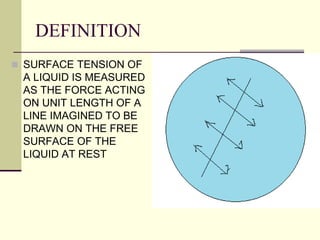
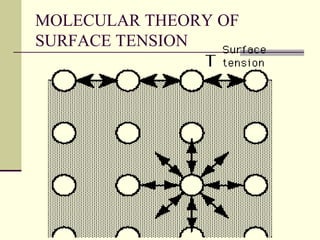
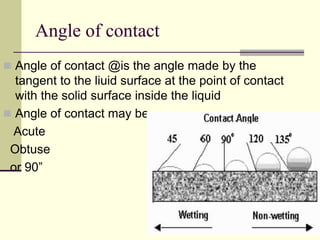
Surface tension is the property of a liquid that allows it to act like a stretched membrane. It is caused by attractive forces between molecules in a liquid that make the liquid behave as if its surface has elastic properties. Surface tension can be defined as the force per unit length acting along an imaginary line within the surface of the liquid. It depends on factors like temperature, impurities, and molecular interactions - generally decreasing with increases in temperature or soluble impurities. Applications of surface tension include cleaning products, preventing mosquito breeding, and antiseptics.