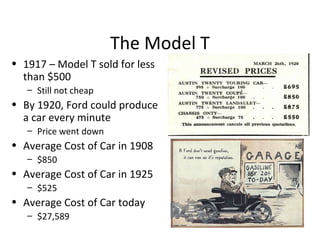
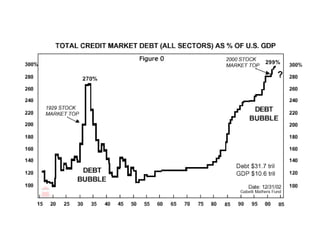
The document summarizes how the economy changed in the 1920s due to industrial innovations like the assembly line. Henry Ford revolutionized car manufacturing using standardized parts and the assembly line, greatly increasing productivity. This led to a boom in the automobile industry and the growth of related industries. Mass production also enabled installment buying, allowing more consumers to purchase new products. Overall, industrialization and mass production transformed the economy and society in the 1920s.