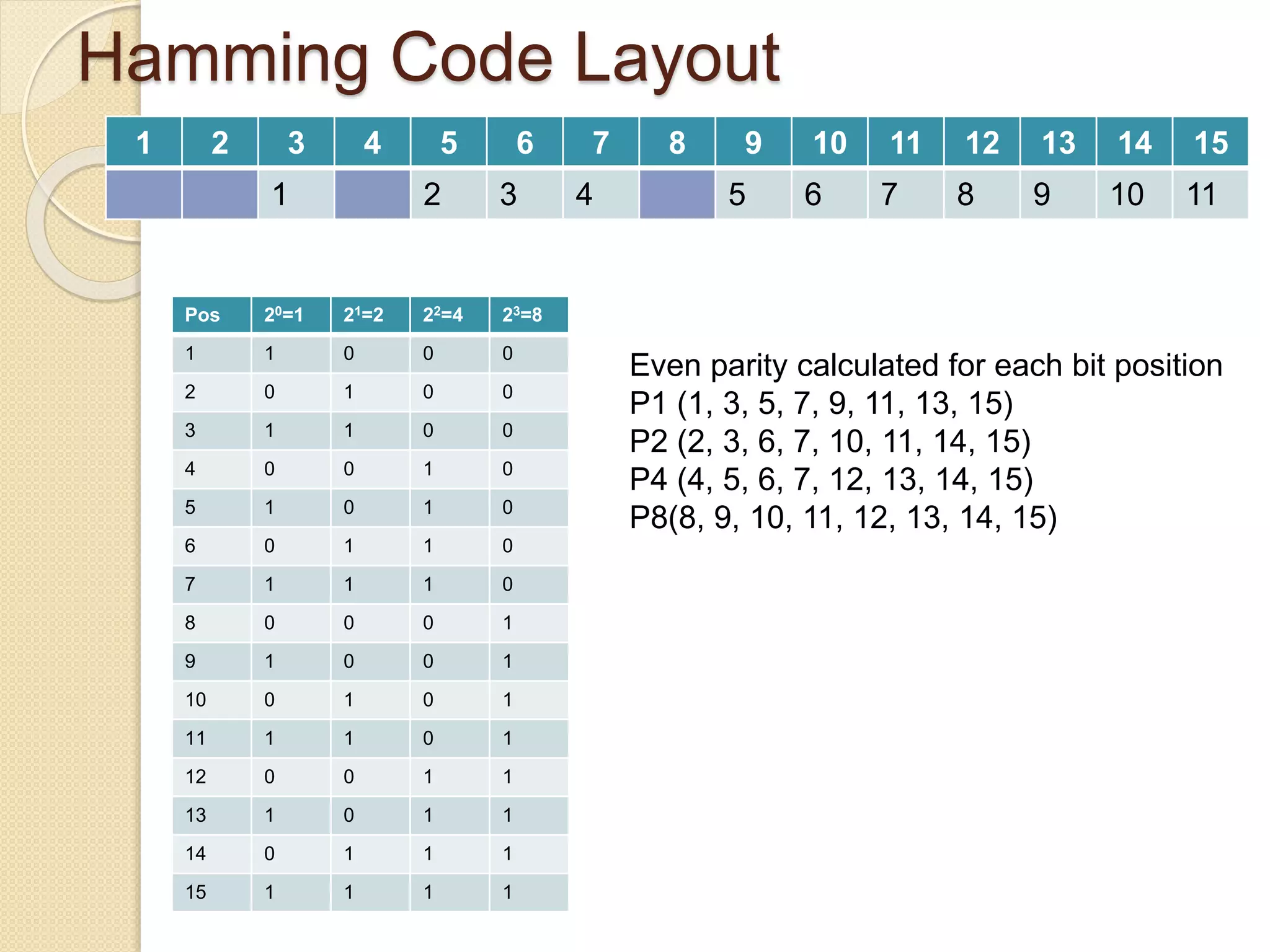
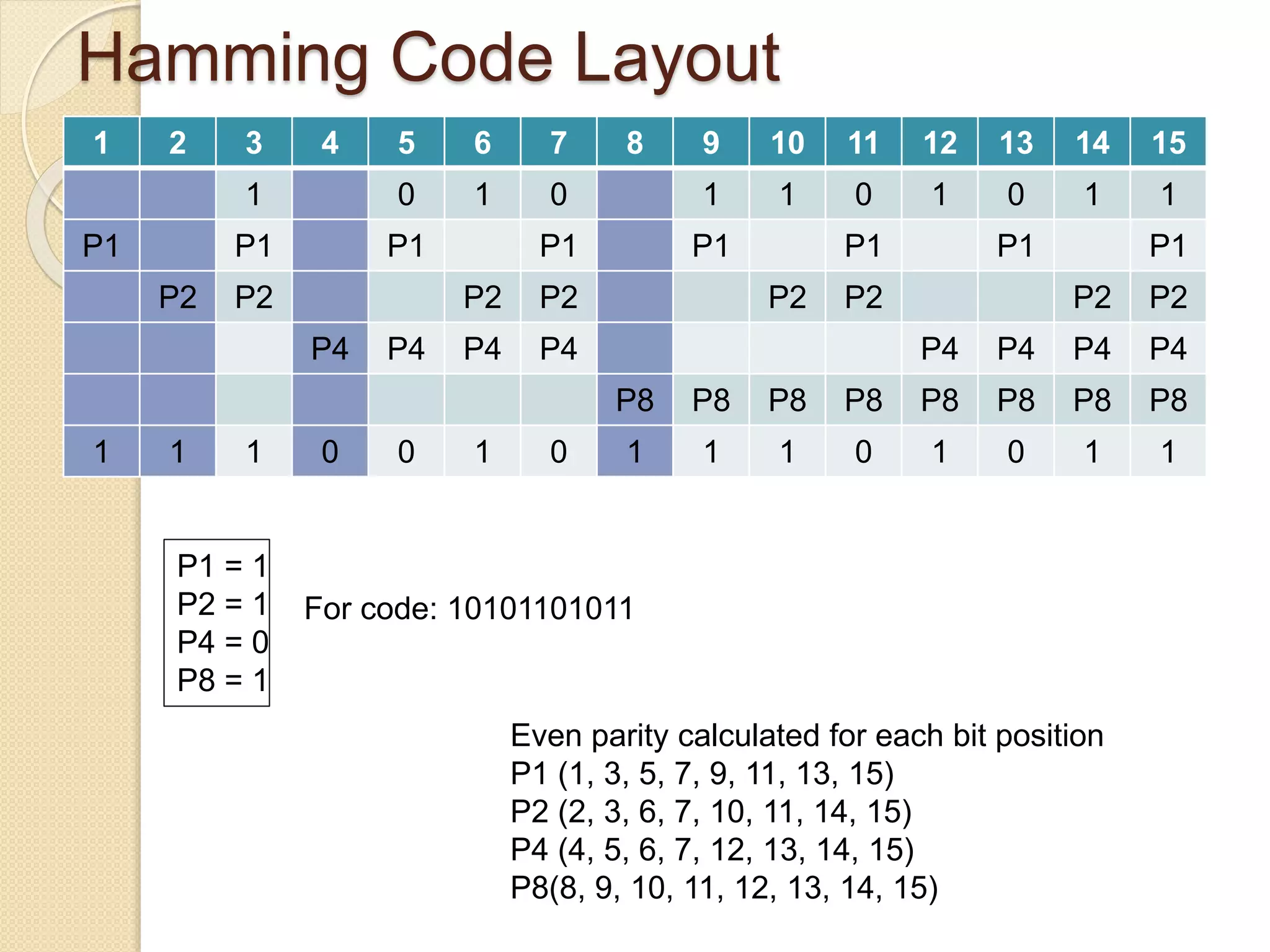
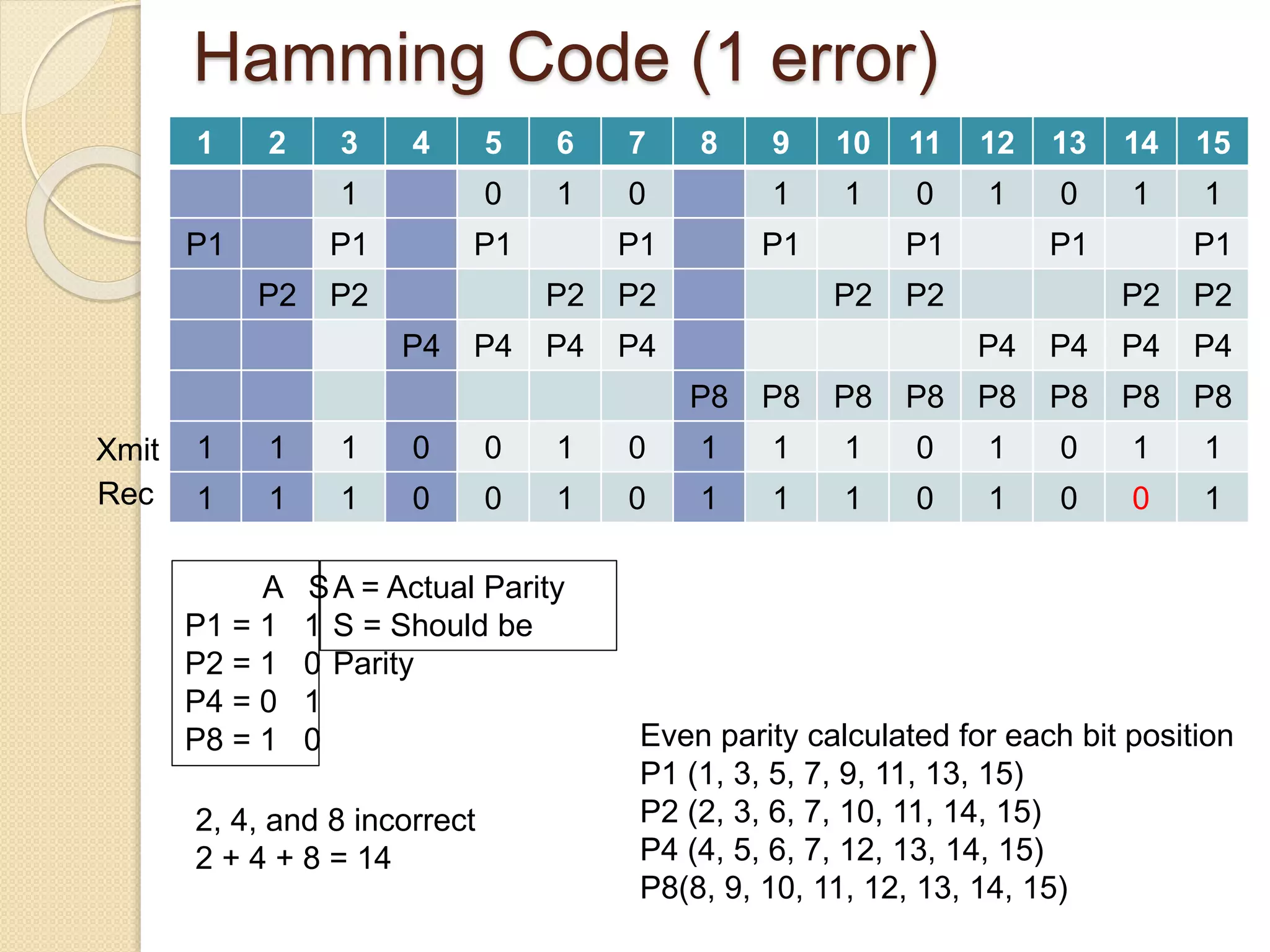
Hamming codes can detect up to two simultaneous bit errors and correct single-bit errors. They work by adding parity bits calculated for groups of bits in positions that are powers of 2. To encode data, parity bits are set to 1 or 0 based on whether the total number of 1s in the corresponding bit positions is odd or even. To decode, the received bits are used to recalculate the parity bits and identify any discrepancies, allowing the location and correction of errors.