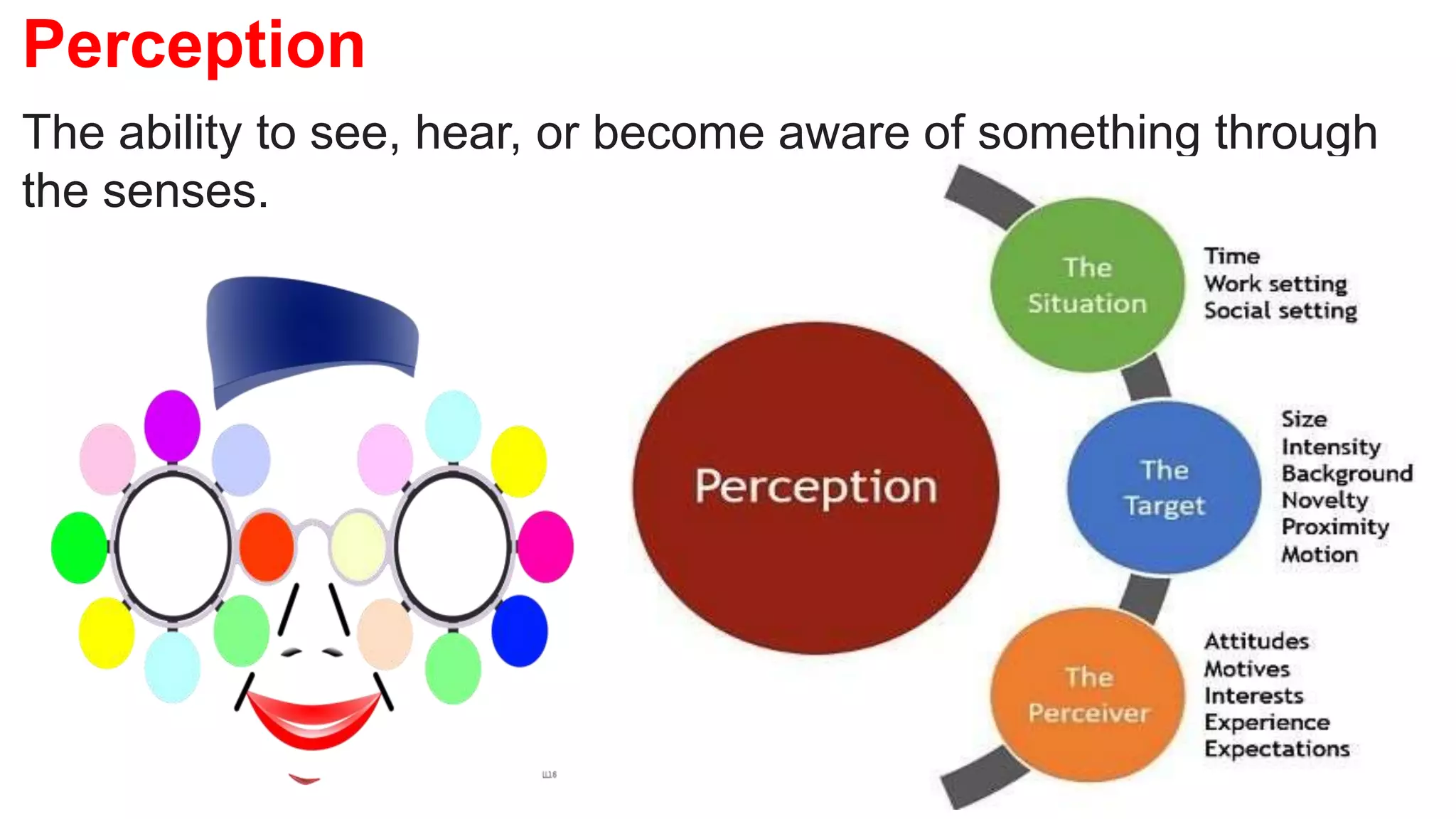
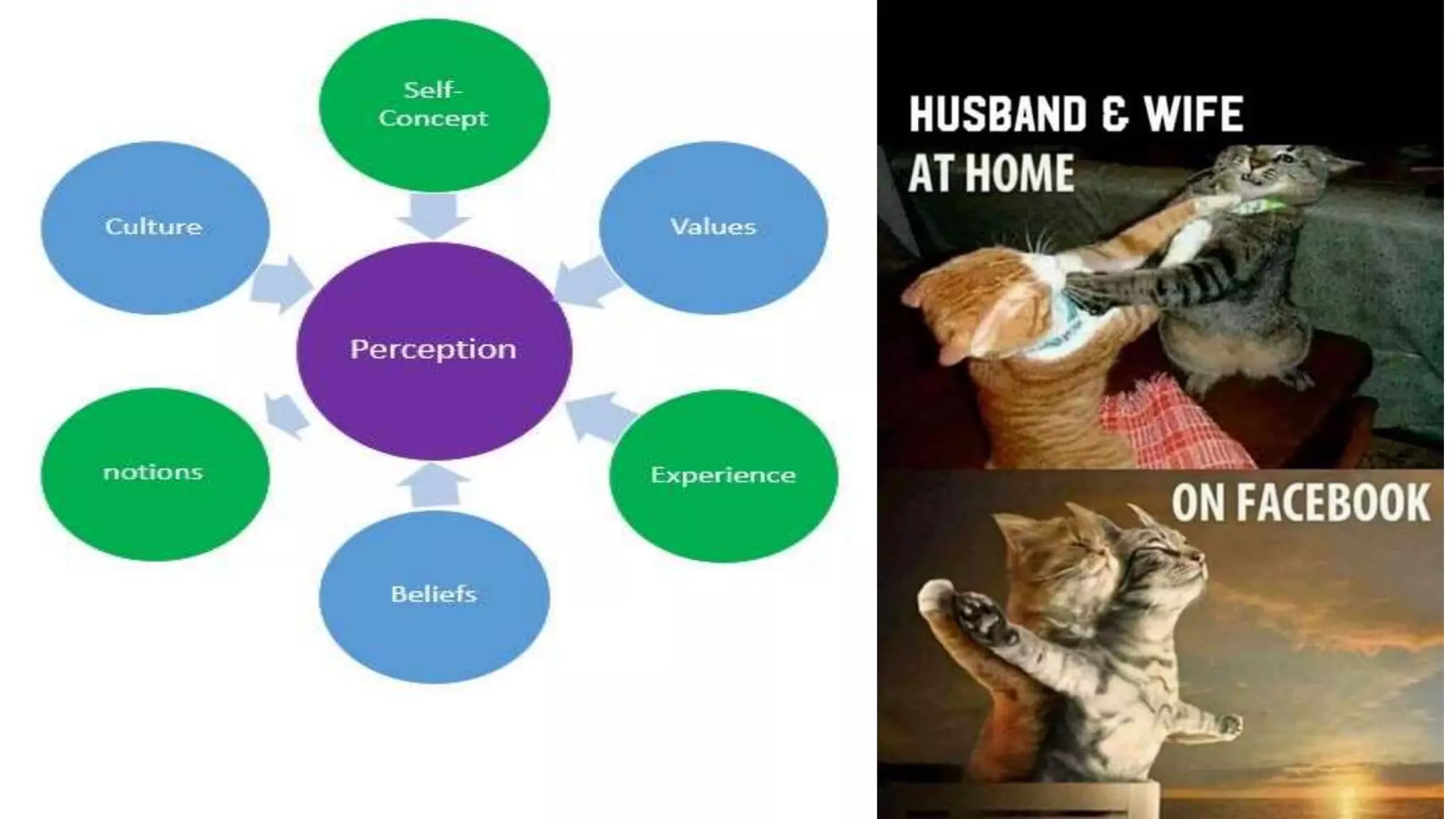
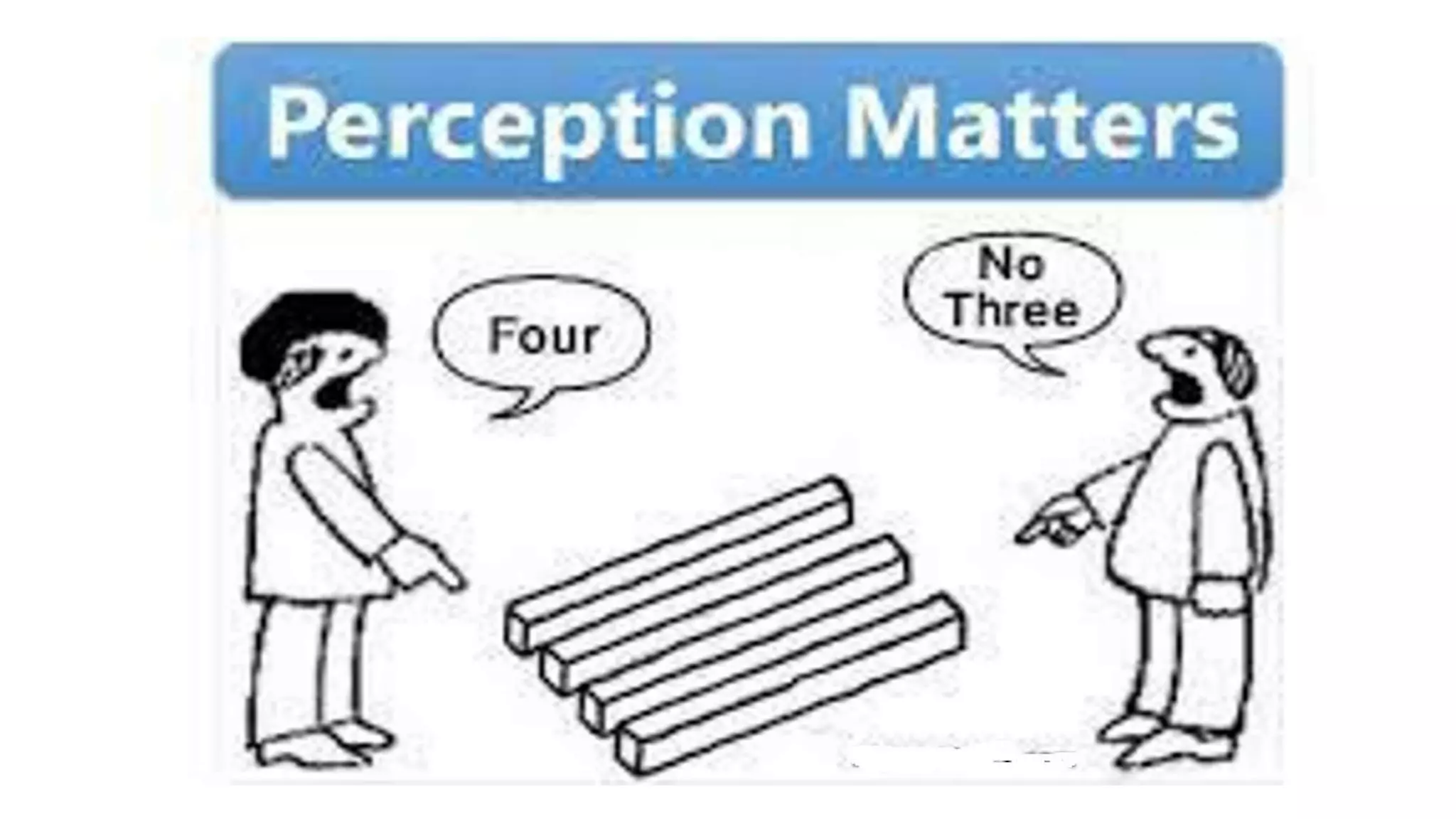
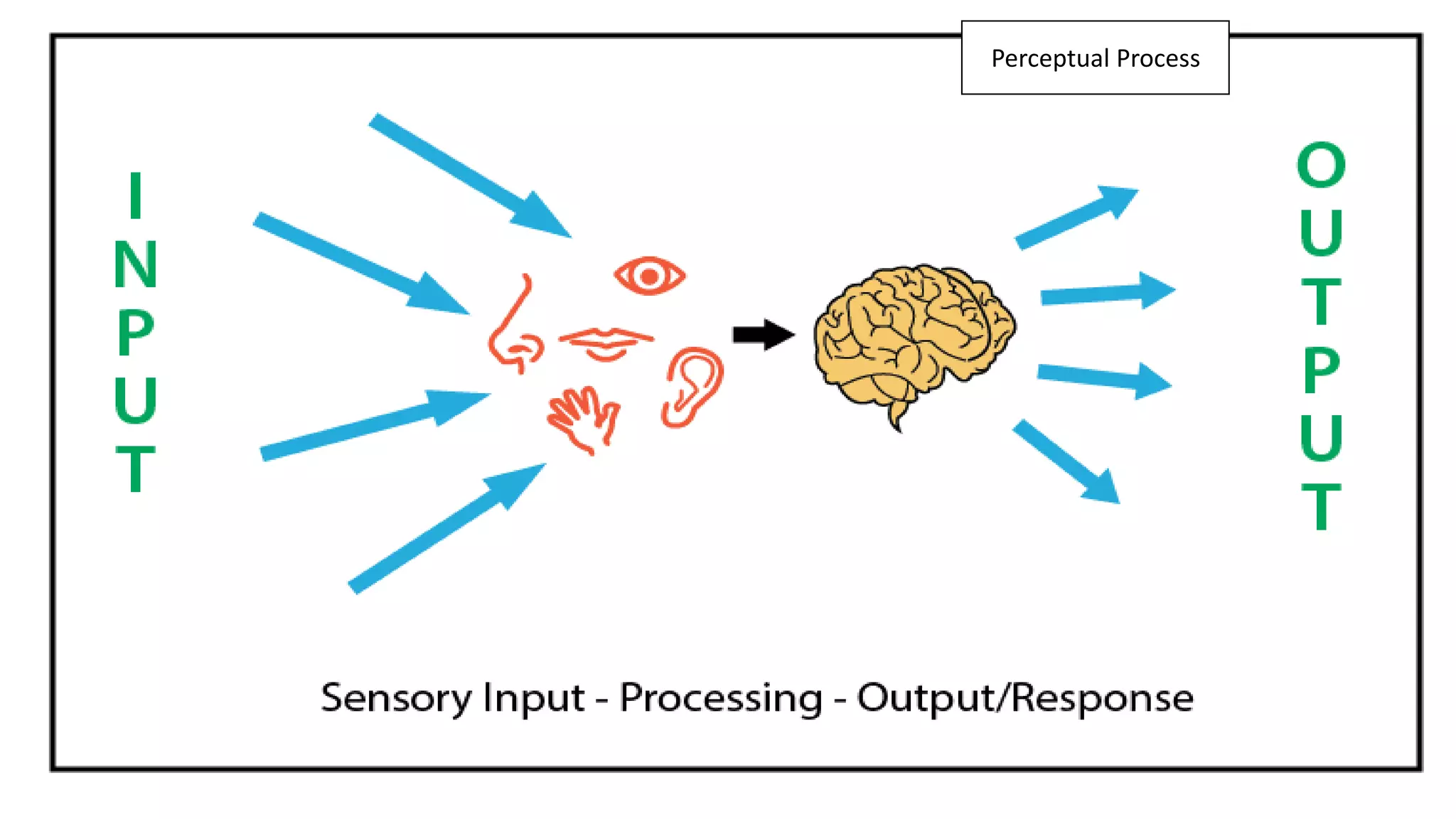
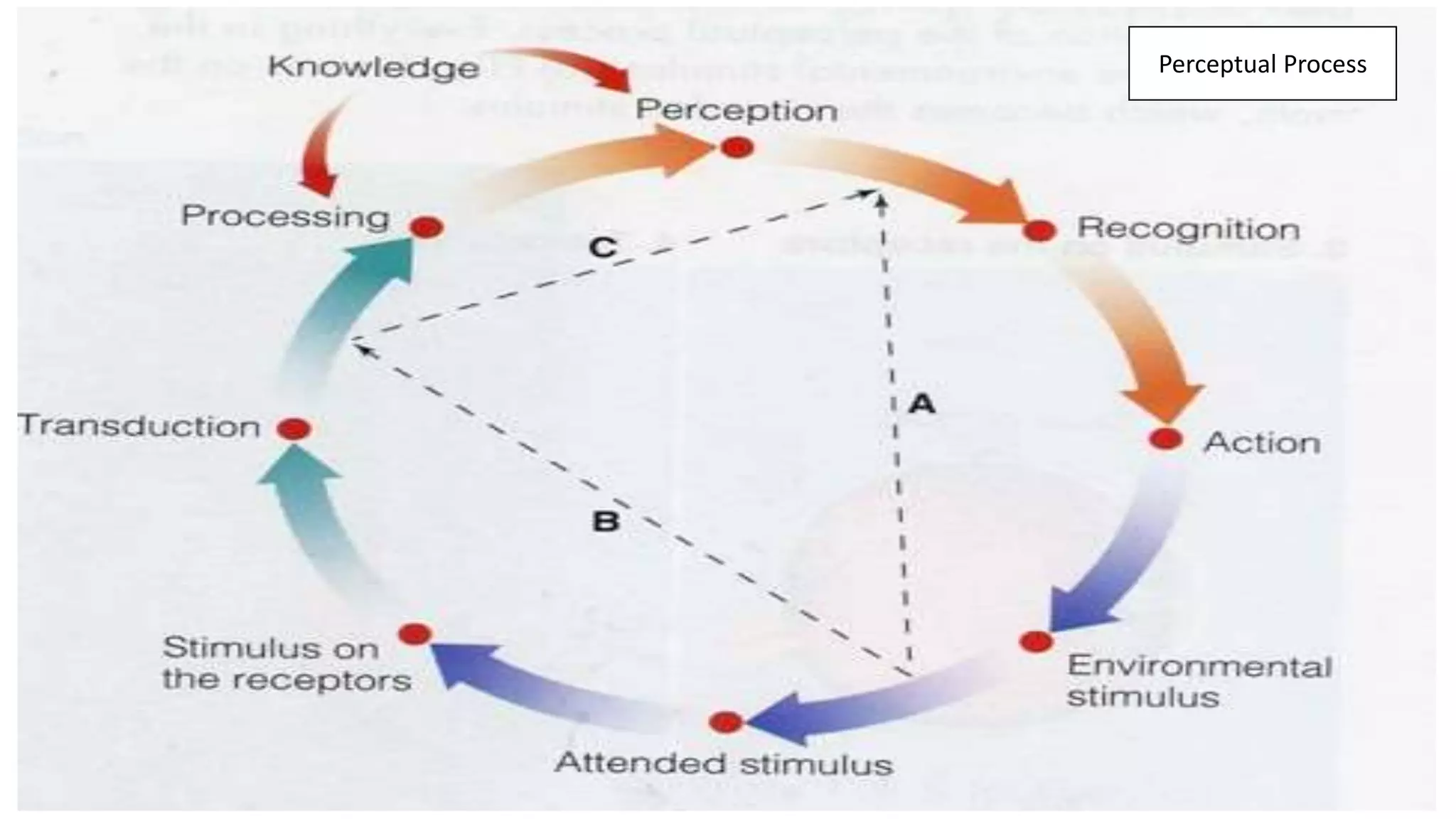
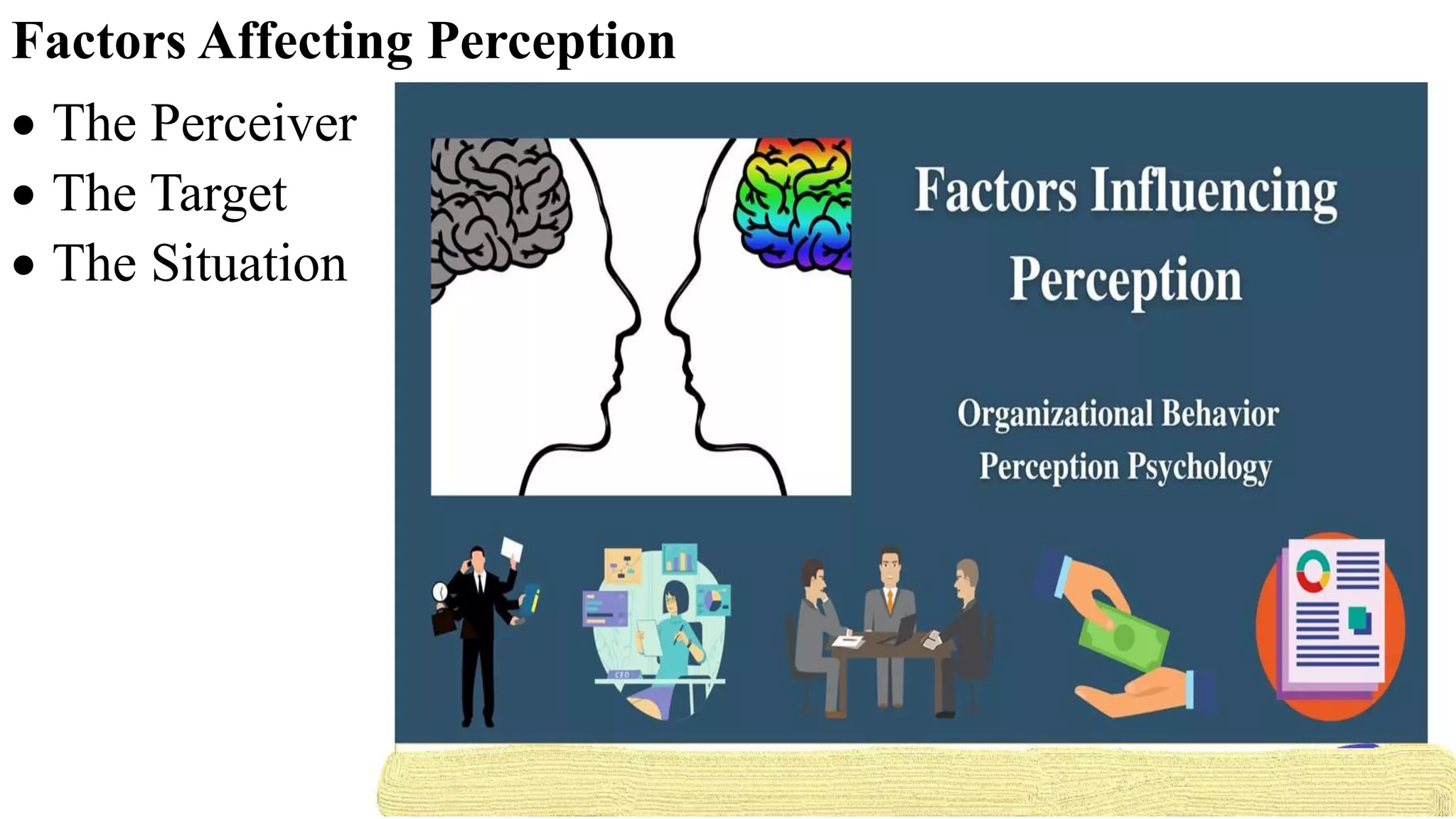
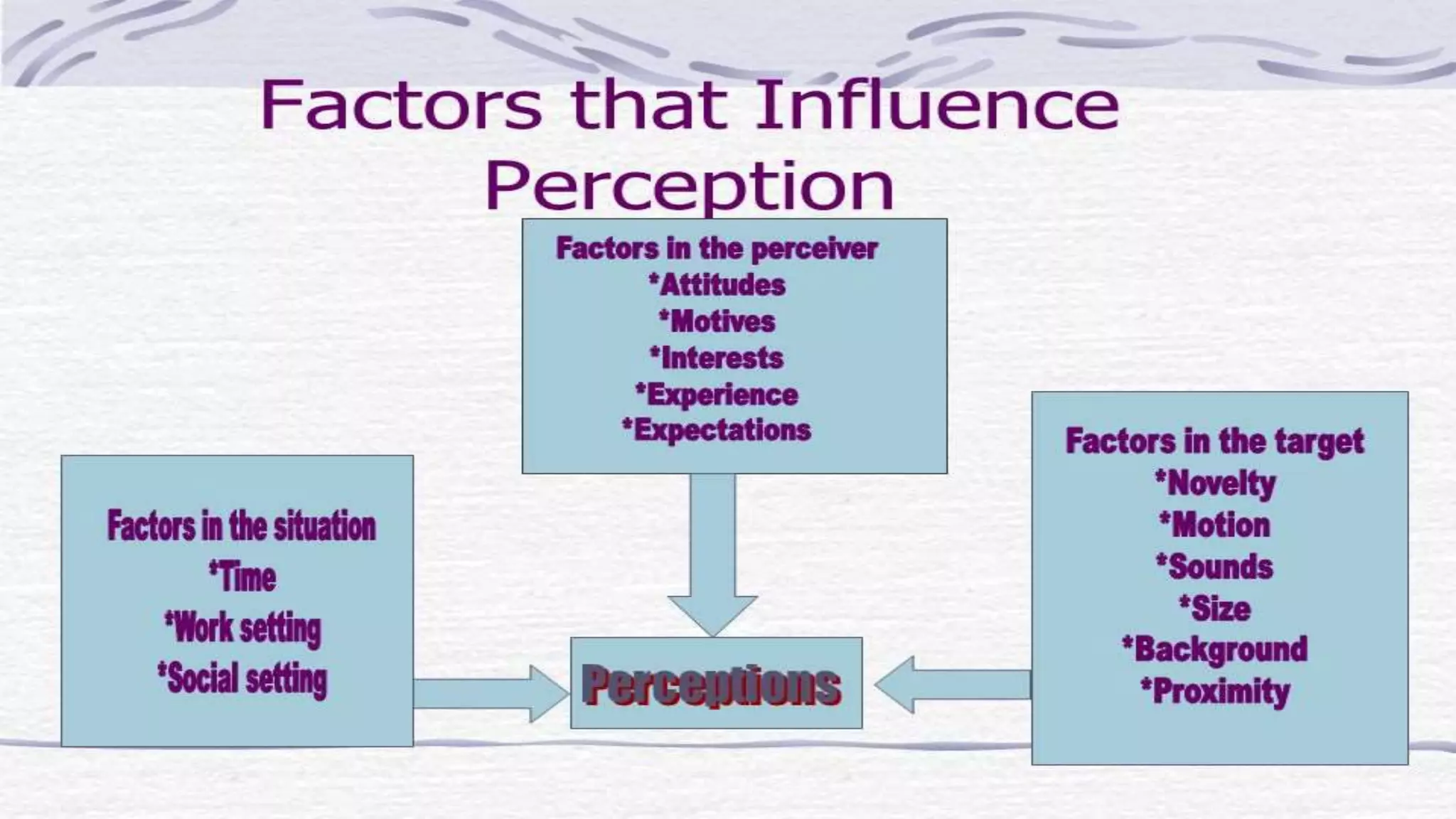
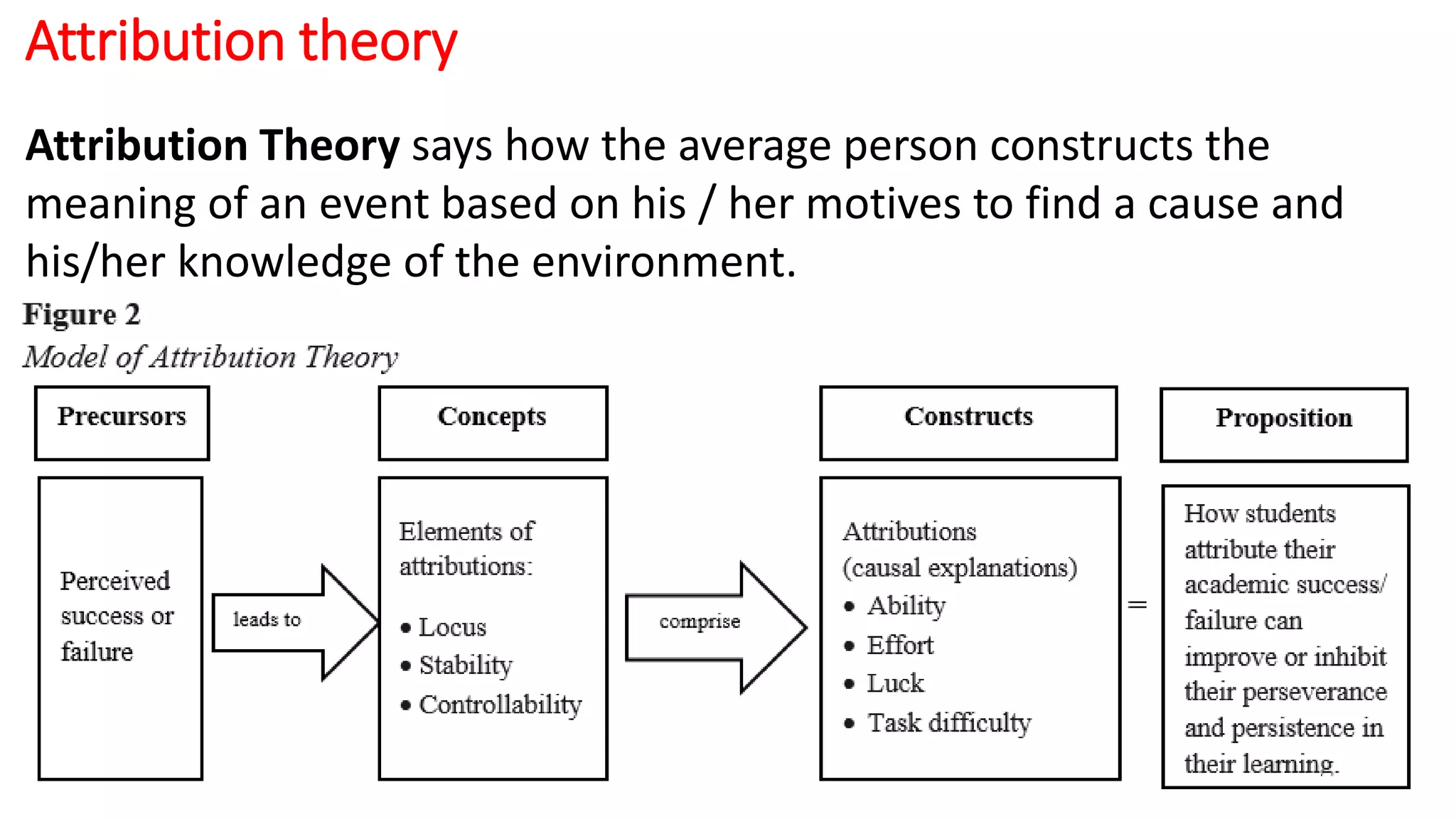
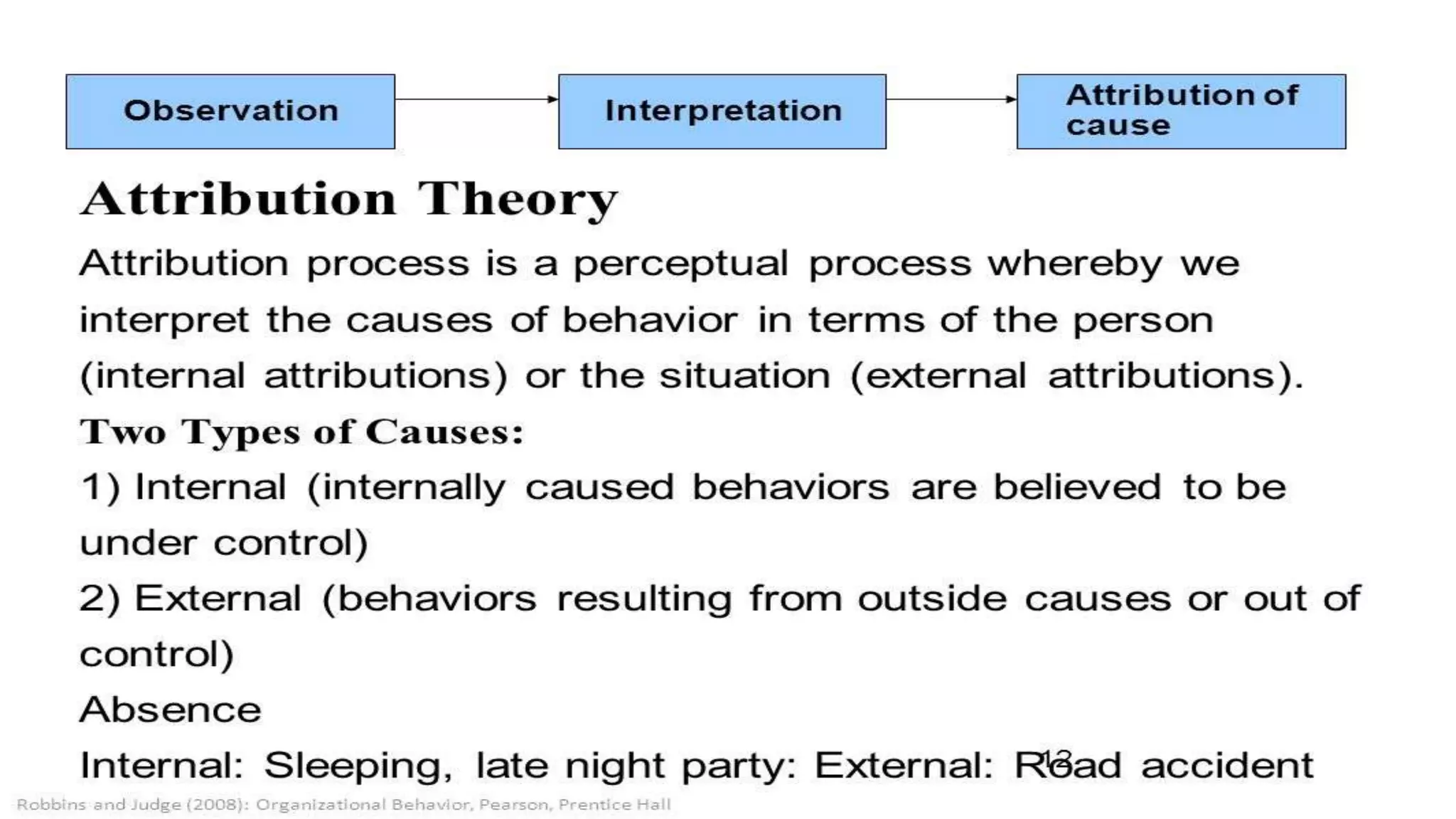
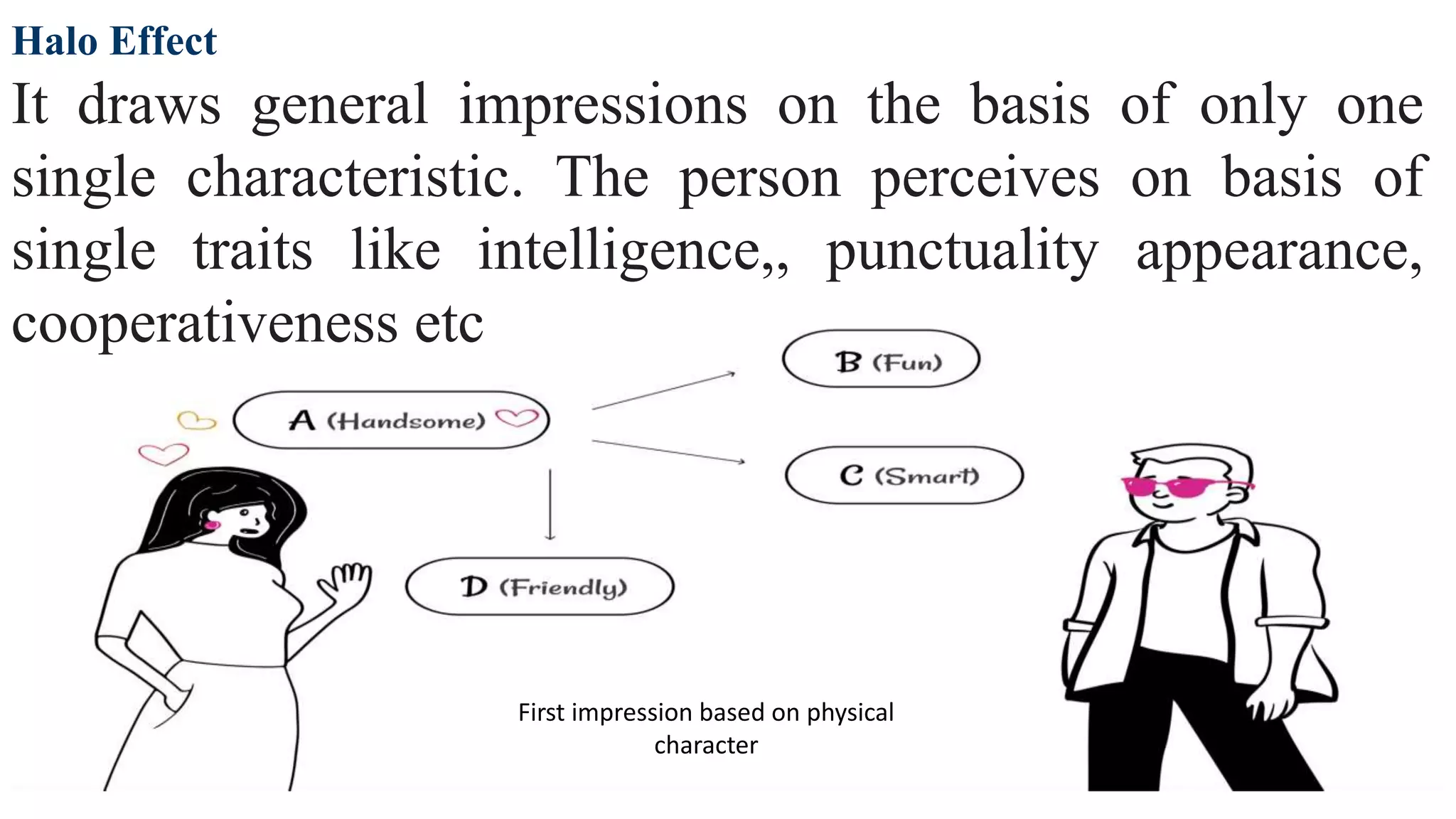
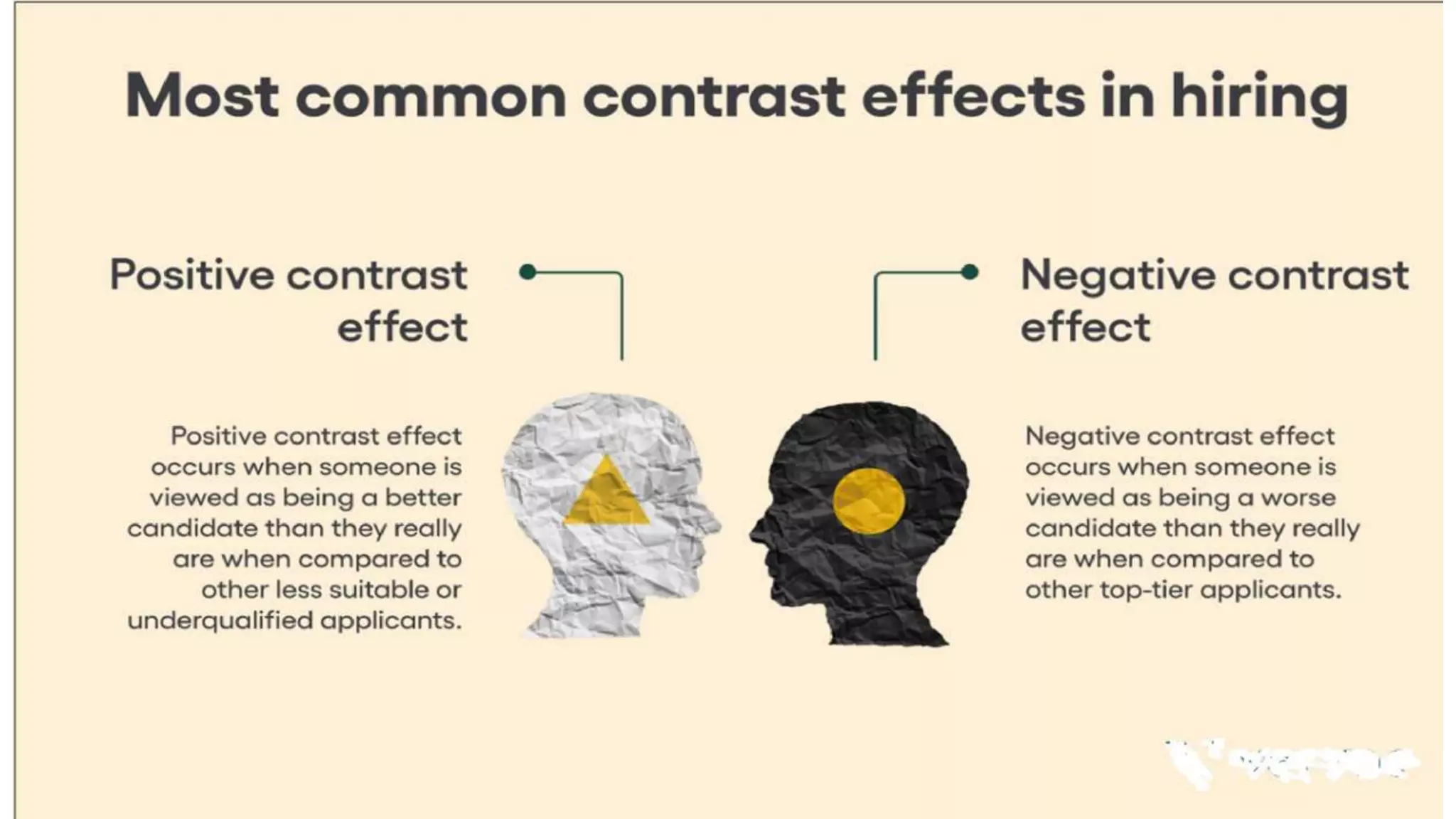
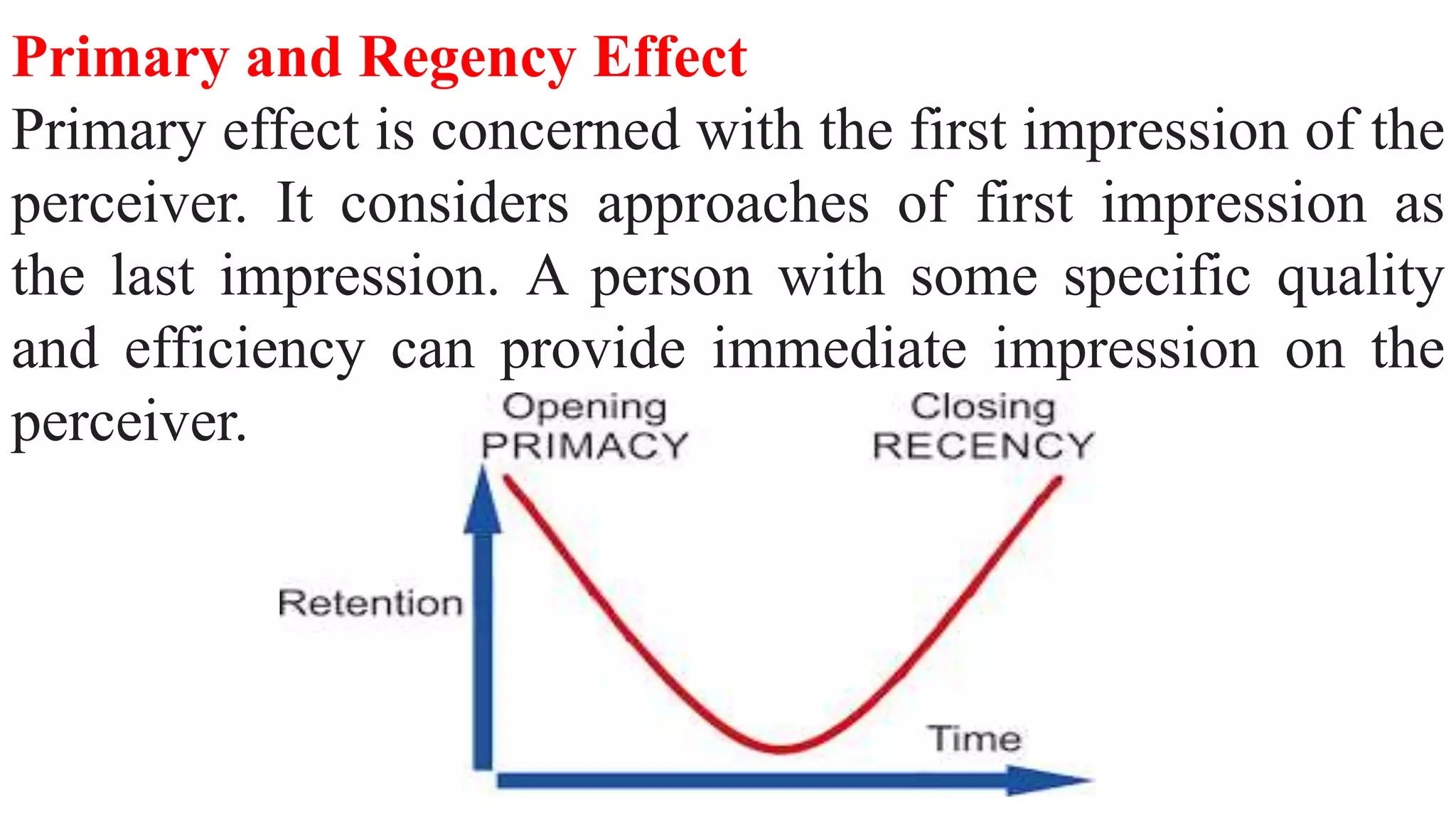
This document discusses perception and attribution theory. It defines perception as the ability to see, hear, or become aware of something through the senses. Attribution theory examines how people construct meaning from events and make attributions about causes. There are several types of attribution errors that can occur, including the fundamental attribution error of overemphasizing internal factors for others' behaviors. The document also discusses concepts like selective perception, halo effect, stereotyping, and projection. Learning is defined as the modification of behavior through experience, and principles of learning include readiness, exercise, effect, primacy, and recency. Cognitive learning theory examines an individual's thoughts and interpretations, while social learning emphasizes learning through observing others.