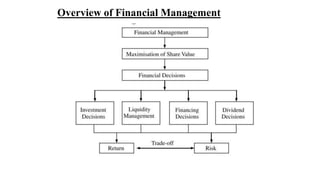
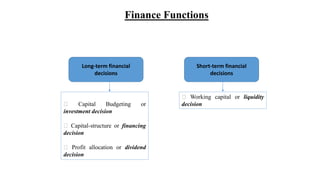
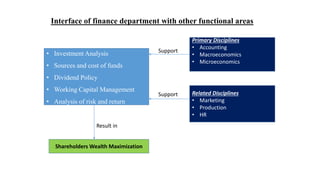
Financial management provides a conceptual framework for making financial decisions to help individuals and businesses grow financially. It involves acquiring, financing, and managing assets to achieve overall goals. The key financial decisions are investment, financing, and managing working capital. Investment decisions evaluate projects and allocate capital. Financing decisions determine optimal debt-equity ratios. Working capital management balances short-term liquidity and long-term profitability. Together, these decisions aim to maximize shareholder wealth over the long run.









![Government Company
• Government company means any company in which not less than fifty-one per
cent of the [paid-up share capital] is held by the Central Government, or by any
State Government or Governments, or partly by the Central Government and
partly by one or more State Governments
One Person Company (OPC)
• One Person Company (OPC) is a company incorporated by a single person.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-introduction-231014173052-08ed1c3b/85/1-Introduction-pptx-10-320.jpg)