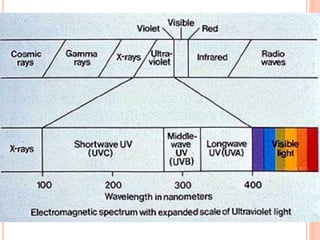
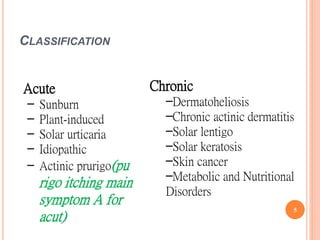
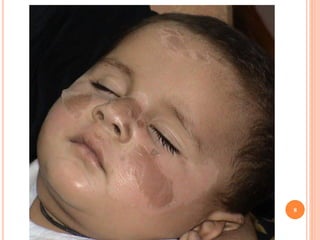
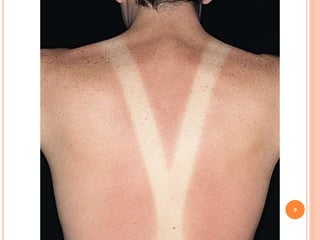
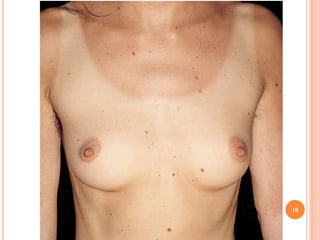
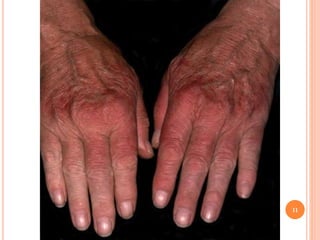
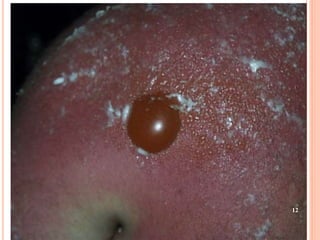
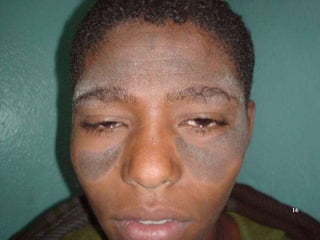
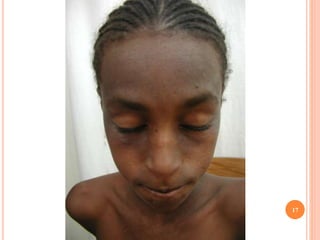
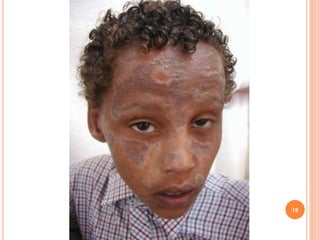
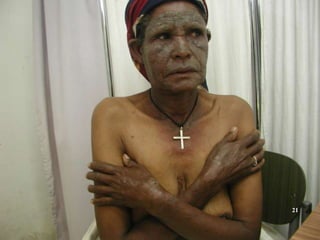
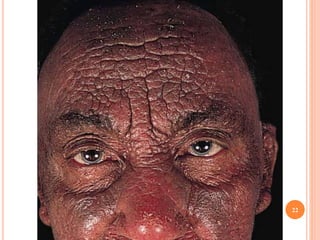
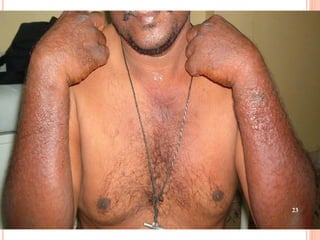
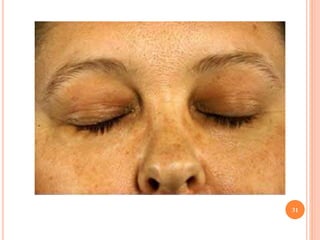
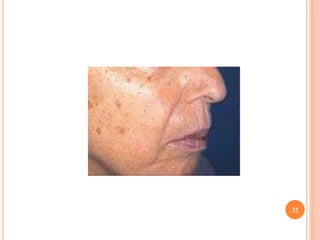
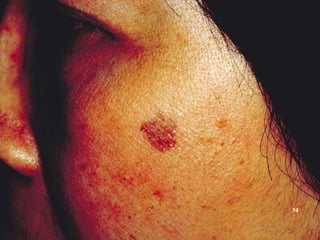
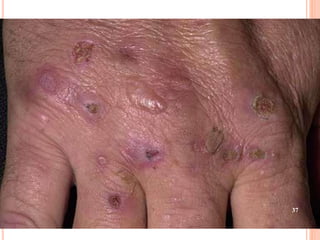
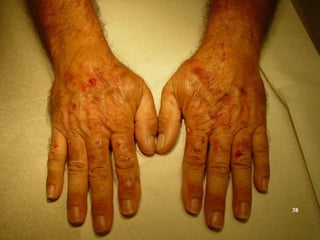
This document discusses various skin conditions caused or aggravated by sun exposure. It begins by classifying conditions as either acute or chronic, then describes acute sunburn caused by UVB radiation damaging DNA. It also discusses phototoxic drug eruptions caused by drugs like amiodarone exacerbating sunburn through UVA damage. Photoallergic drug eruptions are allergic reactions to drugs like sulfonamides previously sensitized individuals experience with UVA. Chronic conditions include photoaging/dermatoheliosis causing premature aging, solar lentigos appearing as brown macules, and porphyria cutanea tarda a metabolic disorder causing fragile skin in exposed areas.