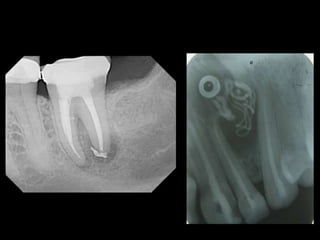
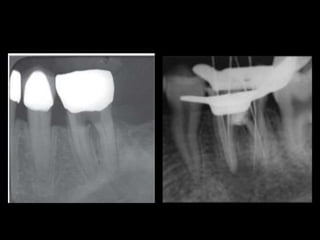
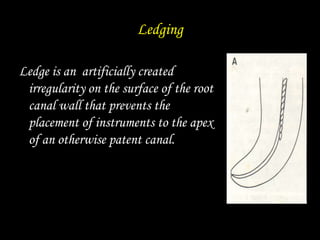
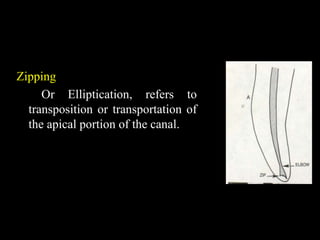
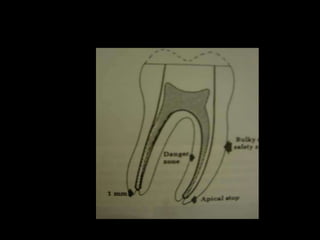
This document classifies endodontic mishaps and errors into four main categories: access related, instrumentation related, obturation related, and miscellaneous. Access related errors include treating the wrong tooth, missed canals, damage to existing restorations, access cavity perforations, and crown fractures. Instrumentation related errors consist of ledge formation, cervical and midroot canal perforations, apical perforations, separated instruments, canal blockage, loss of working length, over or under instrumentation, and blockage of the canal system. Obturation related errors are over- or under-extended root canal fillings and nerve paresthesia. Miscellaneous errors include post space perforation, irrigant related issues, tissue