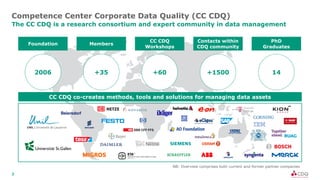
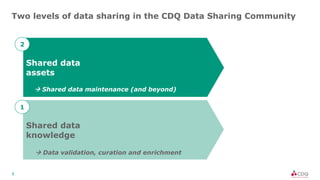
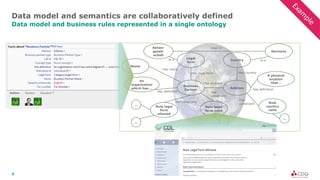
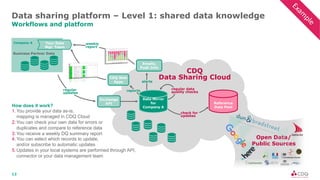
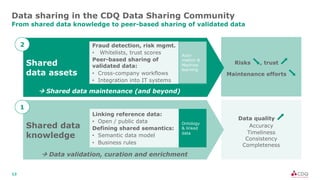
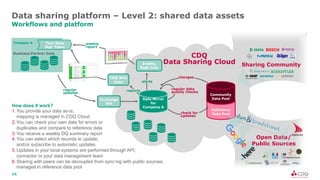
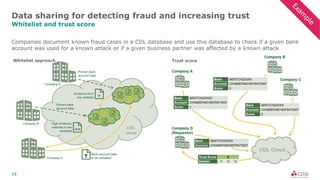
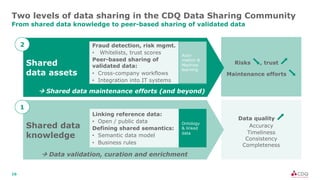
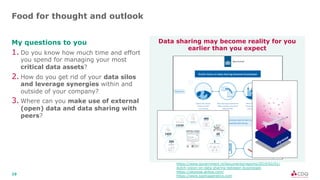
The document discusses data sharing in business ecosystems. It provides an example of a trusted network called the CDQ Data Sharing Community that facilitates two levels of data sharing between companies. The first level involves sharing data knowledge such as reference data and semantics. The second level involves sharing validated data assets. Benefits of data sharing include improved data quality, reduced data maintenance efforts, lower risks, and increased trust in shared data. The document also outlines lessons learned and opportunities for further expanding data sharing between organizations.