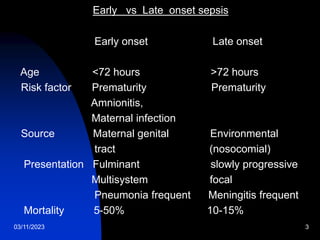
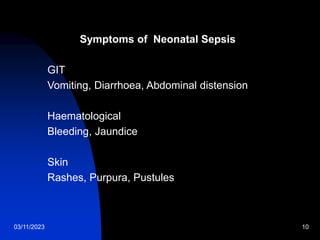
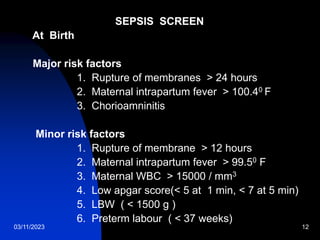
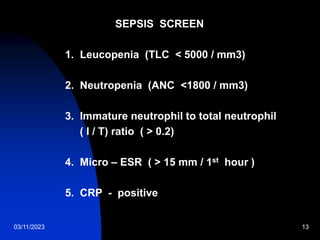
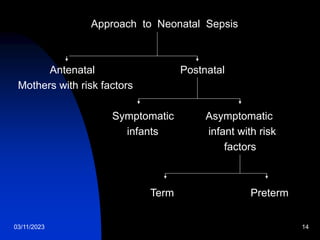
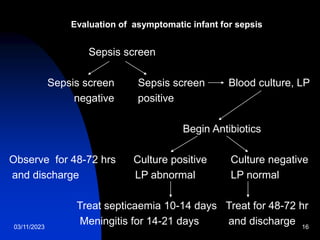
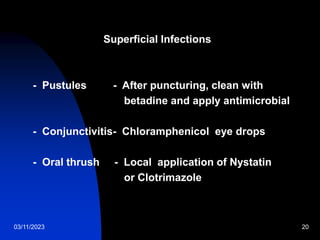
This document discusses neonatal sepsis, including its definition, types (early vs late onset), symptoms, risk factors, diagnosis, treatment and prevention. It notes that neonatal sepsis is a systemic bacterial infection occurring in the first 4 weeks of life. Early onset sepsis occurs within 72 hours of birth and is usually caused by maternal genital tract bacteria. Late onset sepsis occurs after 72 hours and is often hospital-acquired. Diagnosis involves blood, CSF and other cultures as well as sepsis screening tests. Treatment involves supportive care and parenteral antibiotics, with antibiotic choices dependent on the suspected site of infection. Handwashing and other infection control practices are emphasized for prevention.