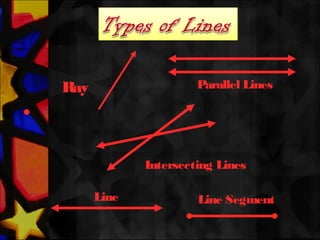
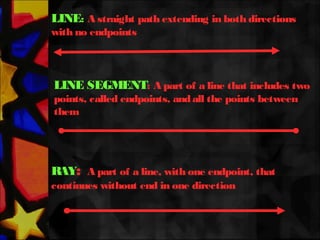
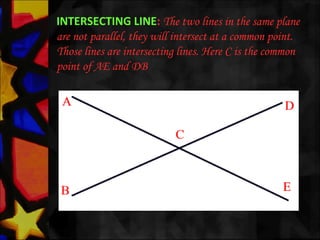
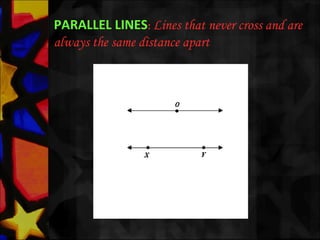
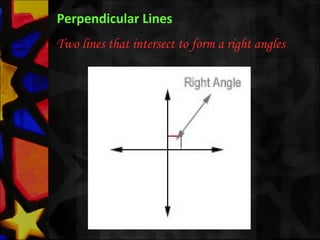
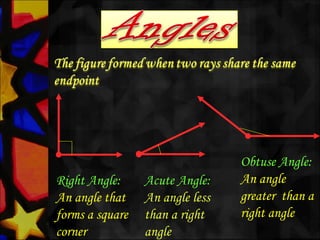
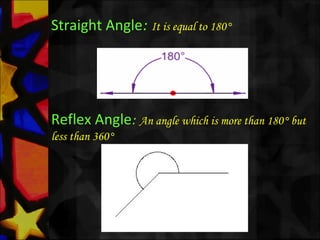
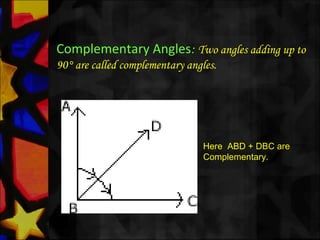
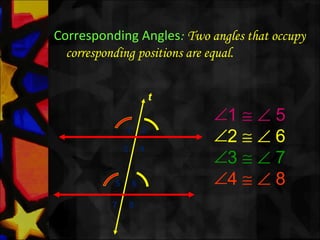
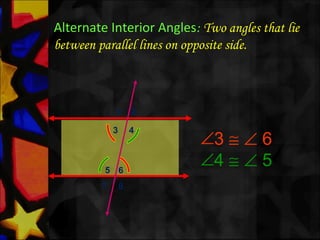
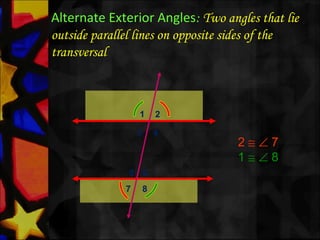
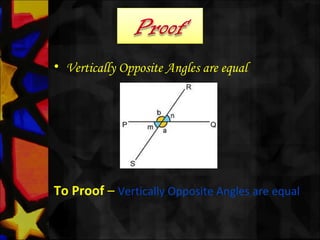
This document defines and describes various types of angles and lines. It defines a ray, line, and line segment. It describes intersecting lines, parallel lines, perpendicular lines, and types of angles such as acute, obtuse, straight, reflex, complementary, supplementary, vertical, and linear pairs. It also defines terms like transversal, corresponding angles, interior angles, exterior angles, and proves properties such as vertically opposite angles being equal and the angle sum of a triangle being 180 degrees.