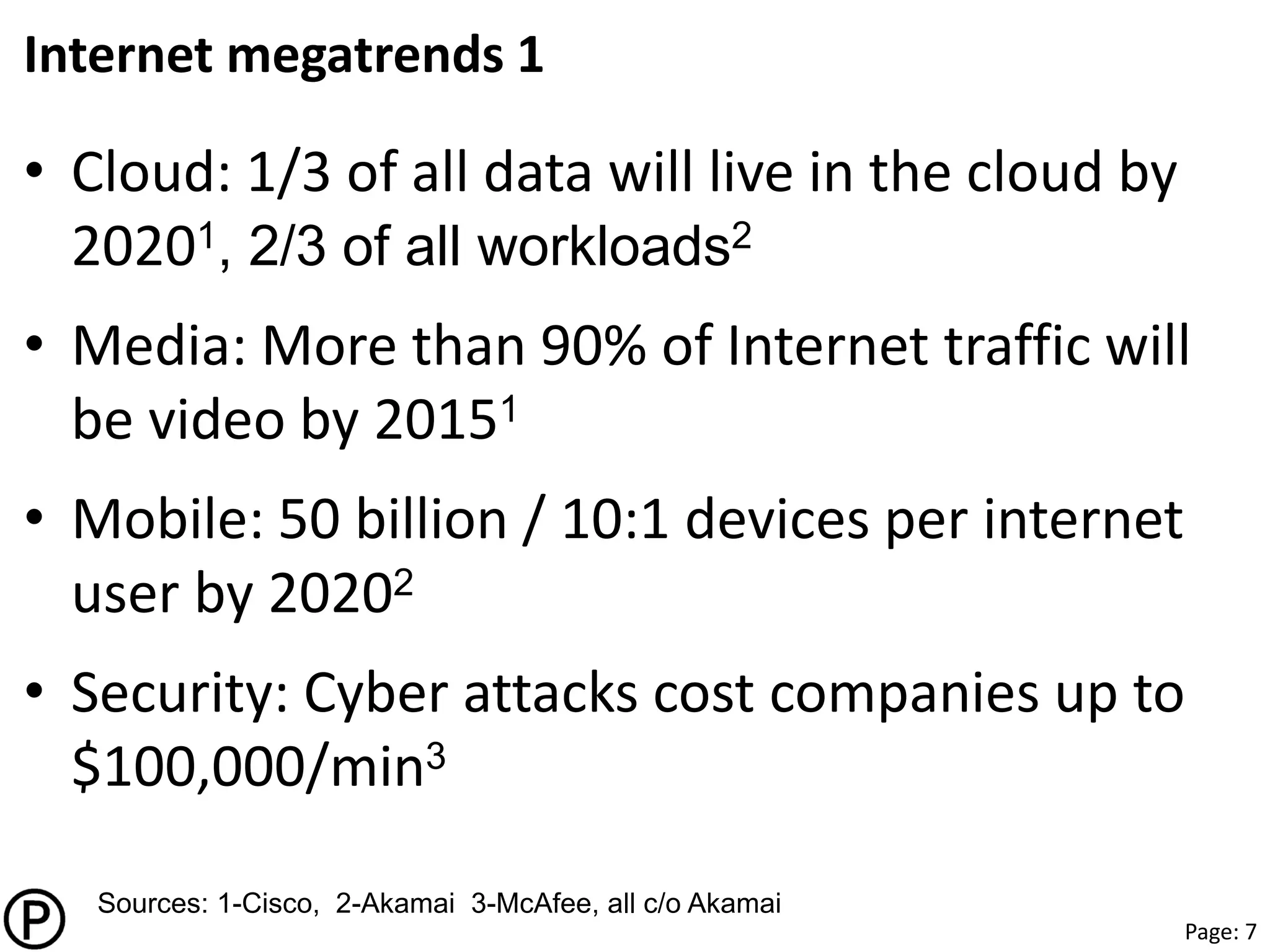
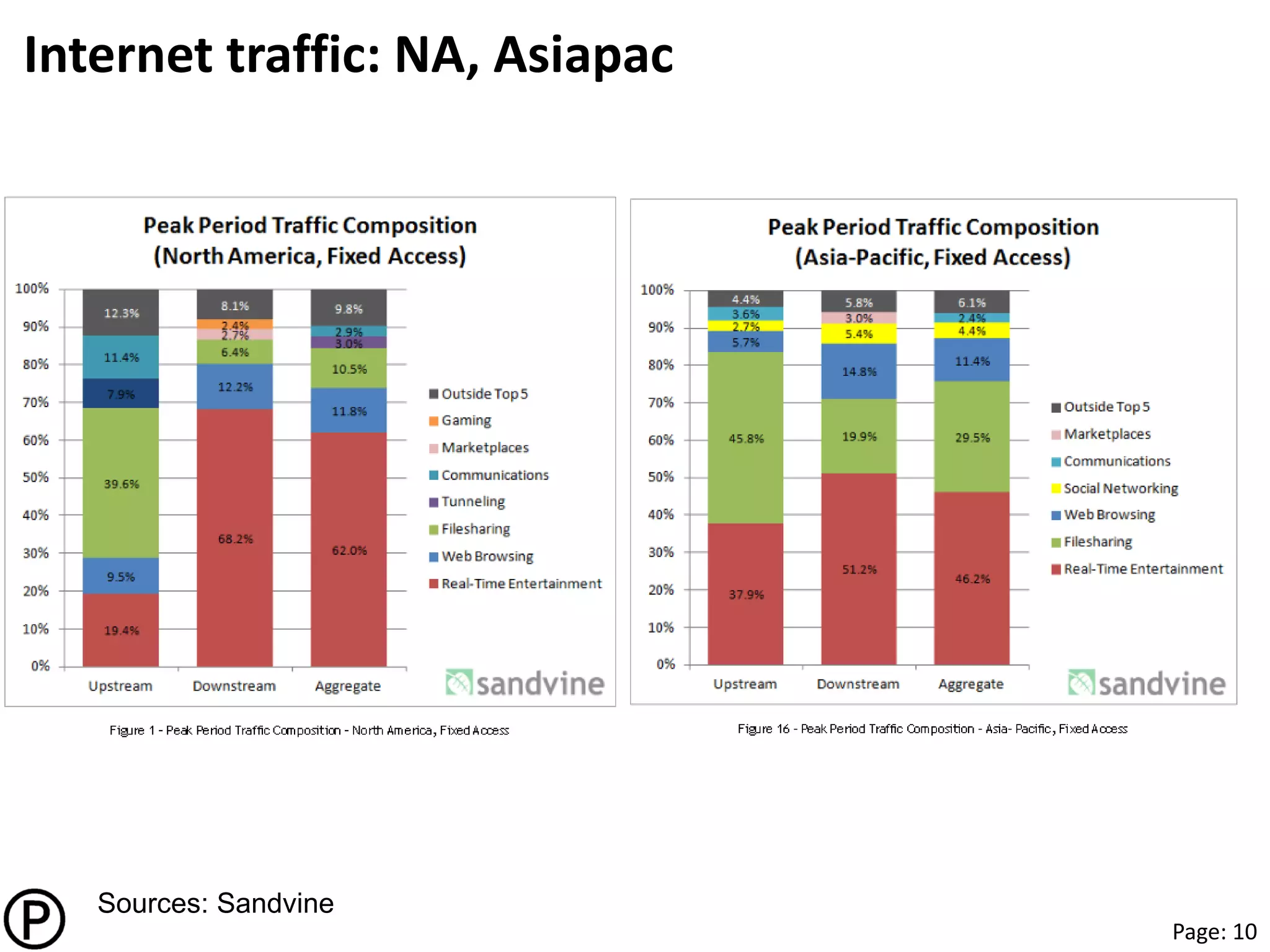
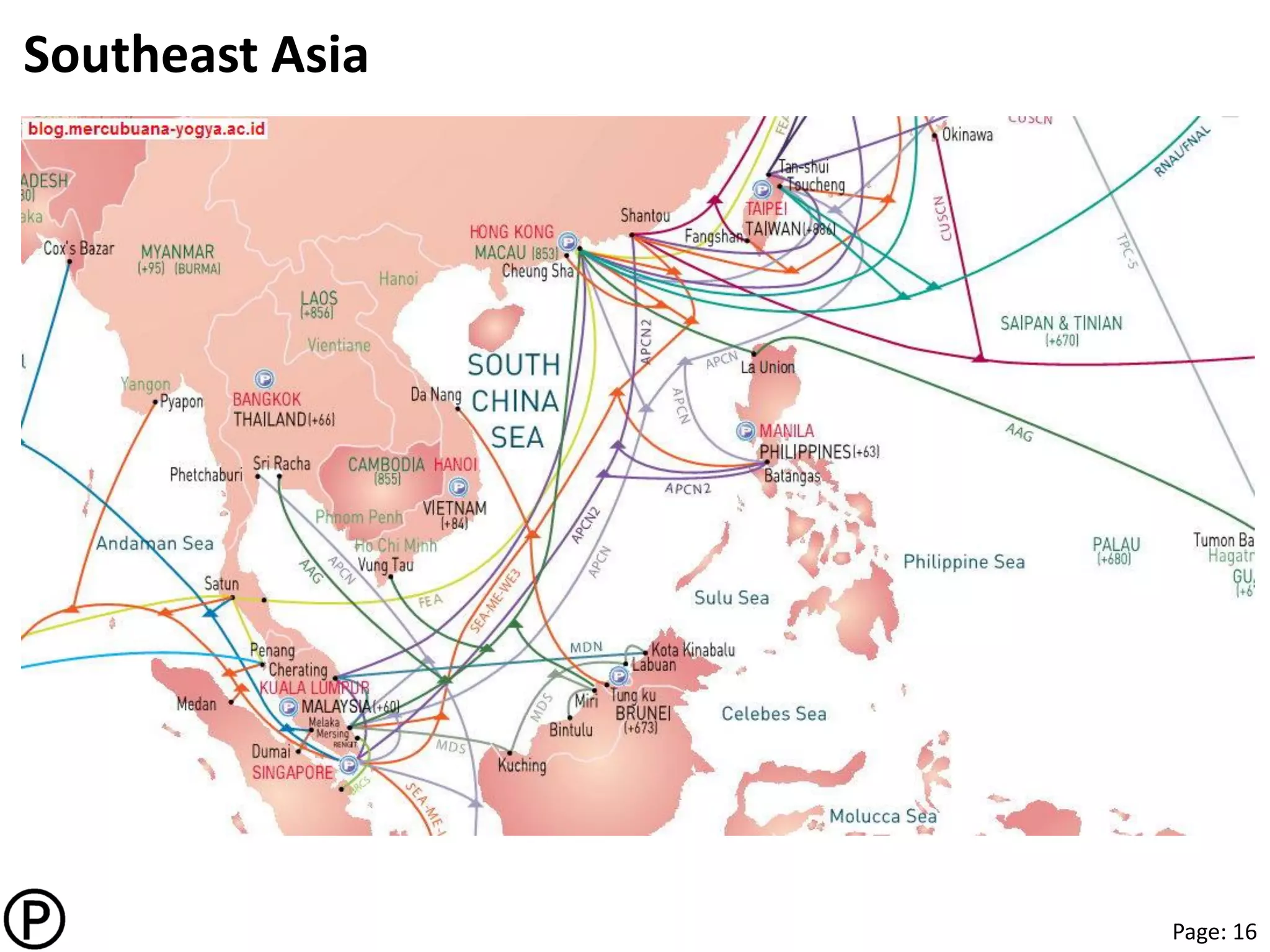
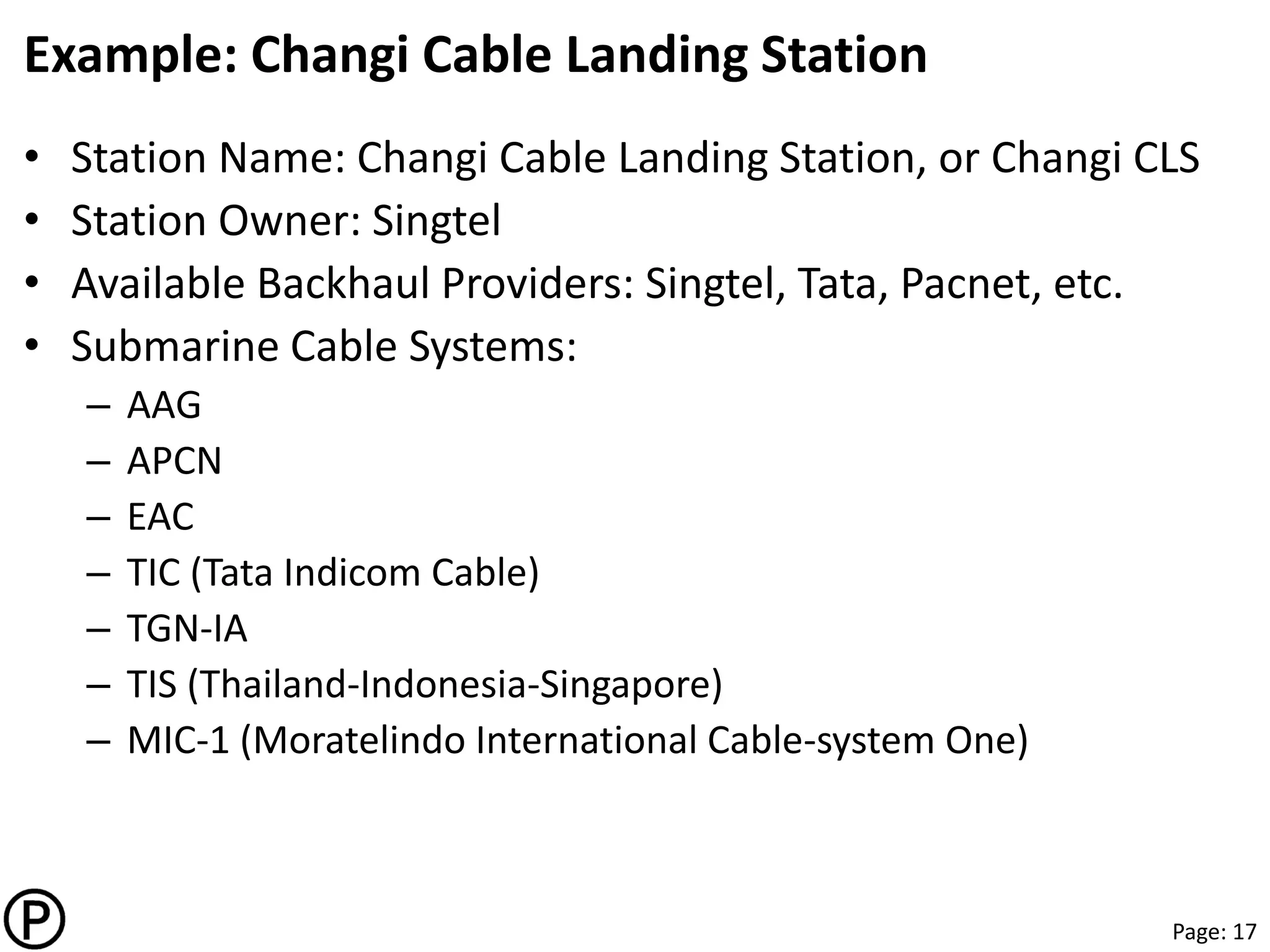
This document provides notes from a presentation on content delivery networks (CDNs). It discusses key internet trends driving growth in CDN usage, including the rise of cloud services, online video, mobile devices, and e-commerce in Asia. The presentation covers how CDNs help deliver content to users more quickly and reliably by caching it at network edges. It also describes different CDN models like traditional CDNs, enterprise CDNs, and transparent caching operated by internet service providers. The document concludes by discussing future directions for CDNs, such as integrating more with cloud platforms, establishing standards, and providing more personalized content delivery.
















![Page: 22
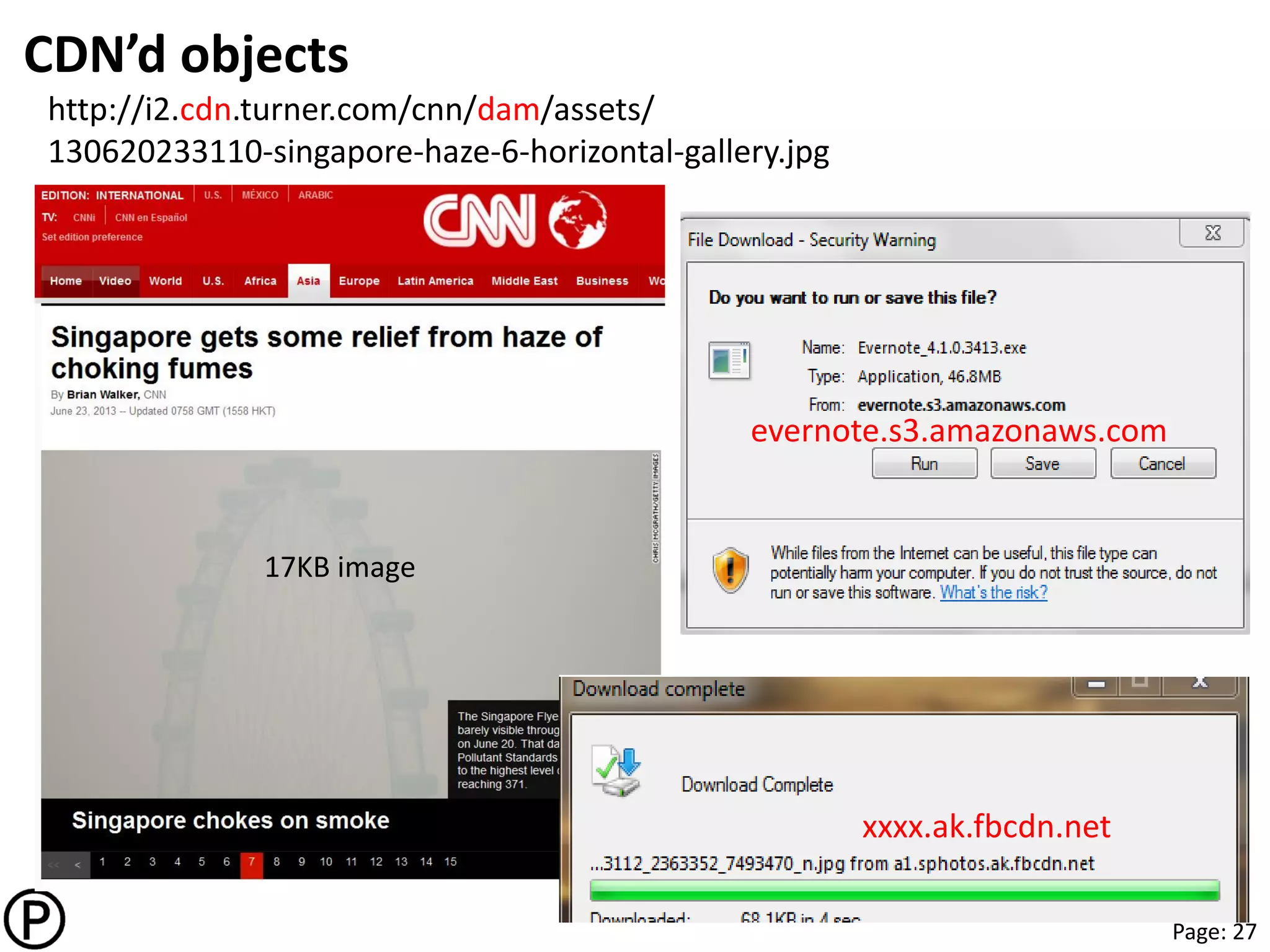
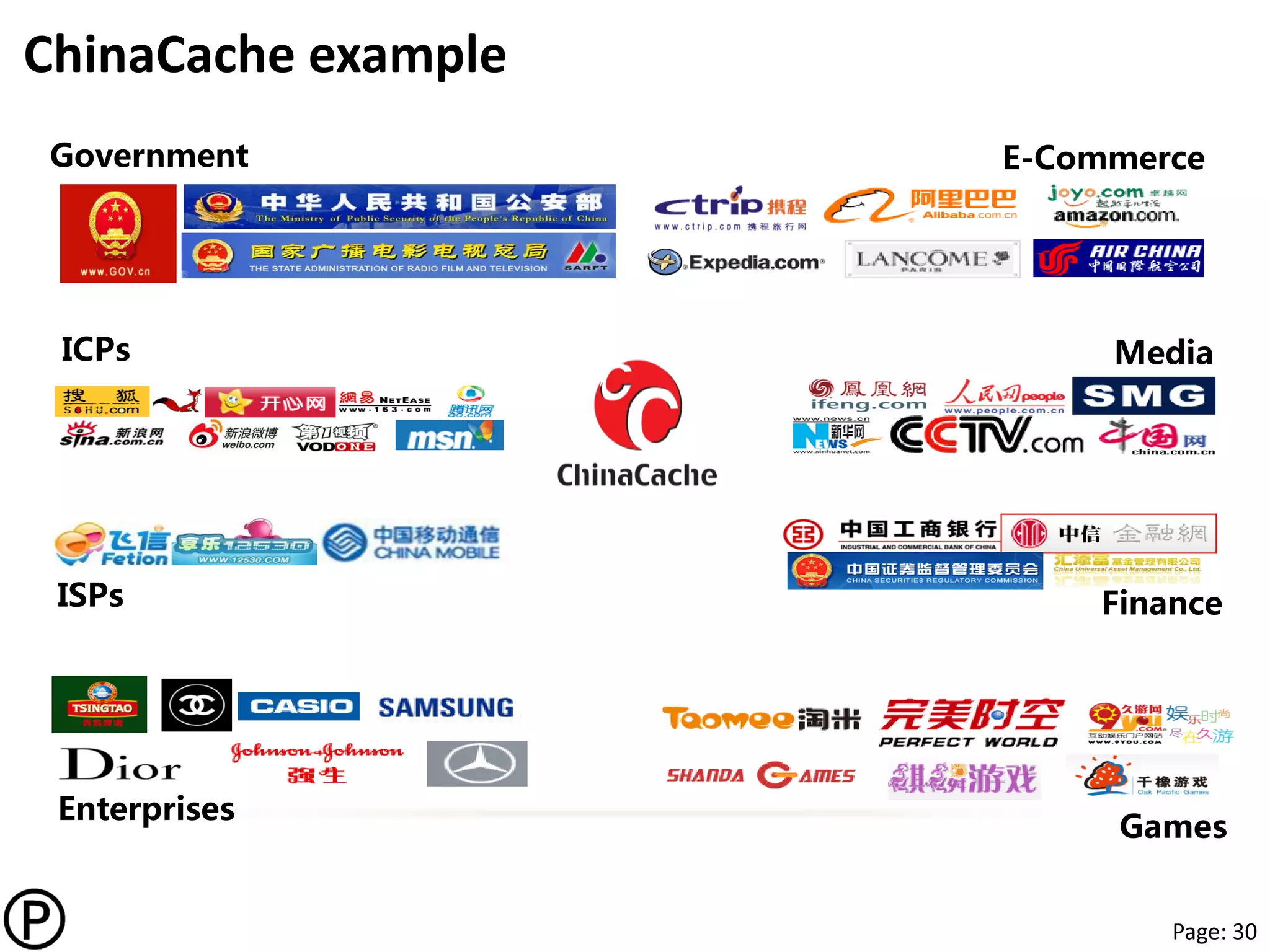
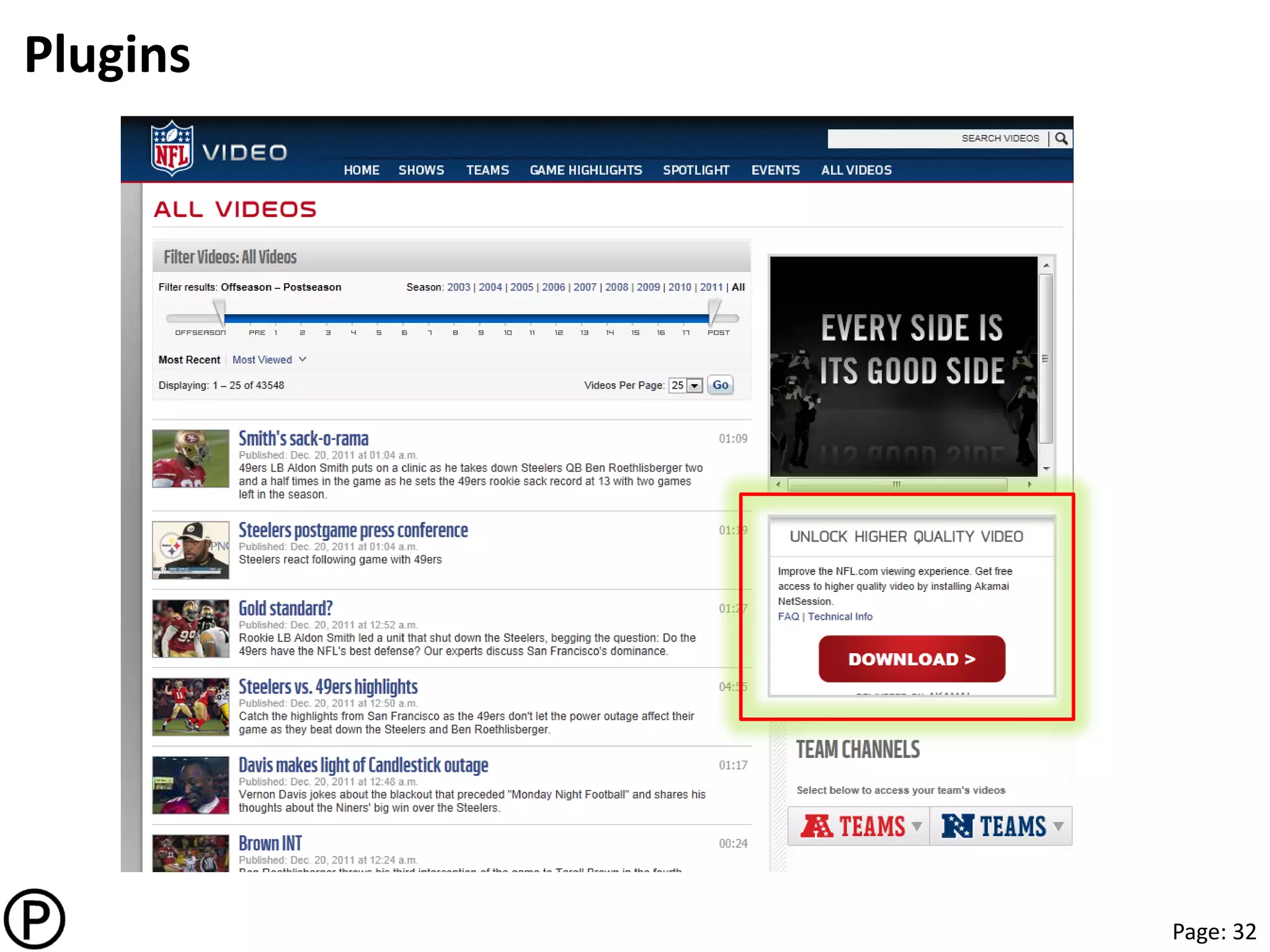
CDN today
• [ BTW, our browsers cache ]
• Proprietary CDNs
– Google: YouTube, Apple: iTunes , etc…
• Multi-tenant CDNs for enterprise
– Objects, downloads, video
– AJAX/JQuery CDNs (hosters)
– Hybrid / partnerships per-country
• Other CDNs
– Mobile CDNs
– Aware CDNs, eg: location, device, language
• Transcode, ad-serve](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/130815-ieeebtstalk-finalpublish-130816033139-phpapp02/75/130815-Content-Delviery-Networks-for-the-IEEE-Singapore-Broadcast-group-22-2048.jpg)