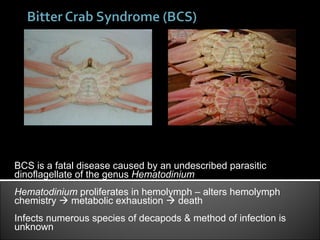
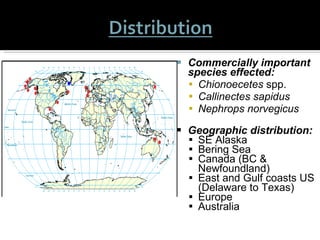
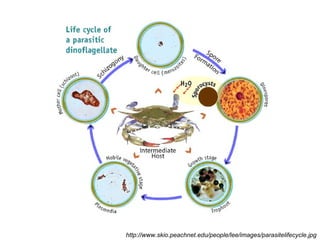
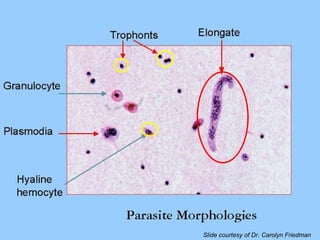
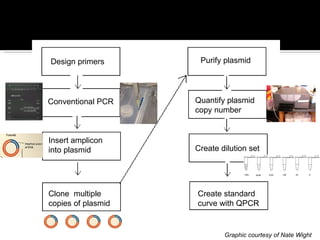
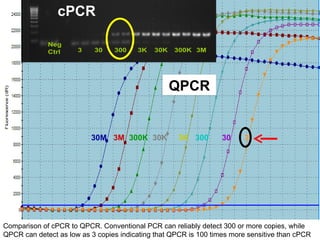
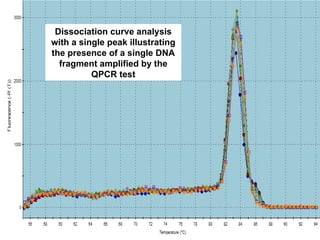
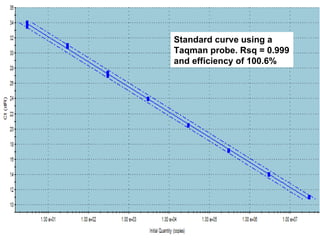
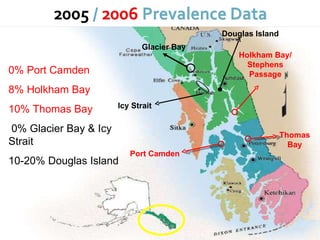
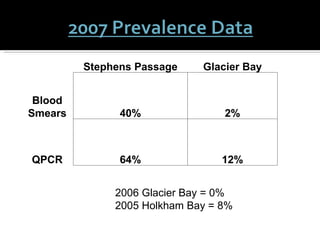
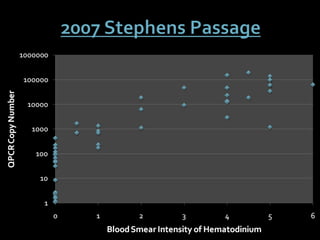
This document summarizes research on Hematodinium, a parasitic dinoflagellate that causes bitter crab disease (BCS) in various crab species. It infects the hemolymph of crabs, proliferates and alters hemolymph chemistry, leading to metabolic exhaustion and death. A qPCR assay was developed to more sensitively detect and quantify Hematodinium infections than previous methods. Testing in Southeast Alaska found increasing prevalence of infections from previous years. Further research aims to better understand transmission and impacts on crab populations.