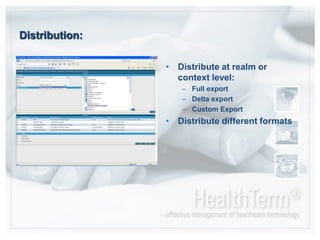
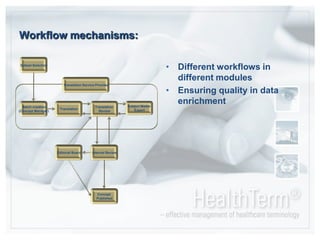
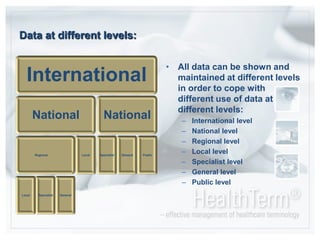
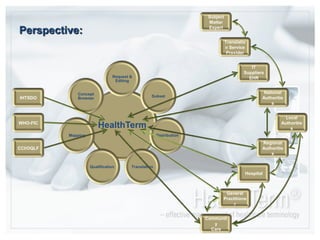
The document discusses CareCom's HealthTerm product, which aims to provide syntactic and semantic interoperability across healthcare systems by serving as a single repository and interface for terminology management. Key points:
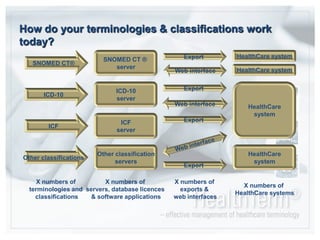
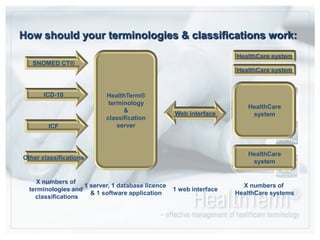
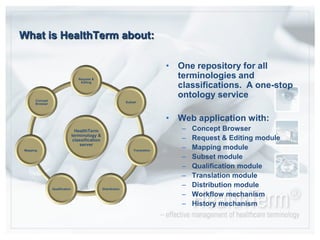
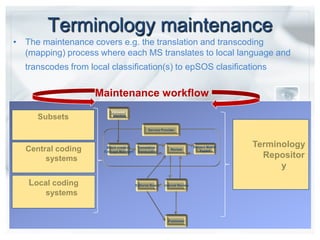
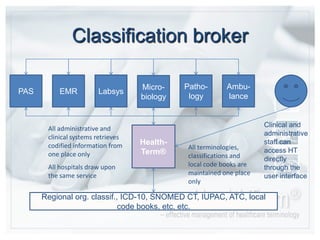
- HealthTerm allows various healthcare systems to access and maintain terminologies and classifications in a single system, rather than each system having separate access. This improves data consistency.
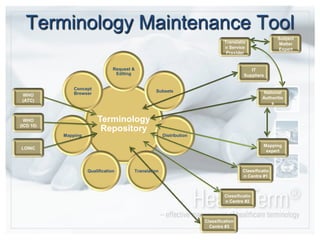
- The system provides interfaces for concept browsing, requests and editing, mapping between terminologies, creating subsets of data, qualification of clinical concepts, and translation of terms.
- Using a single source of terminologies provides advantages of improved security, data quality, and cost savings compared to multiple disconnected systems.