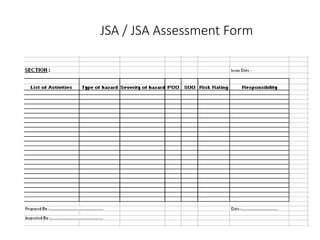
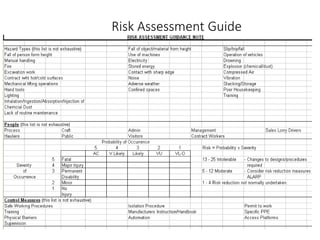
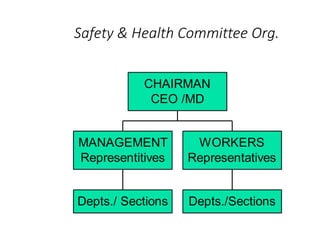
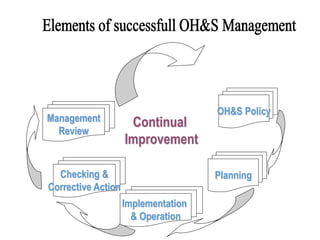
This document discusses occupational health and safety (OHS) management systems. It outlines the key elements of an OHS management system including identifying hazards and risks, managing risks, establishing policies and objectives, and monitoring performance. It also describes the purpose of an OHS management system in establishing procedures for risk assessment and control, integrating OHS into business processes, and meeting performance standards. Planning, doing, checking, and acting (PDCA) is discussed as a framework for an OHS management system.