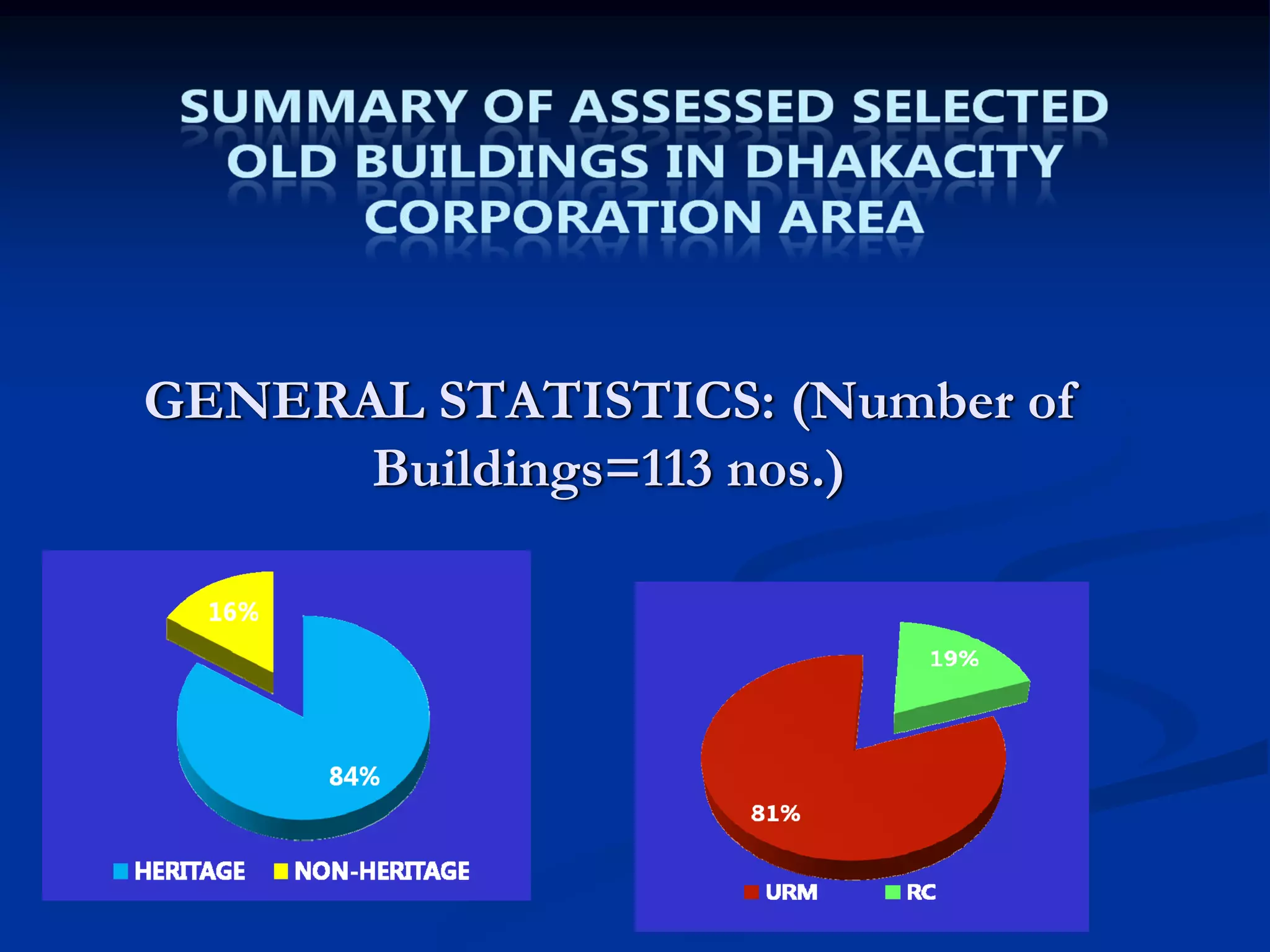
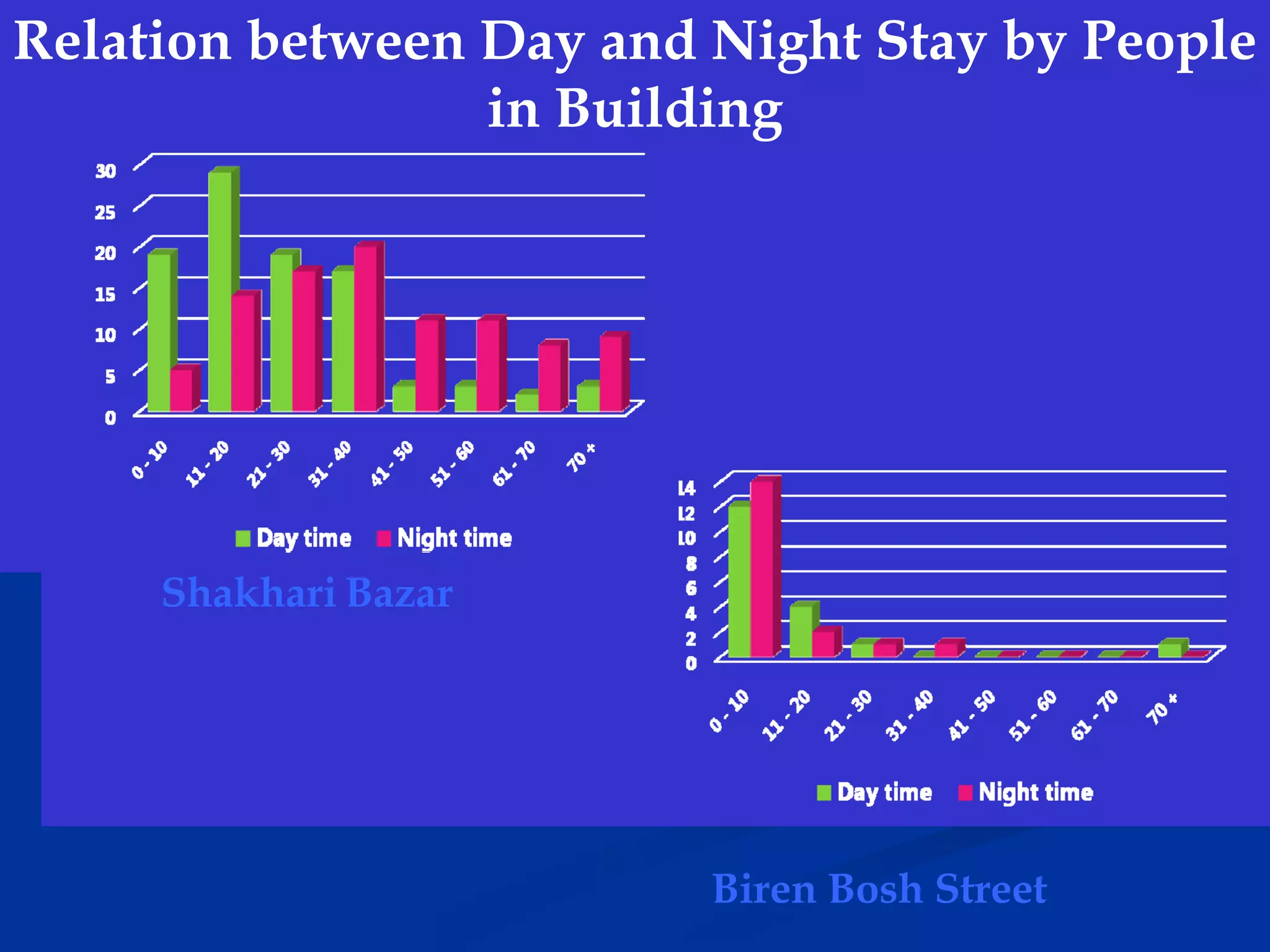
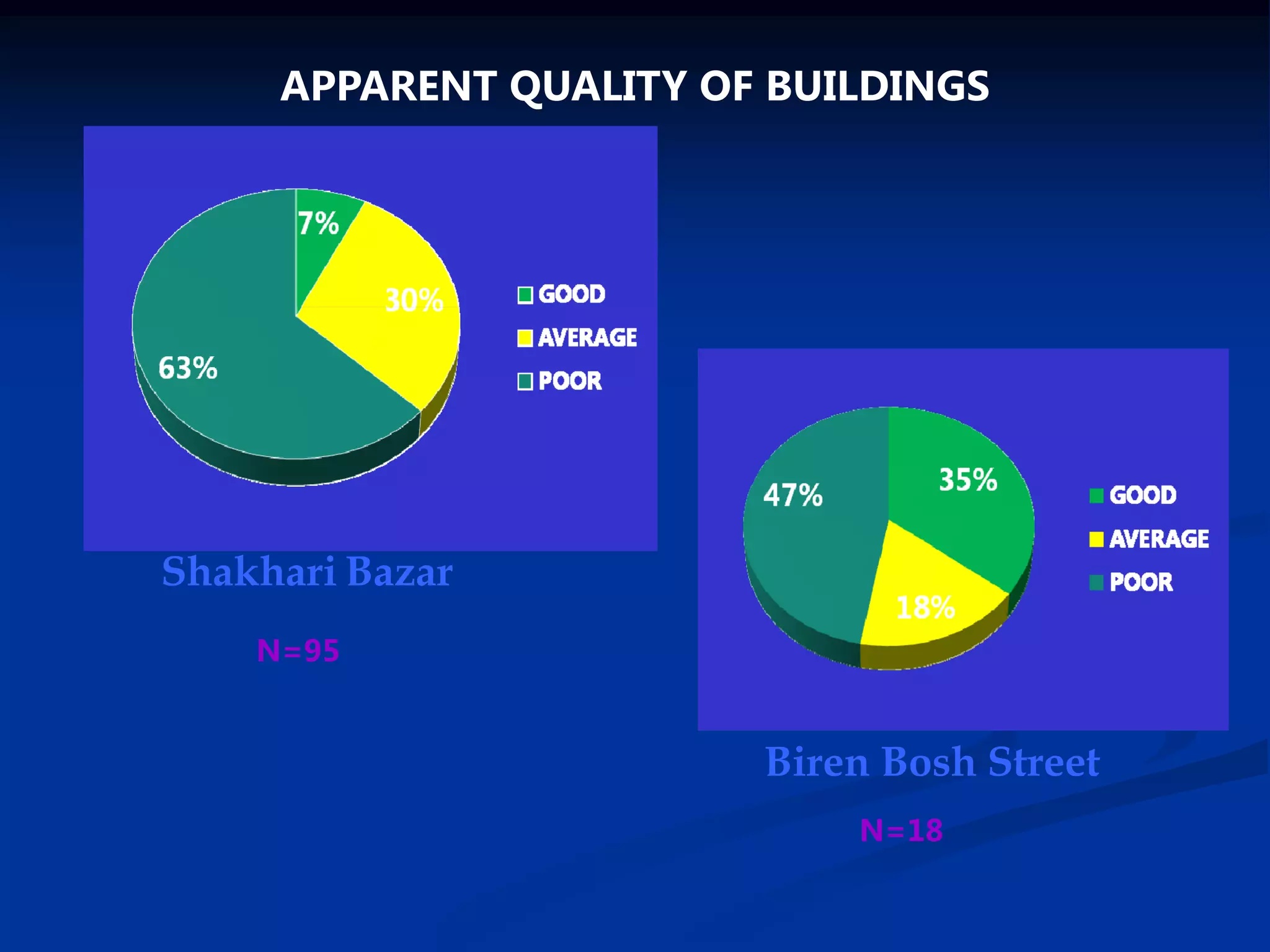
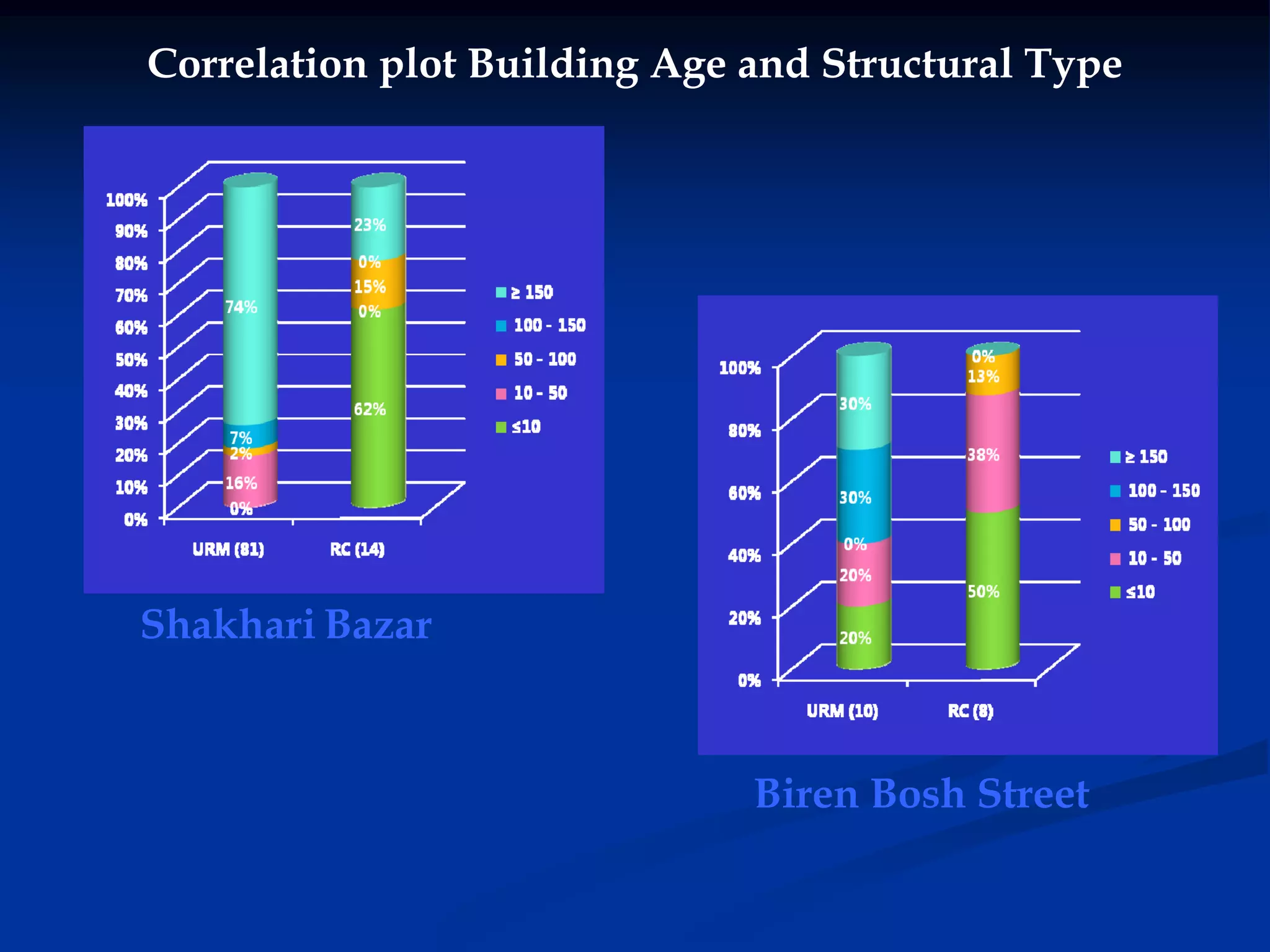
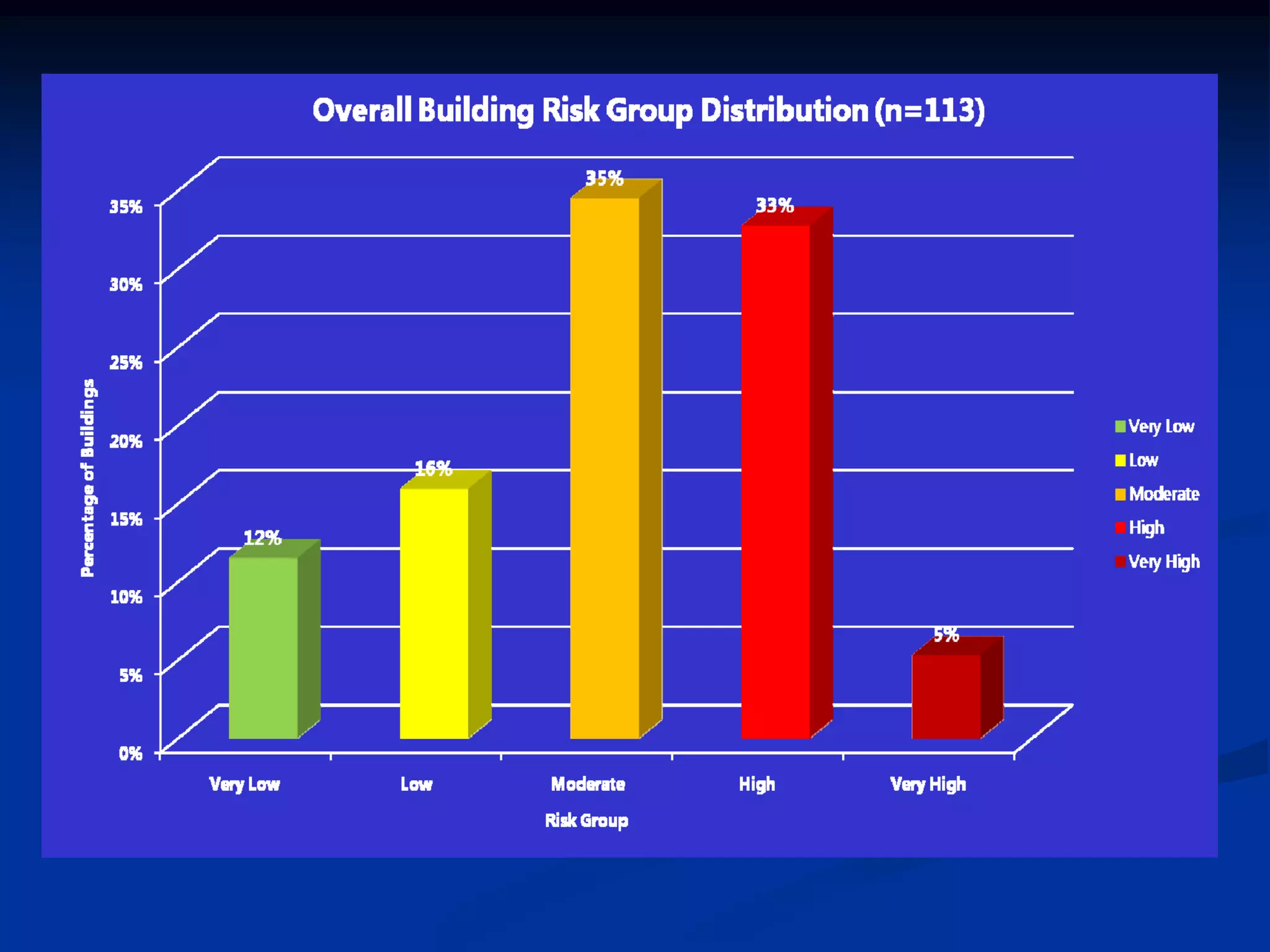
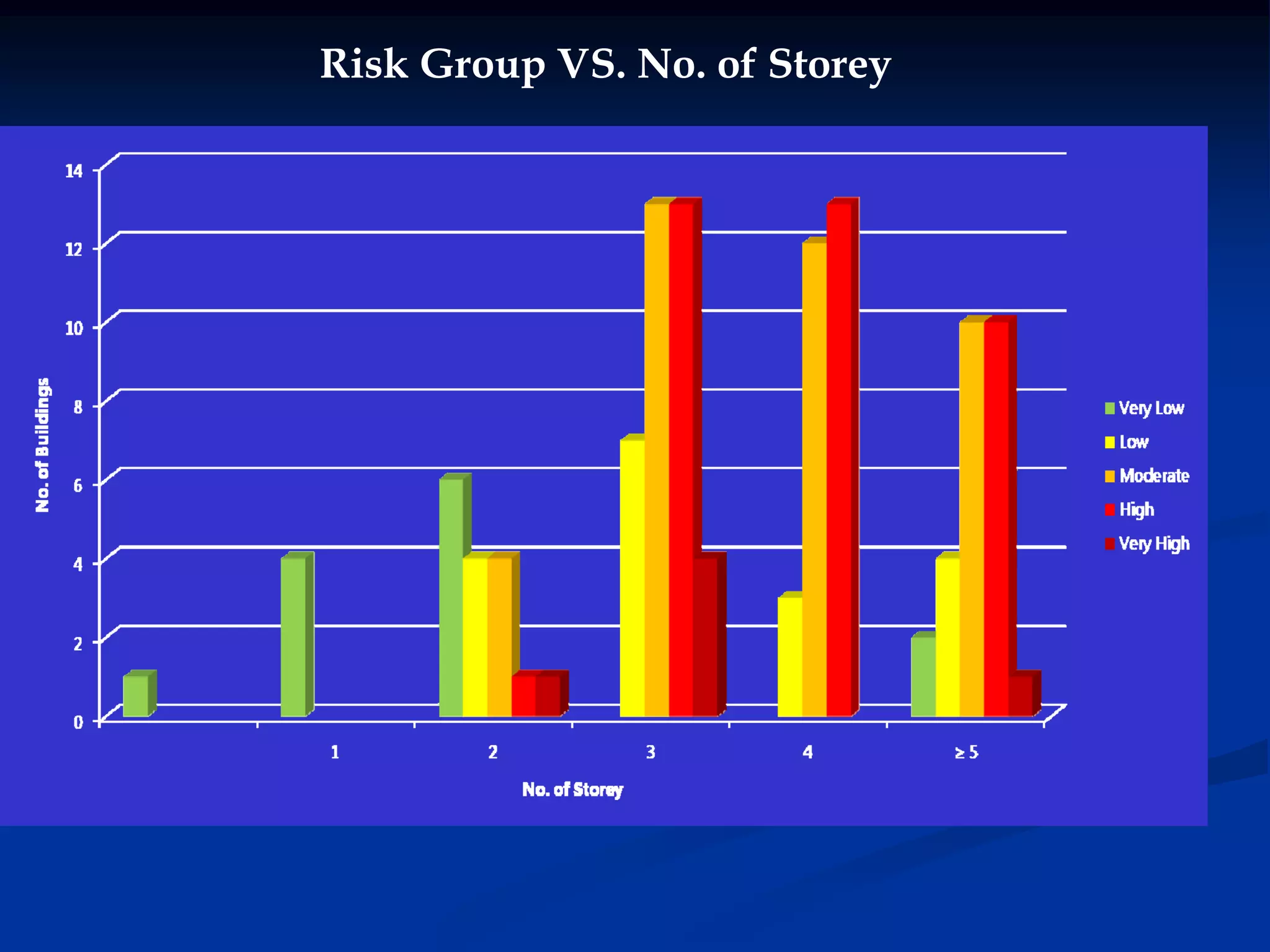
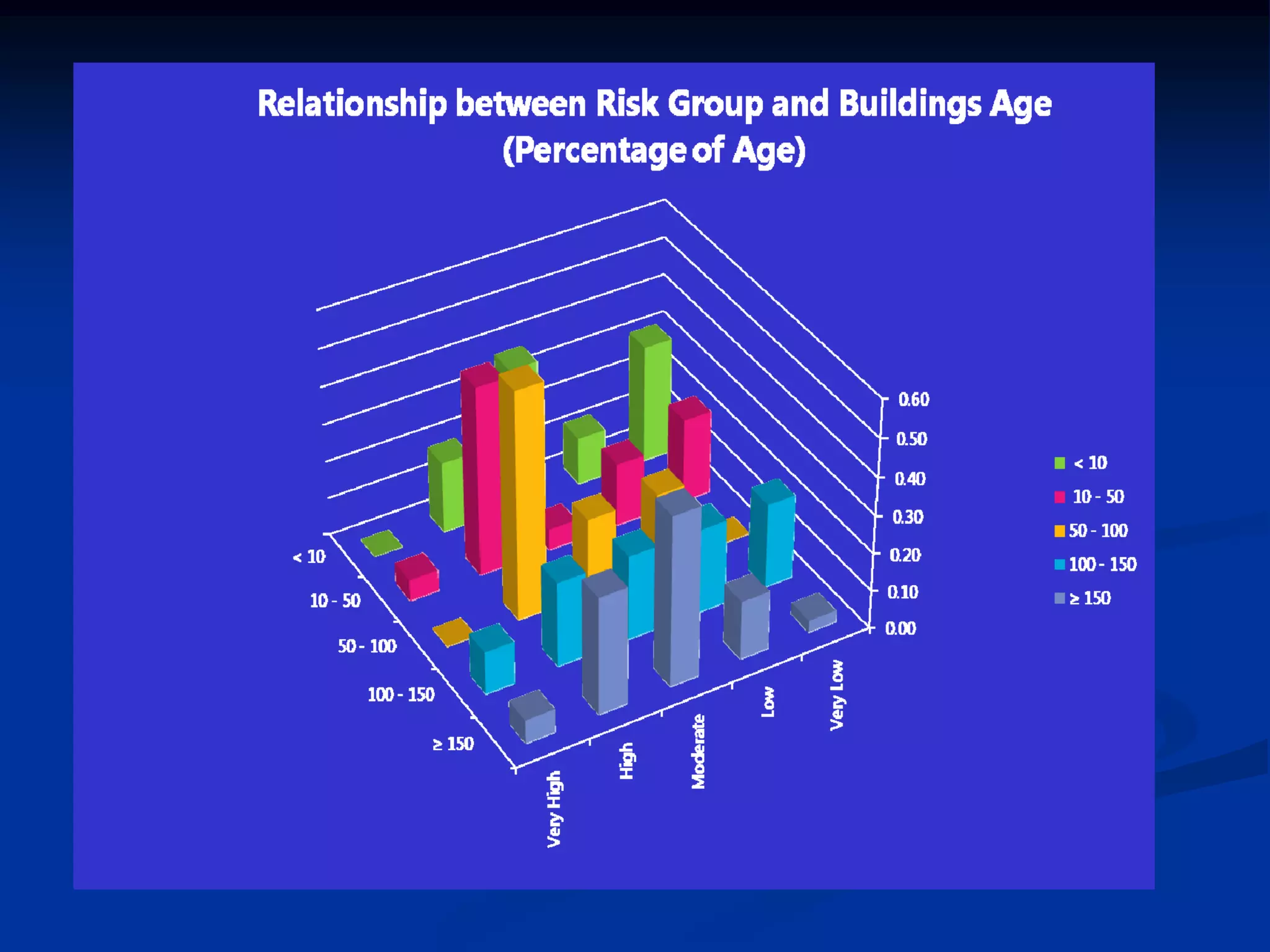
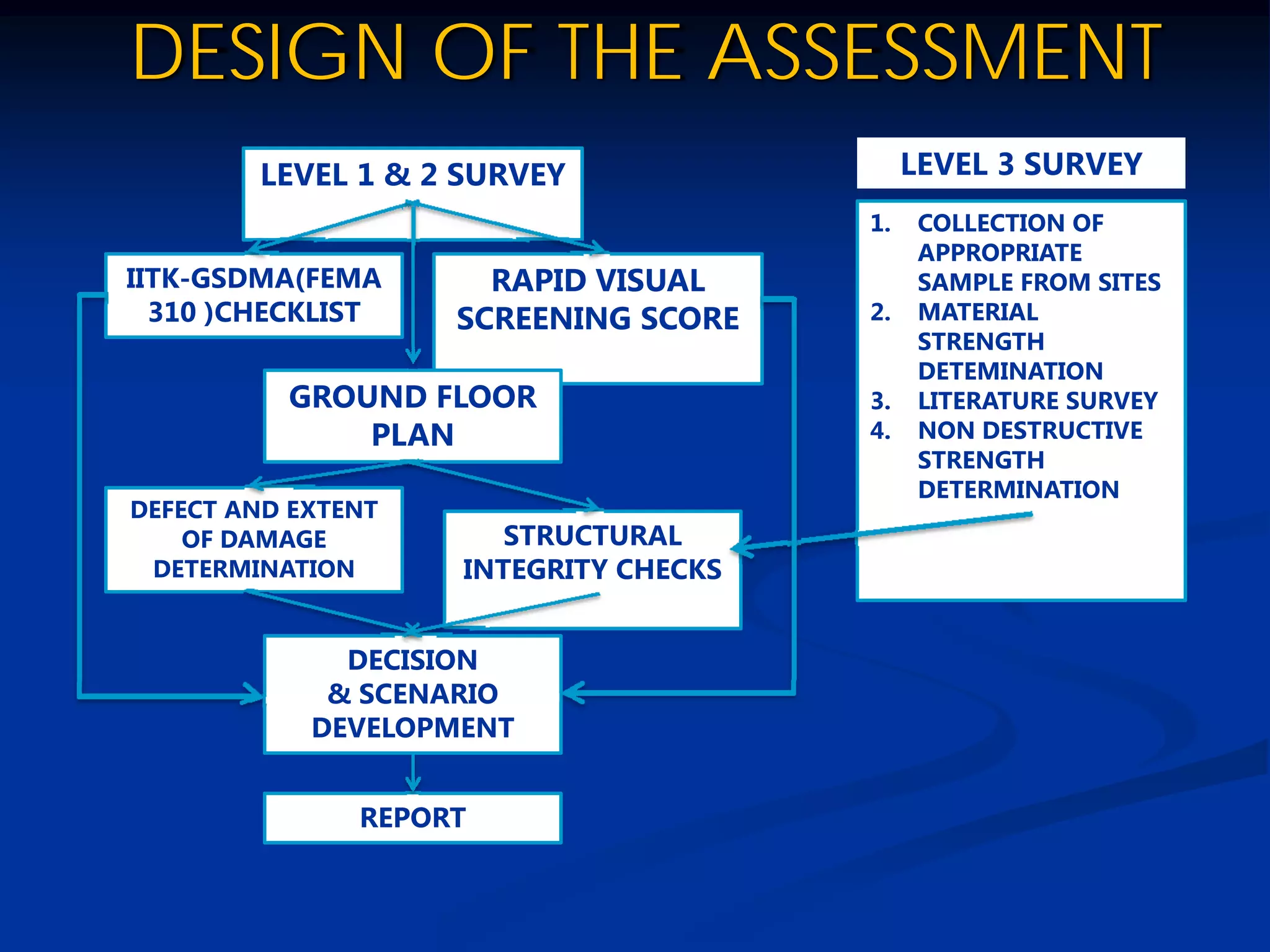
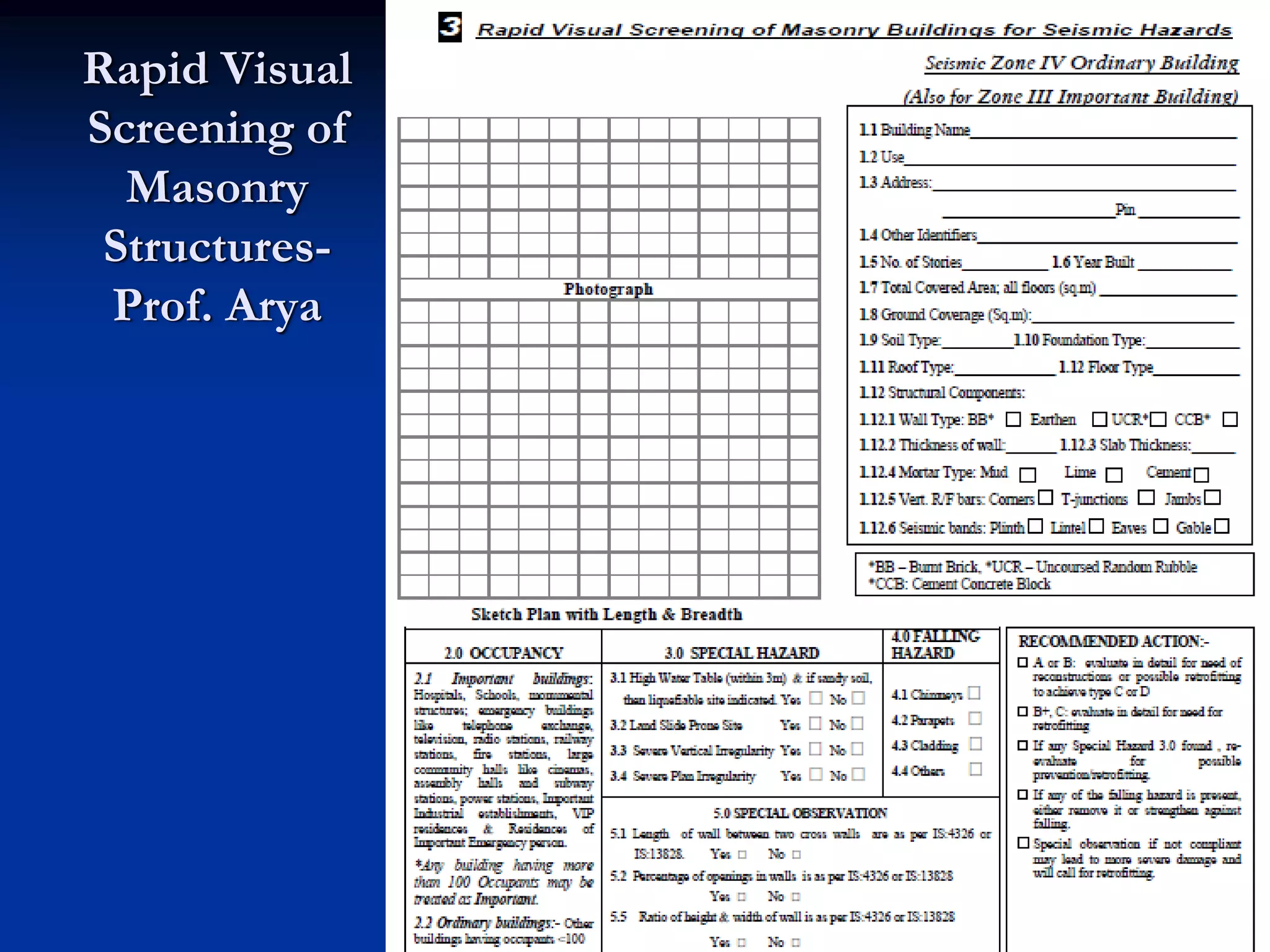
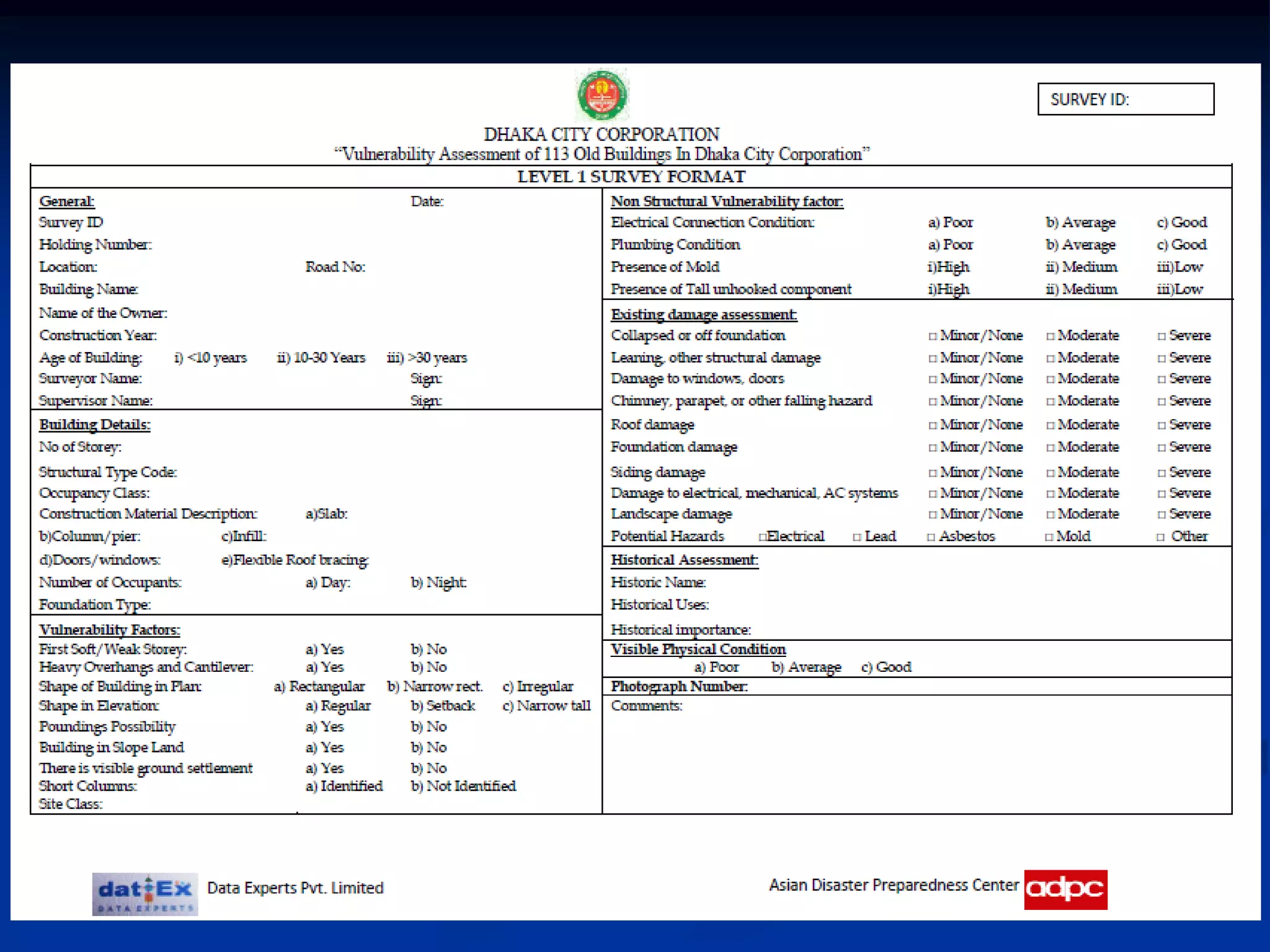
This document summarizes information about Bangladesh and its capital city of Dhaka. It provides background on Bangladesh's population, geography, climate, and economic growth. It then focuses on Dhaka, outlining its history and growth. Key points include:
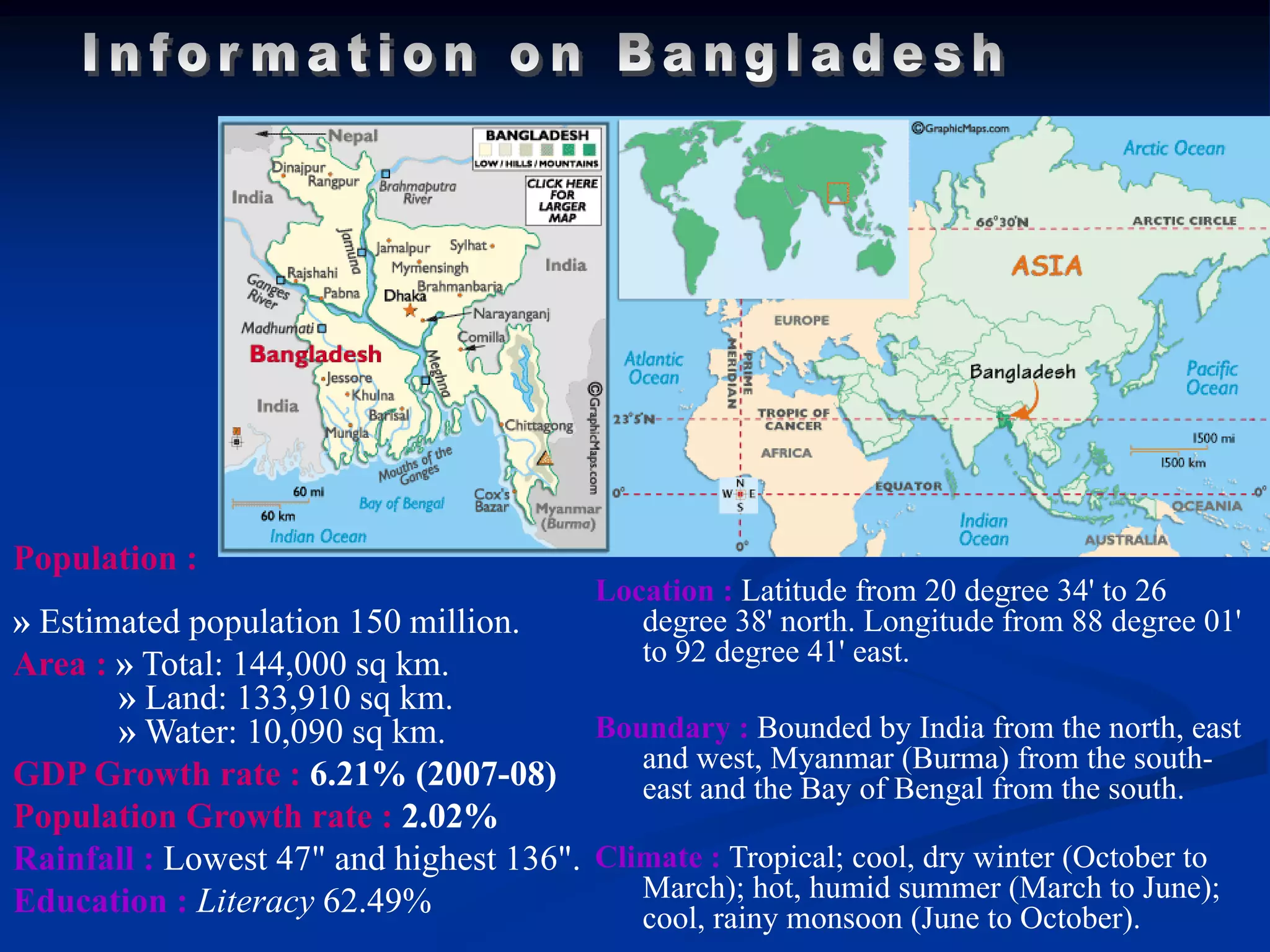
- Bangladesh has a population of over 150 million within an area of 144,000 square kilometers.
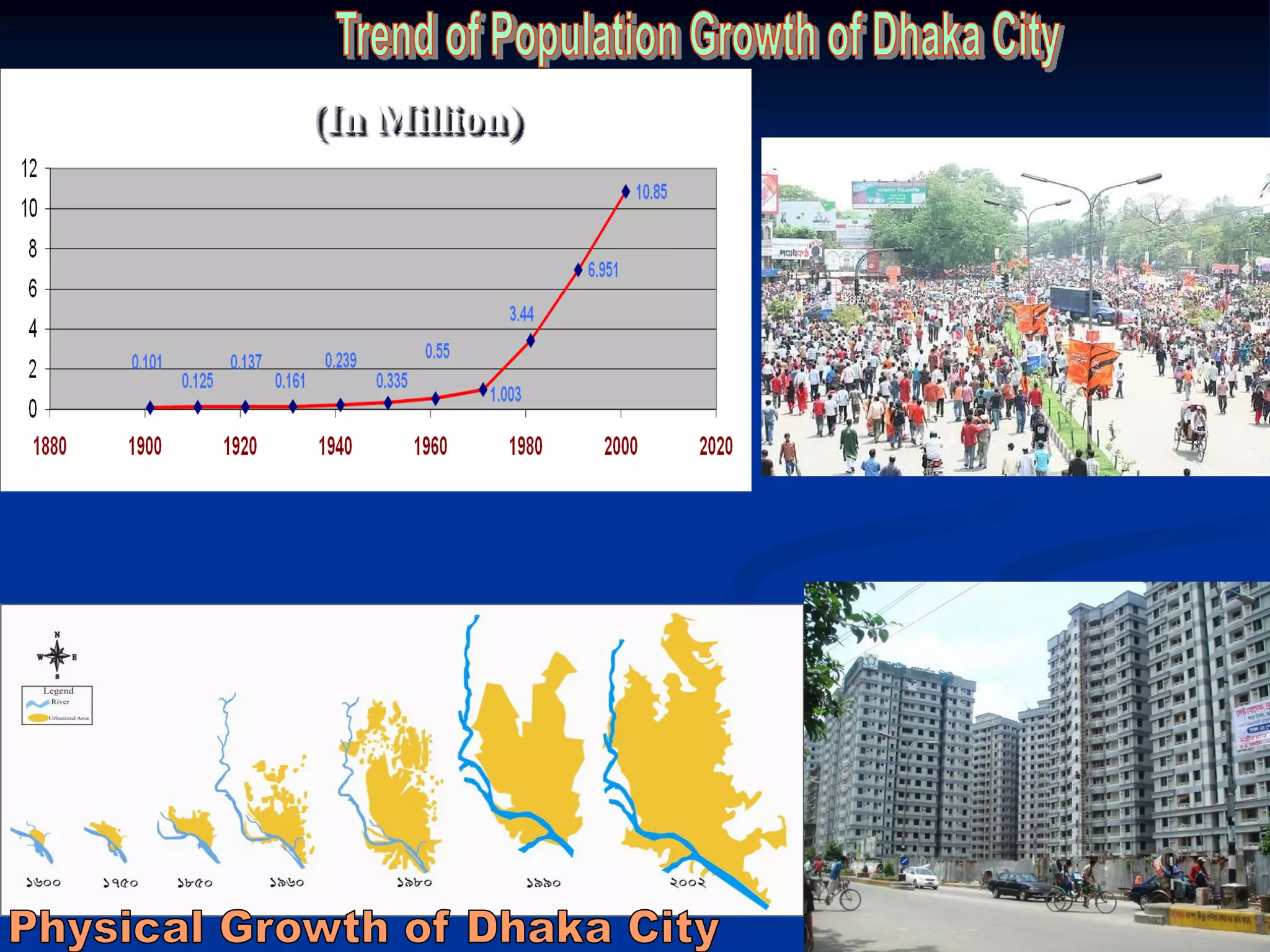
- Dhaka has a population of over 12 million and has experienced rapid population growth of around 6% annually.
- The document analyzes various natural hazards that affect Bangladesh like floods, cyclones, droughts, and earthquakes.
- It then summarizes efforts by Dhaka City Corporation to improve disaster management, including training, workshops, and identifying