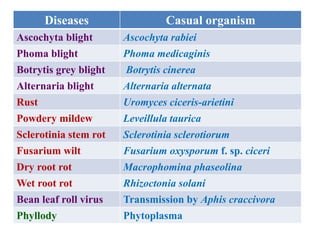
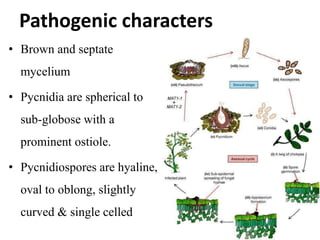
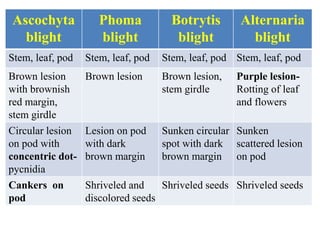
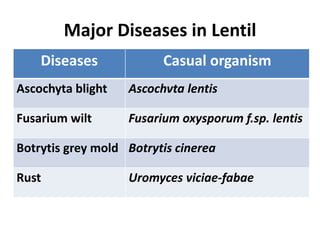
This document describes several common diseases that affect chickpea and lentil crops. For chickpea, it lists 12 diseases including Ascochyta blight, Phoma blight, Botrytis grey blight, Alternaria blight, Rust, Powdery mildew, Sclerotinia stem rot, Fusarium wilt, Dry root rot, Wet root rot, Bean leaf roll virus, and Phyllody. For each disease, it provides the causal organism, symptoms, and brief management strategies. It also provides more detailed information on symptoms and characteristics for Ascochyta blight. For lentil, it lists four major diseases: Ascochyta blight, Fusarium