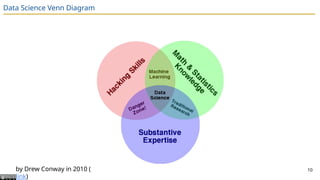
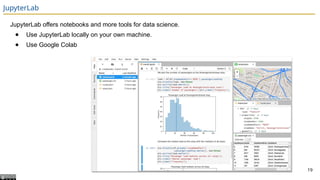
The document presents an overview of the CS 577 Data Science course, outlining its goals, structure, and key topics like exploratory data analysis and model design. It highlights the interdisciplinary nature of data science and emphasizes the importance of deriving insights from data rather than merely applying statistical methods. The course includes assignments, exams, and a group project, with clear grading logistics and deadlines.