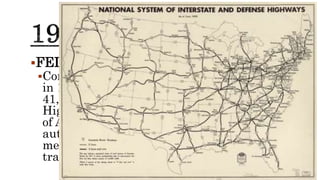
The document summarizes important events from 1953 to 1965 related to the end of the Korean War, McCarthyism, the Civil Rights movement in the US, space race developments, and escalating US involvement in Vietnam. Key events included the 1954 Geneva Accords ending the Korean War, Brown v. Board of Education Supreme Court ruling against segregation in 1954, launch of Sputnik satellite by the Soviet Union in 1957 intensifying the space race, sit-ins and Freedom Rides protesting segregation, and President Johnson sending combat troops to Vietnam in 1965.