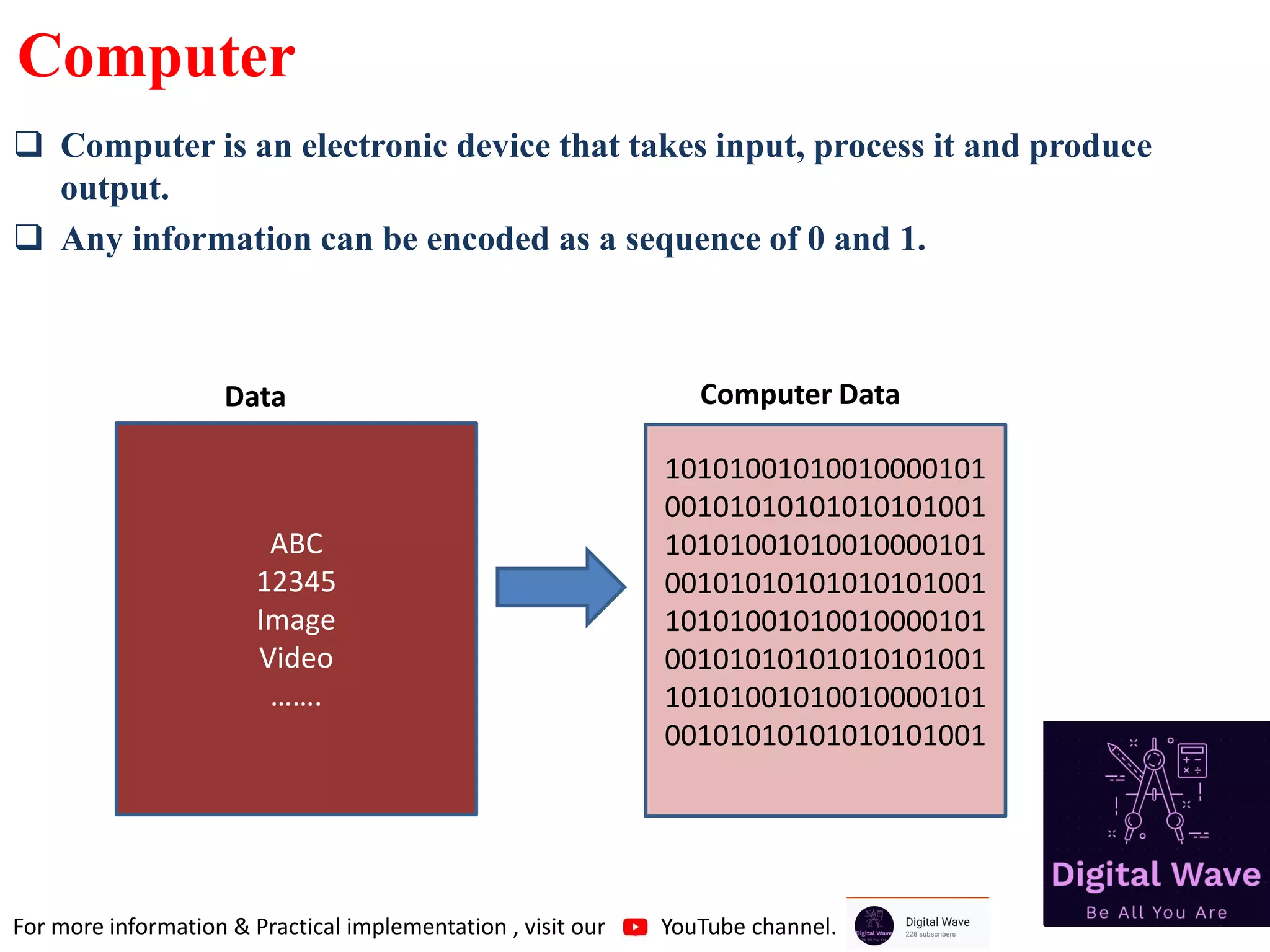
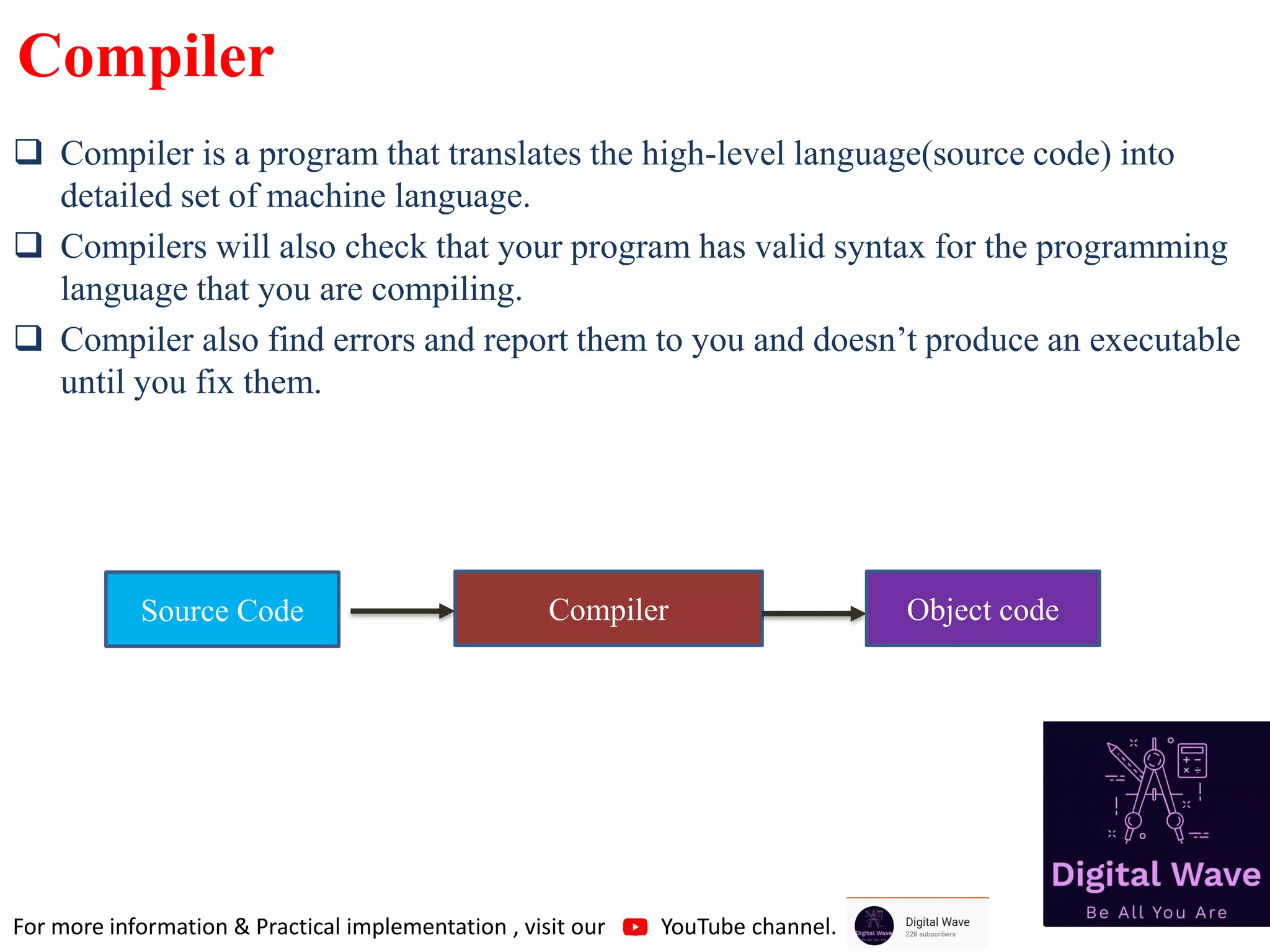
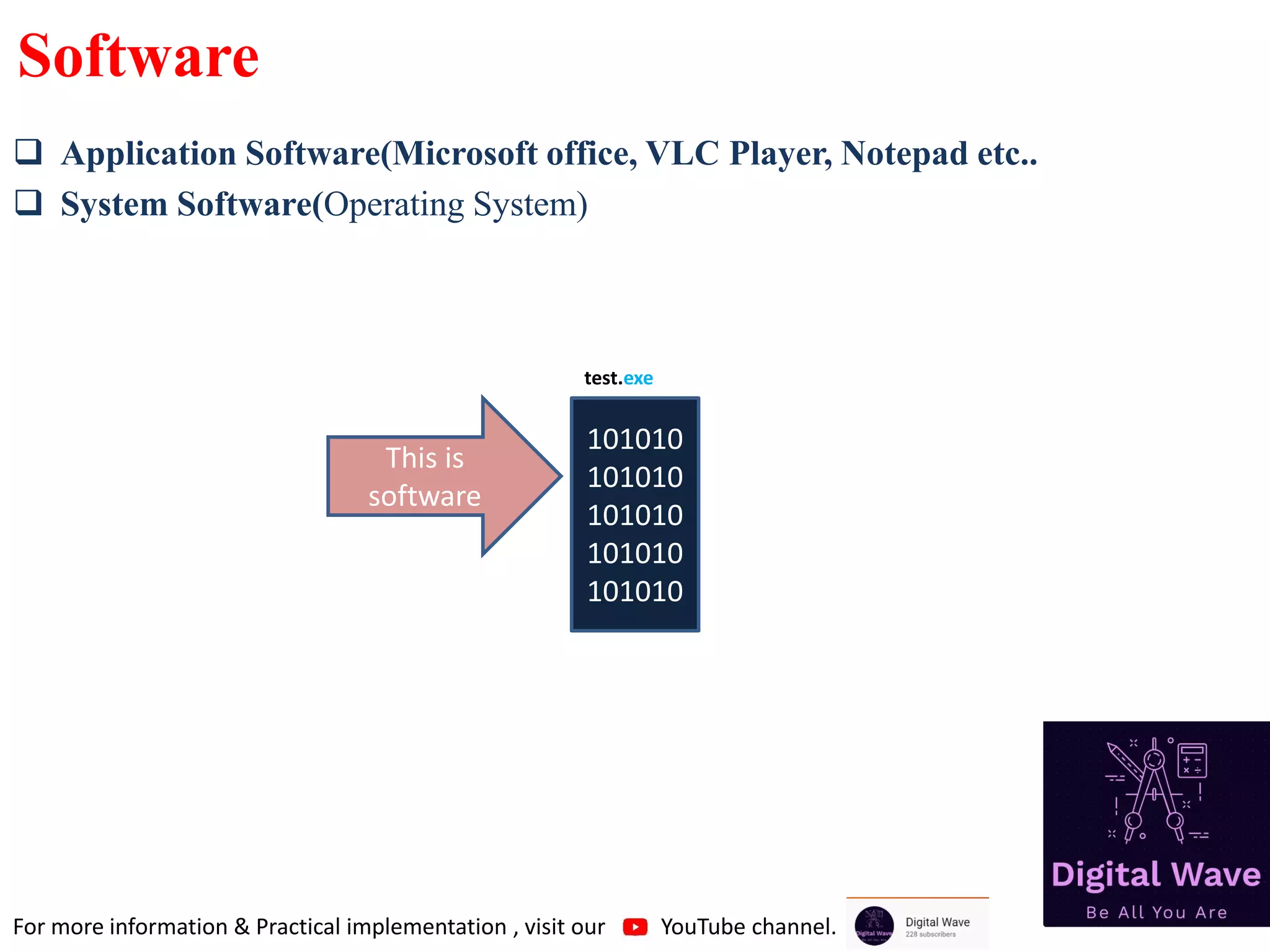
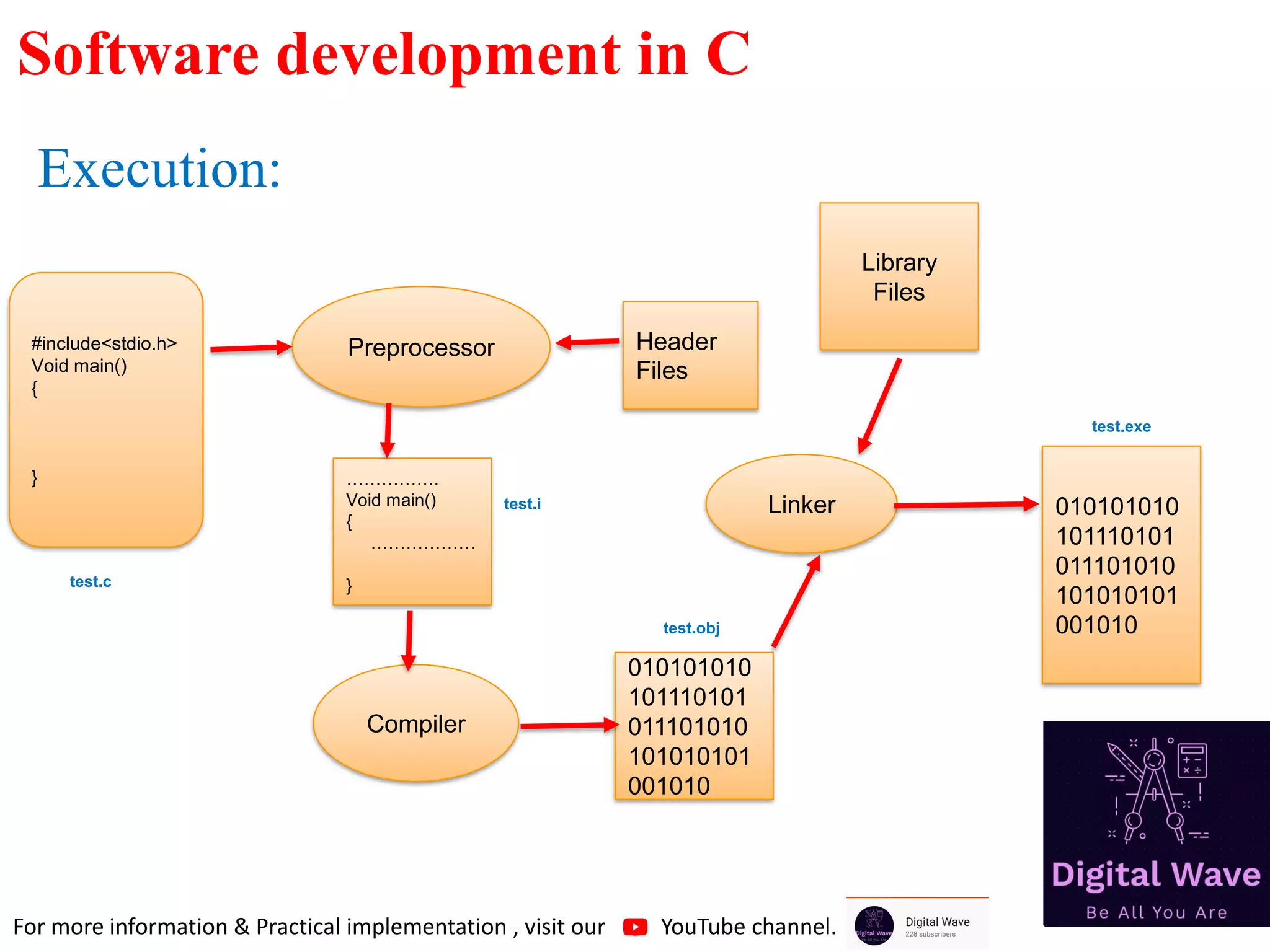
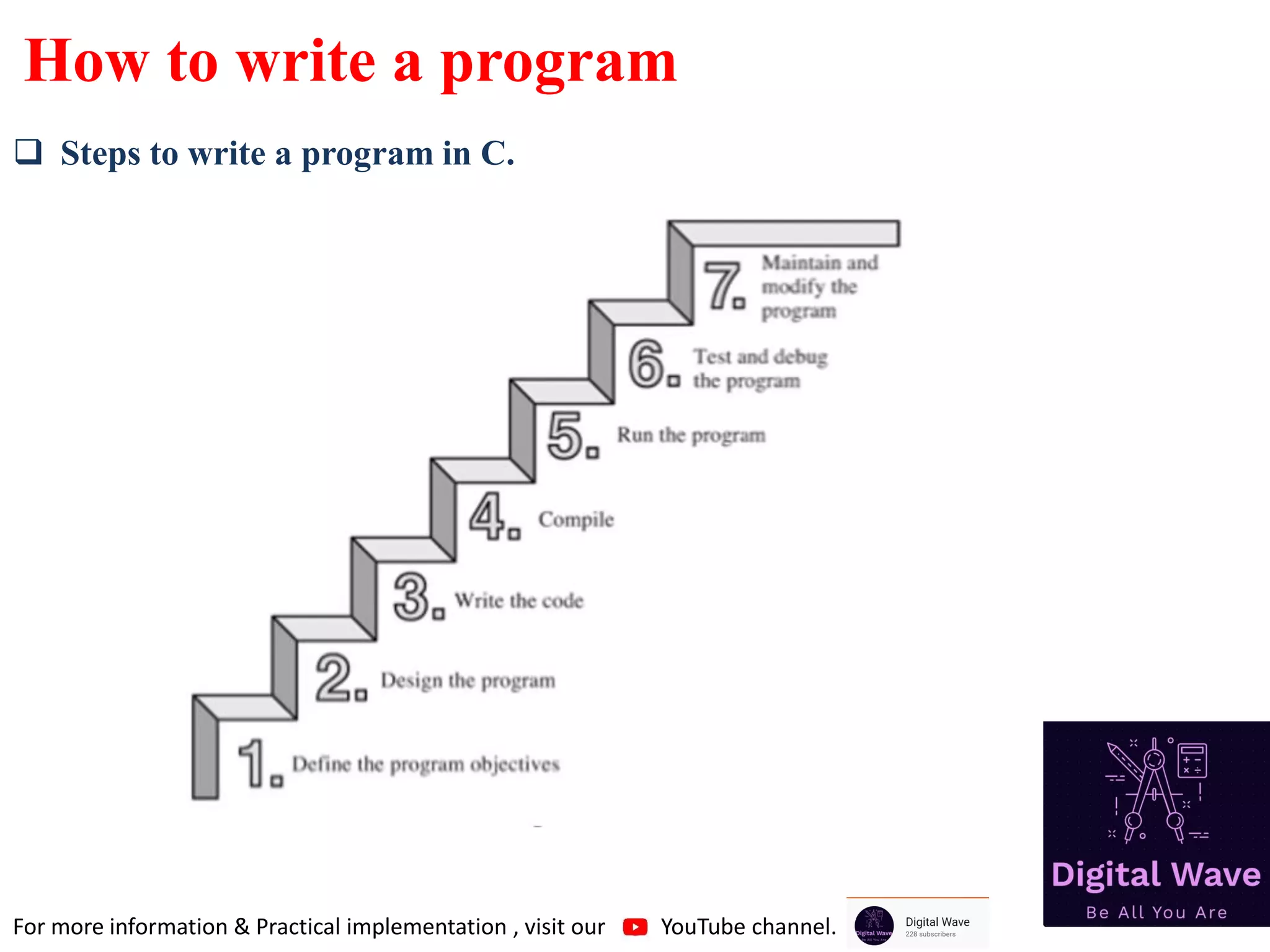
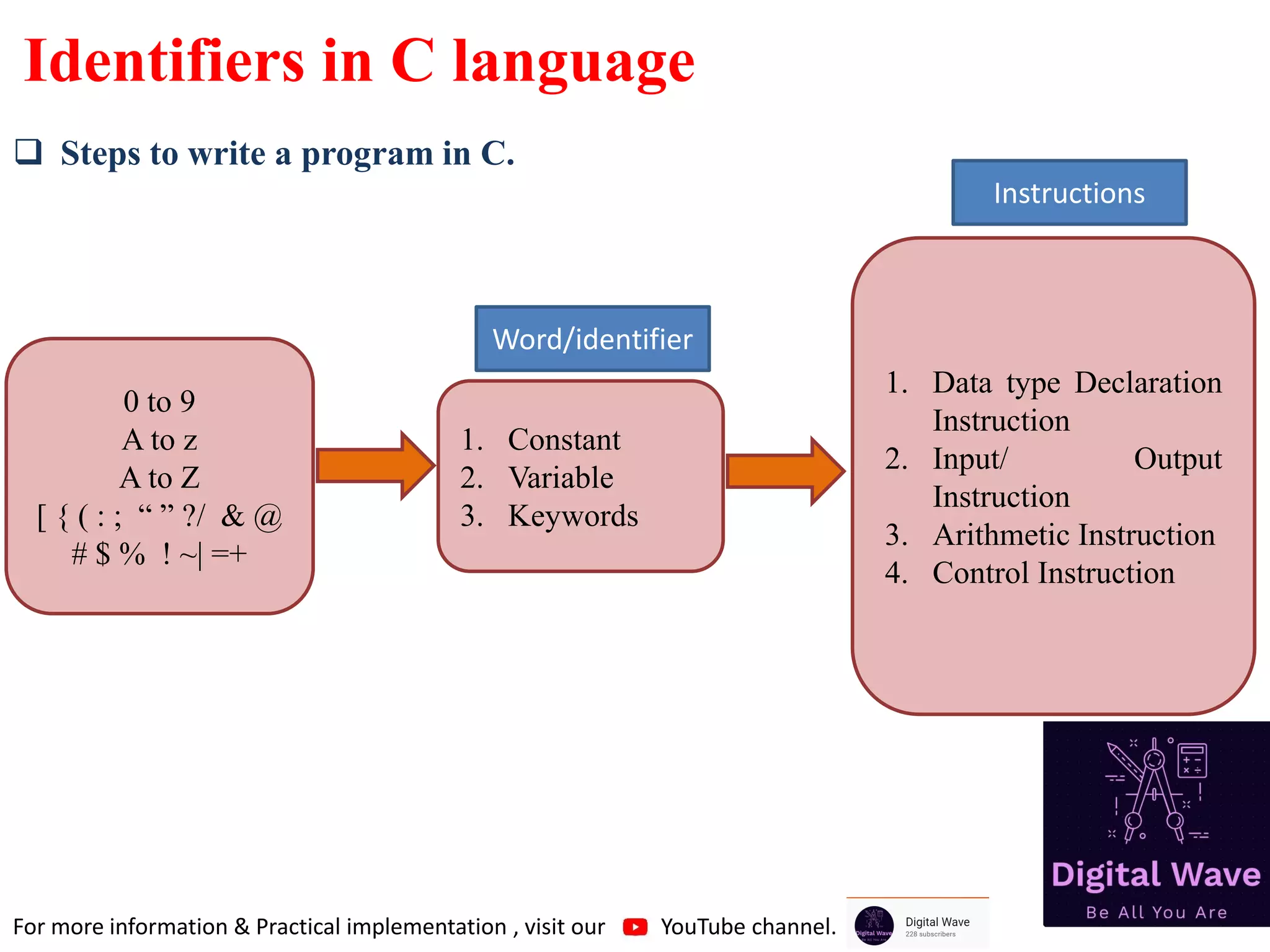
The document is an introduction to computer programming in C, detailing its basics, history, and importance in software development. It explains algorithms, the role of compilers, and fundamental computer terminology, including hardware and software concepts. Additionally, it emphasizes C's significance in programming embedded systems and various applications like web browsers and databases.