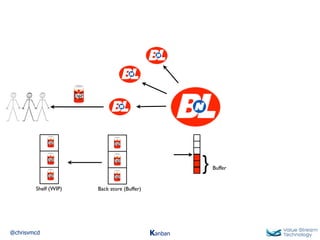
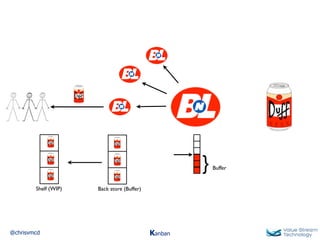
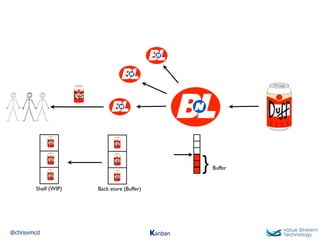
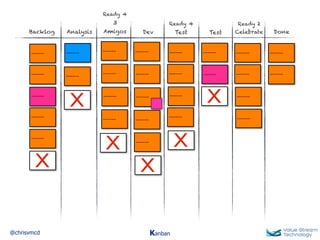
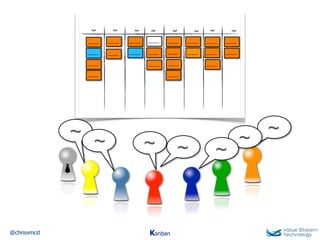
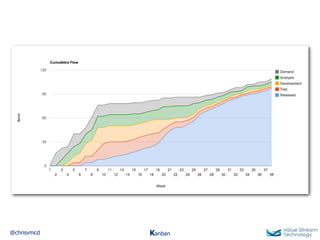
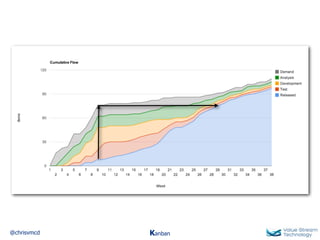
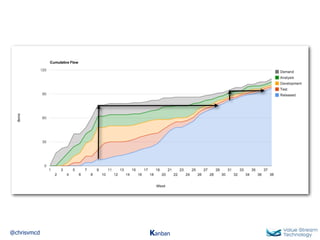
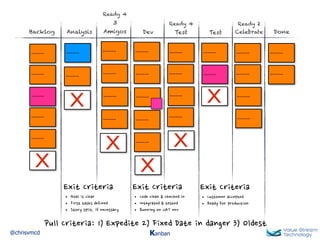
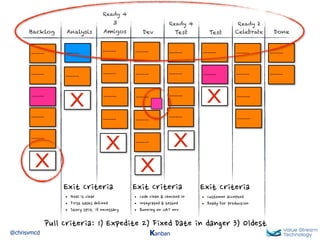
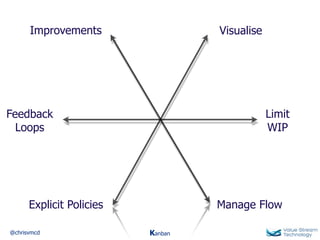
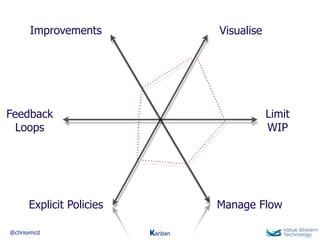
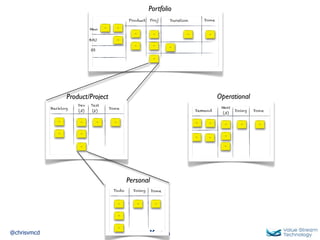
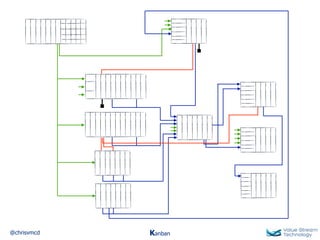
The document discusses Kanban, including principles of starting with the current process and pursuing incremental changes. It provides examples of Kanban implementations at Microsoft and Corbis. Kanban concepts explained include workflows, work in progress limits, and pull signals. Exit and pull criteria for work items are also outlined.