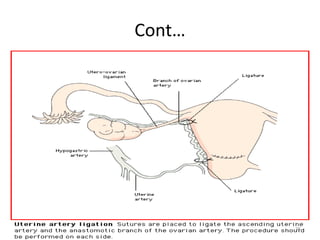
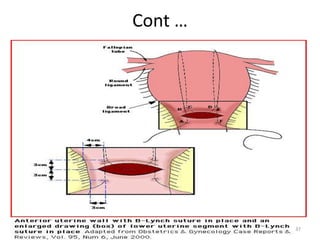
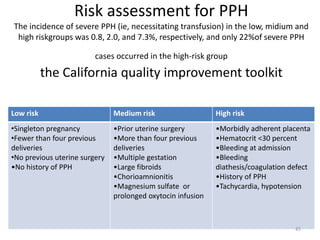
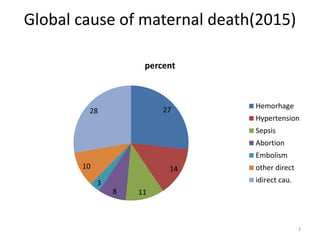
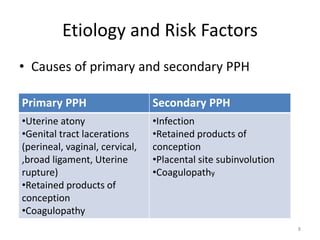
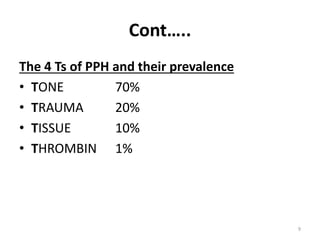
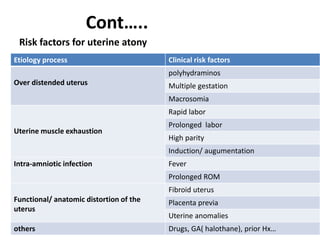
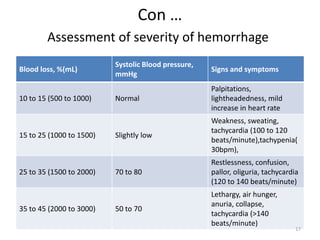
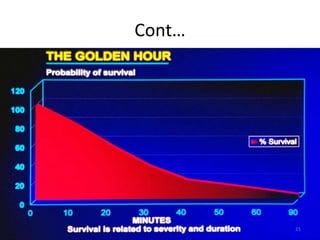
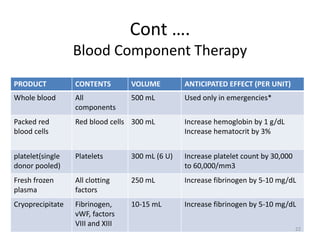
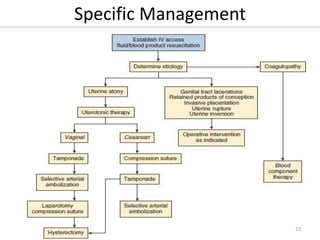
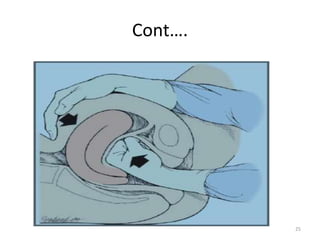
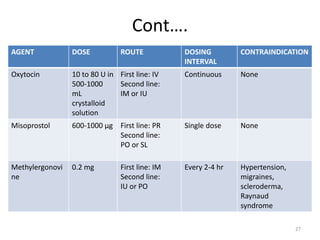
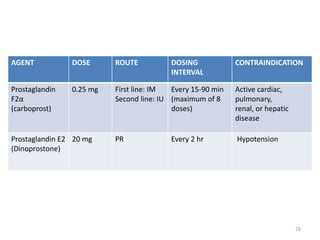
Postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) is the leading cause of maternal mortality worldwide, responsible for 27% of deaths. PPH occurs in 1-5% of deliveries and is defined as blood loss of 500mL or more following vaginal delivery, or 1000mL or more following cesarean delivery. The main causes of PPH are uterine atony (70%), genital tract trauma (20%), retained placental tissue (10%), and coagulopathy (1%). Management of PPH focuses on restoring circulatory volume and oxygenation through fluid resuscitation and blood transfusion, as well as treating the underlying cause through uterotonic drugs, uterine tamponade, arterial embolization, or surgery.



















![Cont..
• SELECTIVE ARTERIAL EMBOLIZATION:is an increasingly
common therapeutic option for hemodynamically stable
patients with PPH.
• The procedure can be performed alone or after failed
surgical intervention.
• Diagnostic pelvic angiography is used to visualize bleeding
vessels, and gelatin (e.g., Gelfoam]) pledgets are placed
into the vessels for occlusion.
• Cumulative success rates of 90% to 97%
• Selective arterial embolization has several advantages over
surgical intervention.
1. First, it allows for selective occlusion of bleeding vessels
2. Second, the uterus and potential future fertility are
preserved
32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/12-240127073845-777bba4e/85/12-Post-Partum-H-lacture-0-Copy-pptx-32-320.jpg)