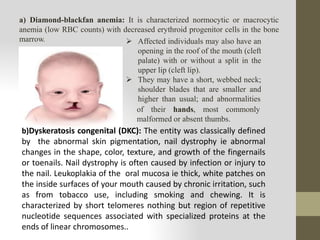
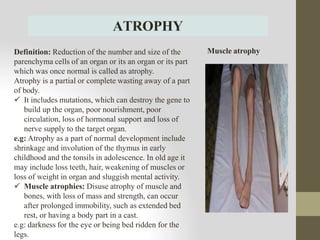
Cell injury can be caused by genetic factors or acquired stresses from the environment. The main causes of acquired cell injury are hypoxia/ischemia, physical insults, chemicals/drugs, microbial infections, immune reactions, and nutritional imbalances. These stresses can damage cell membranes, mitochondria, ribosomes, or the nucleus, leading to diseases. Reversible cell injury causes swelling while irreversible injury involves necrosis or programmed cell death. The document provides examples of diseases associated with specific organelle damage and morphological changes seen in injured cells.