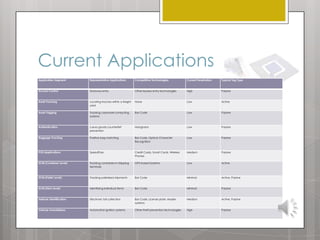
This document discusses RFID (radio frequency identification) technology. It describes the basic components of an RFID system including RFID tags, readers, and software. It outlines different types of RFID tags and provides examples of current RFID applications in various industries like access control, asset tracking, transportation, and retail. The document also summarizes the results of an online survey that found benefits of RFID include improved efficiency, enhanced customer satisfaction, and reduced costs. It concludes that while RFID offers advantages over barcodes, costs remain relatively high and standards are still being developed.