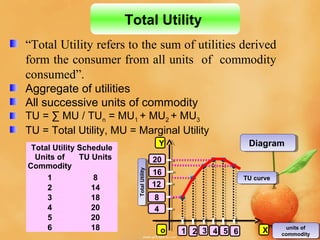
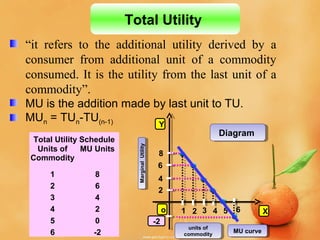
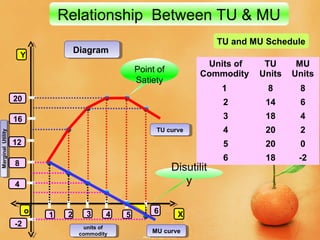
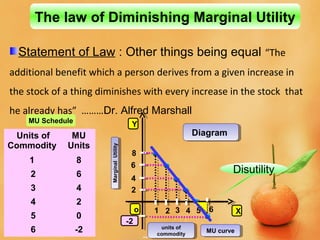
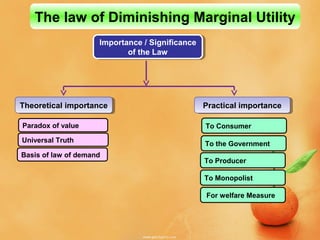
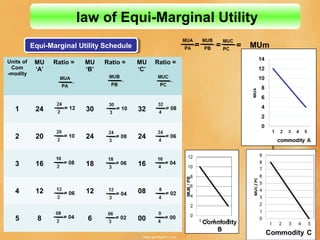
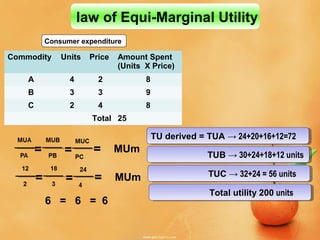
This document discusses concepts related to consumer behavior and utility analysis in economics. It defines key terms like total utility, marginal utility, and introduces important laws like the law of diminishing marginal utility and the law of equi-marginal utility. Specifically, it provides definitions of total utility and marginal utility. It explains the relationship between total utility and marginal utility through schedules and diagrams. It also outlines the assumptions, statement, exceptions and importance of the law of diminishing marginal utility and the law of equi-marginal utility.