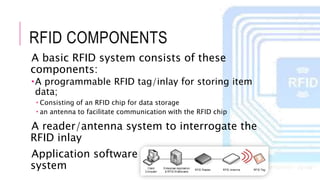
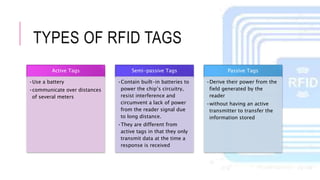
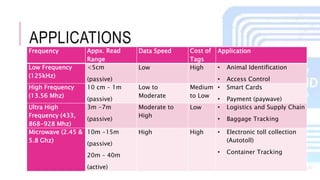
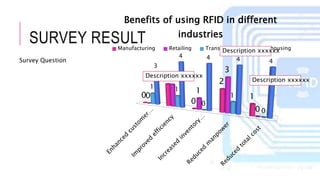
The document summarizes a project presentation on RFID technology. It includes sections on the introduction, details about RFID components and tags, current applications such as credit cards and electronic toll collection, results of an online survey on perceived benefits in different industries, findings that RFID is useful for medical and library applications, and a conclusion that RFID provides benefits like contactless reading and rewritable data but has higher costs than barcodes.