The Hamming code is an error-correcting code invented by Richard Hamming. It works by adding redundant parity bits that allow the detection and correction of single-bit errors. The key aspects are:
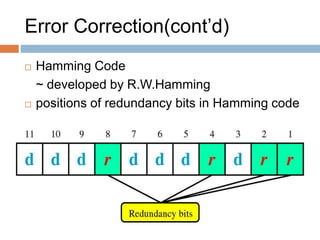
- Parity bits are placed in bit positions that are powers of 2, with data bits filling other positions.
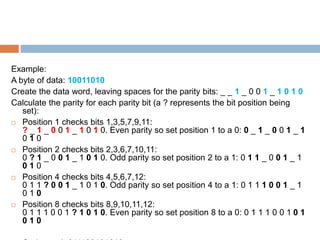
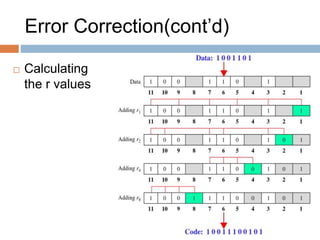
- Each parity bit checks a specific subset of bits based on its position, alternating between checking and skipping bits.
- This arrangement allows the identification of which bit is in error based on the parity bits. Hamming codes can correct single-bit errors and are commonly used for error detection.