Several philosophers throughout history have proposed different understandings of the self based on their philosophical orientations:
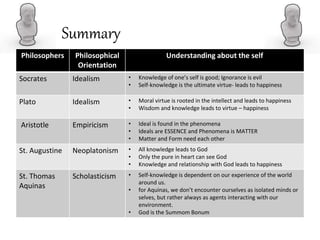
- Pre-Socratics like Thales saw the self as the soul which gives movement and is the primal matter underlying all things. Socrates viewed self-knowledge as the key to virtue and happiness. Plato believed the rational soul should govern the other parts.
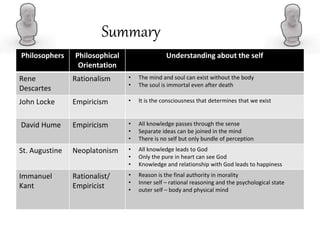
- St. Augustine and St. Thomas Aquinas incorporated Christian theology, seeing the soul as immortal and what distinguishes humans from animals. Descartes defined the self as mind/soul separate from the body.
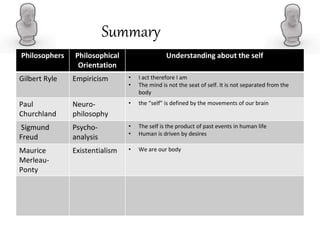
- Later empiricists like Hume and Locke rejected the immaterial soul, seeing the self as a bundle of perceptions or