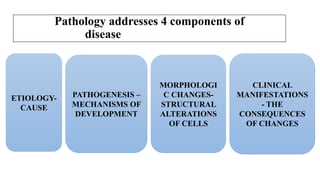
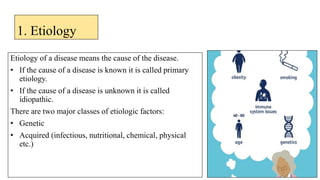
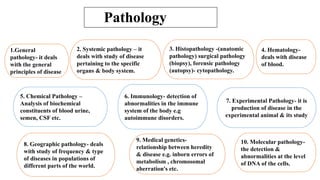
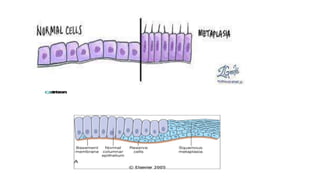
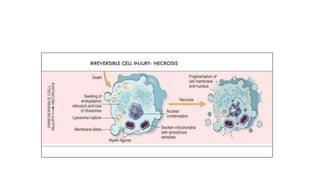
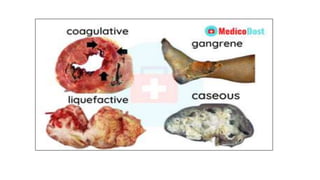
The document discusses general pathology, aiming to provide students with an in-depth understanding of disease mechanisms, including etiology, pathogenesis, morphological changes, and clinical manifestations. It outlines the importance of studying pathology and describes various types of cellular adaptations and injuries, leading to cell death through necrosis or apoptosis. Furthermore, it highlights the evolution of pathology and its diverse branches, including systemic and histopathology, contributing to clinical practice and patient care.