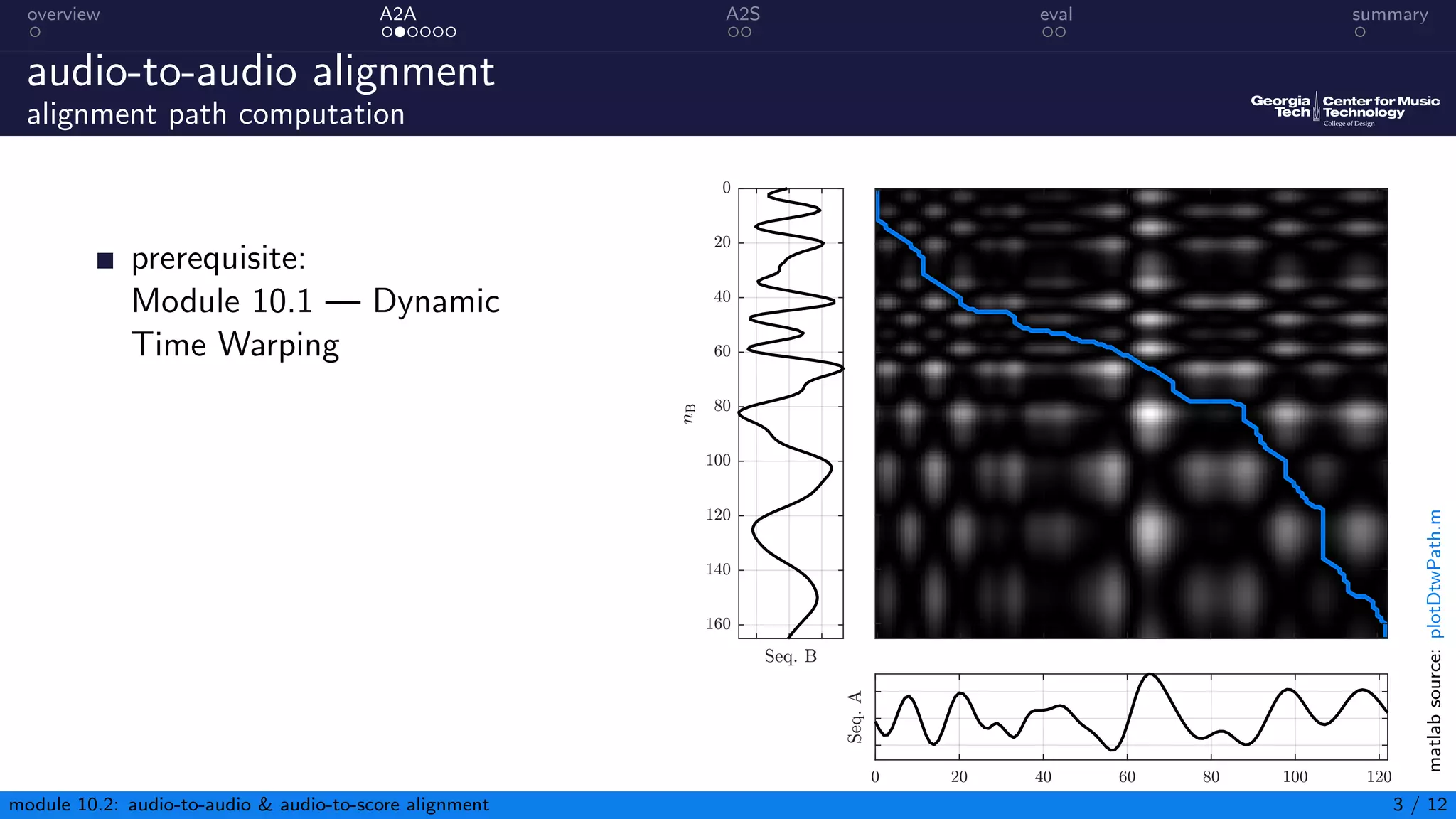
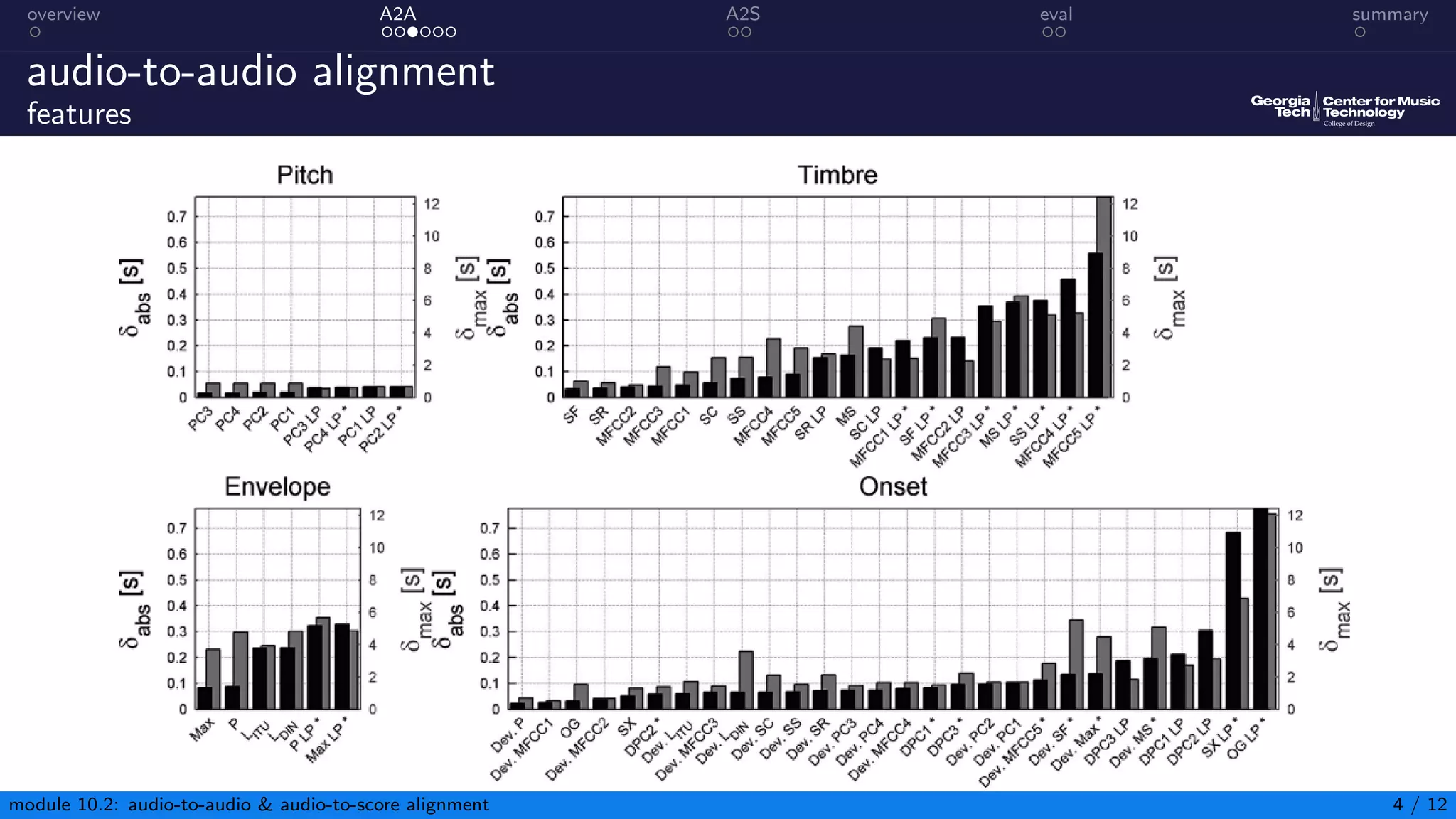
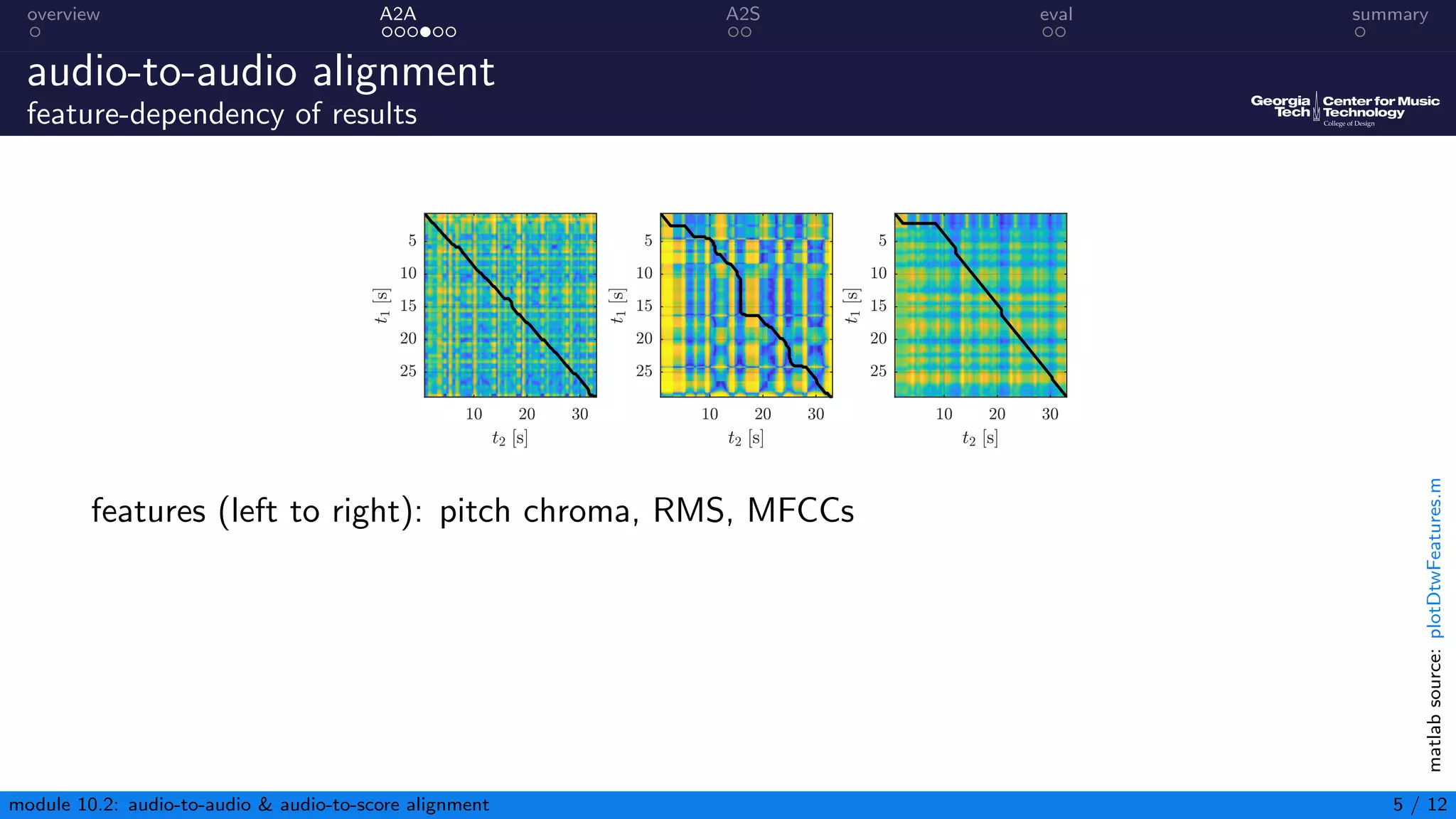
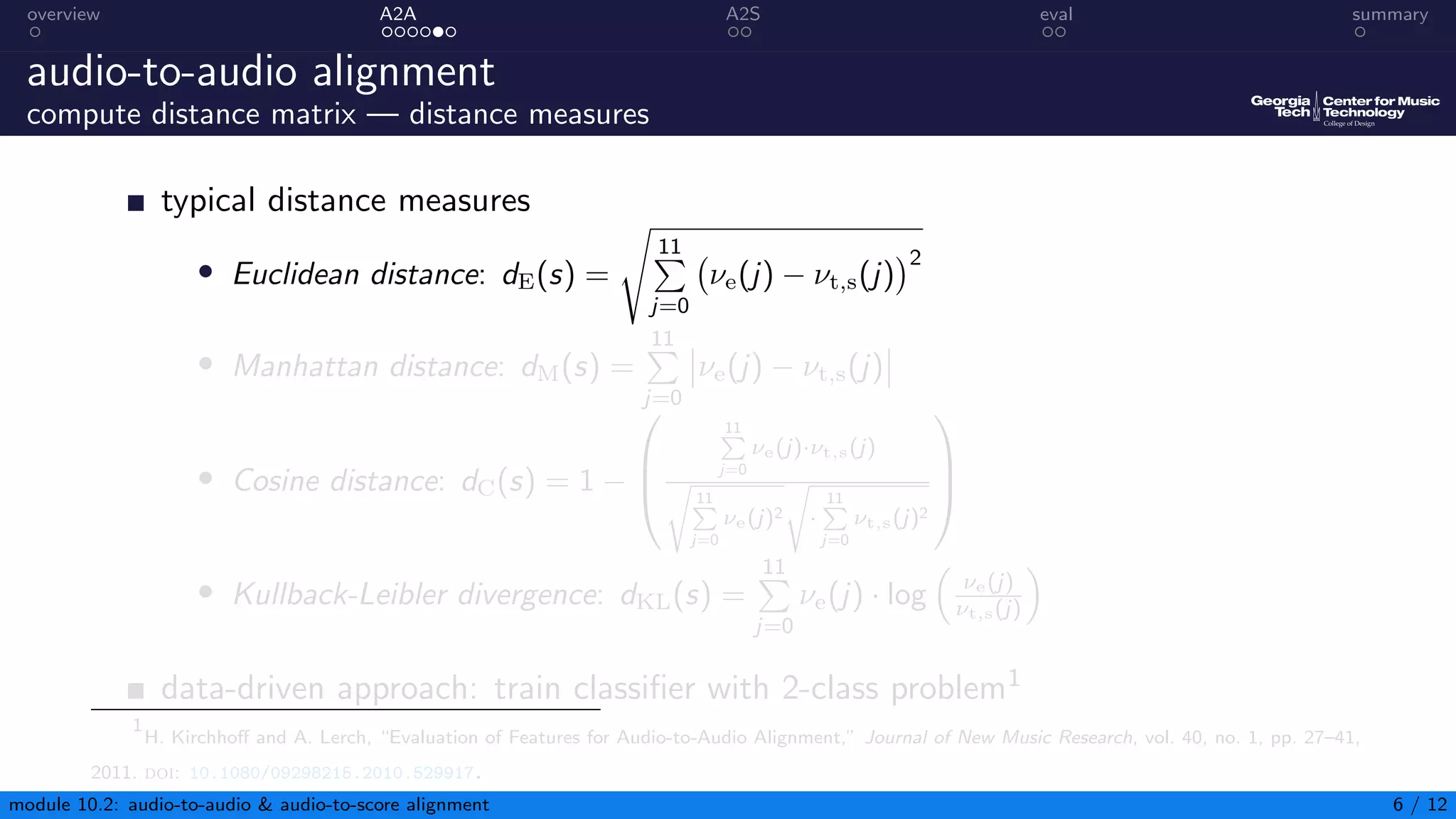
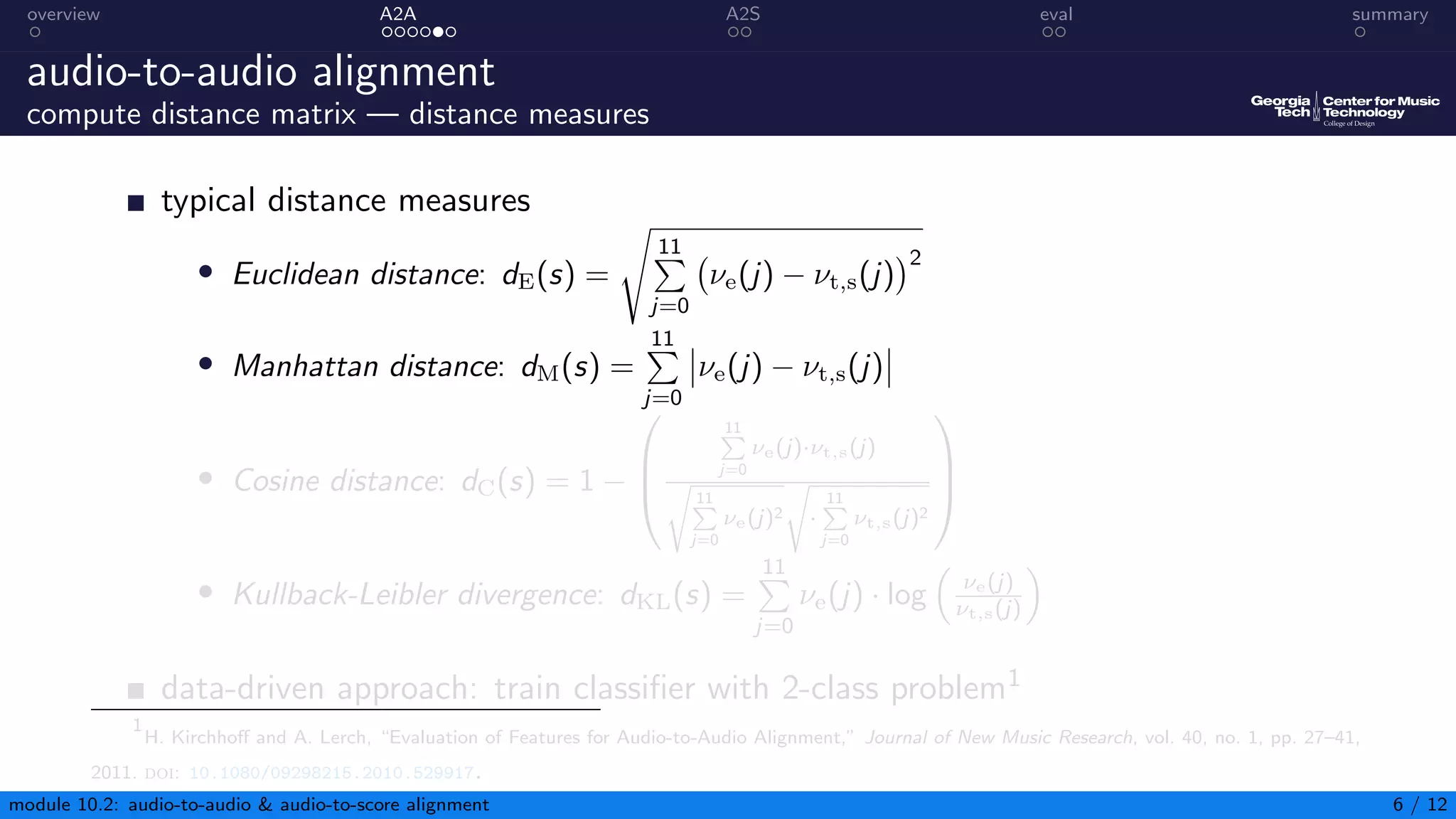
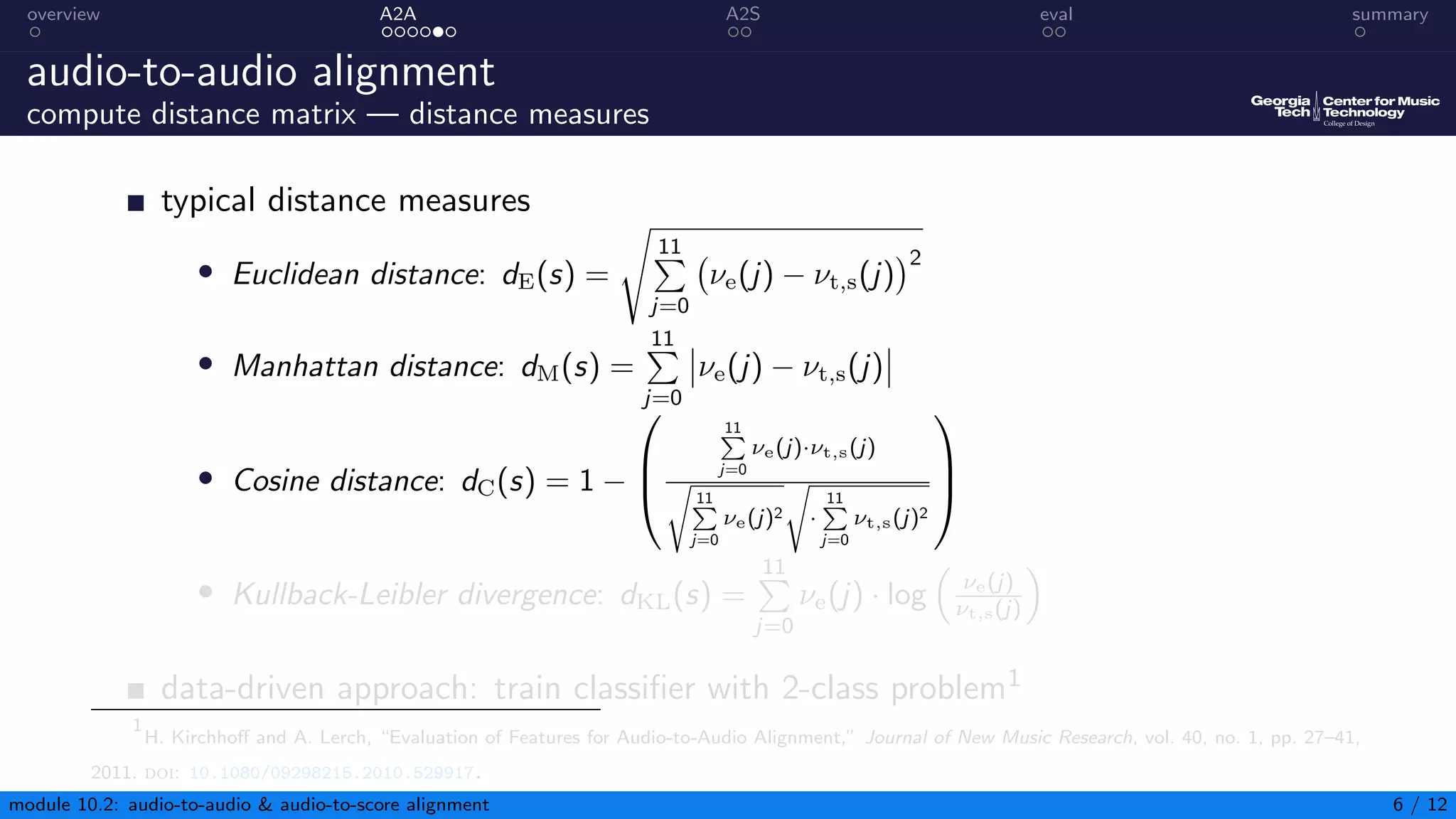
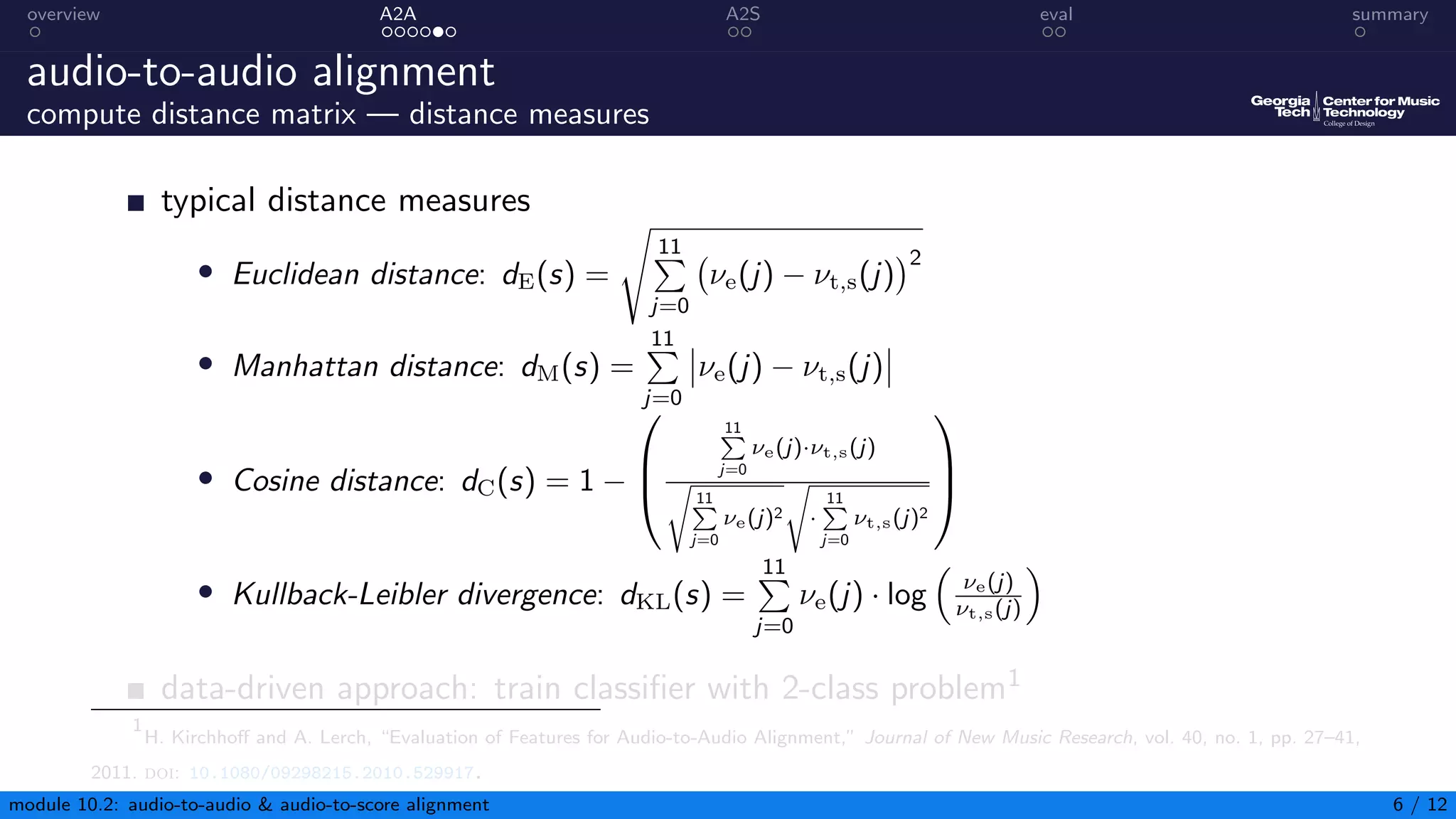
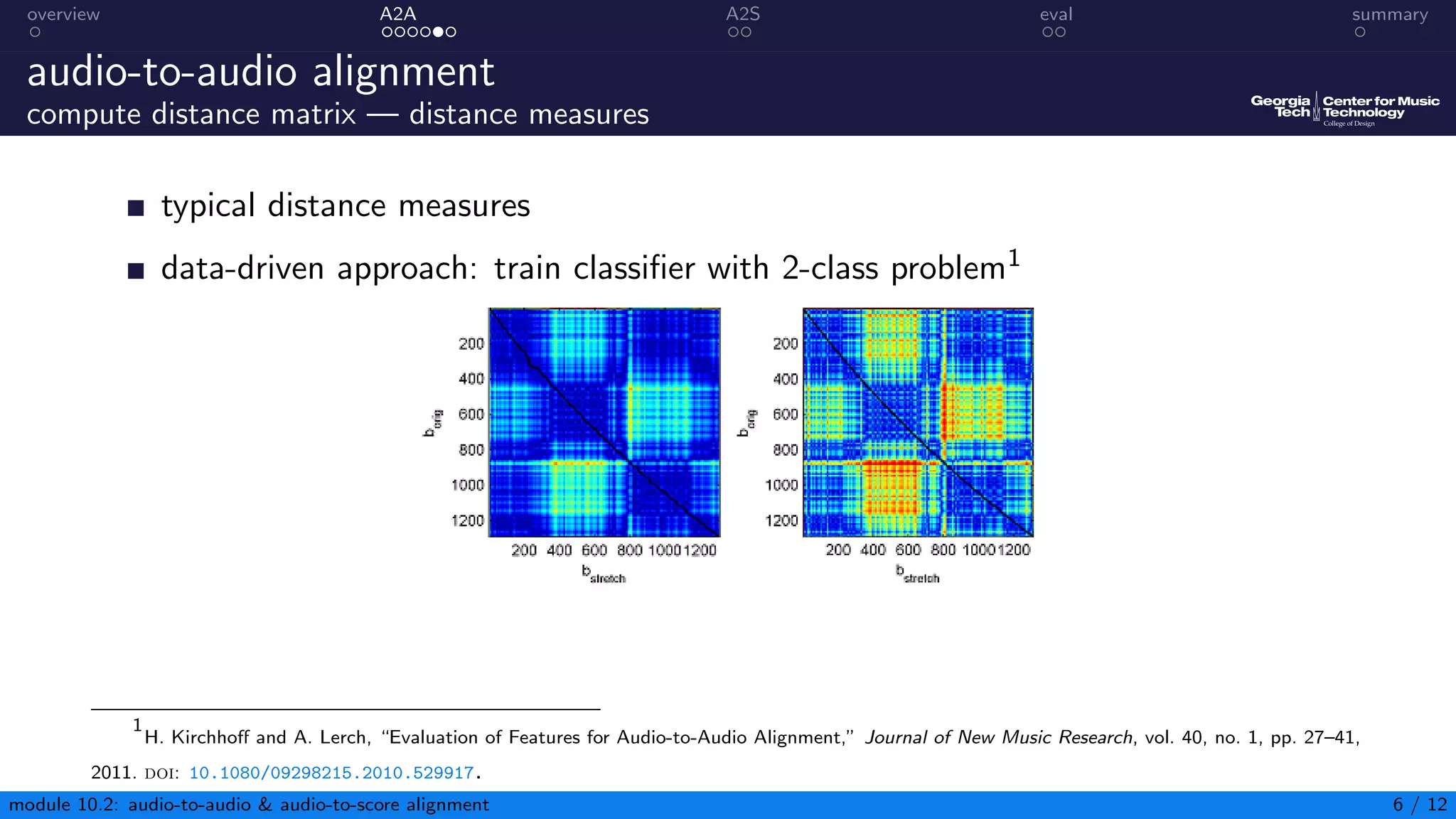
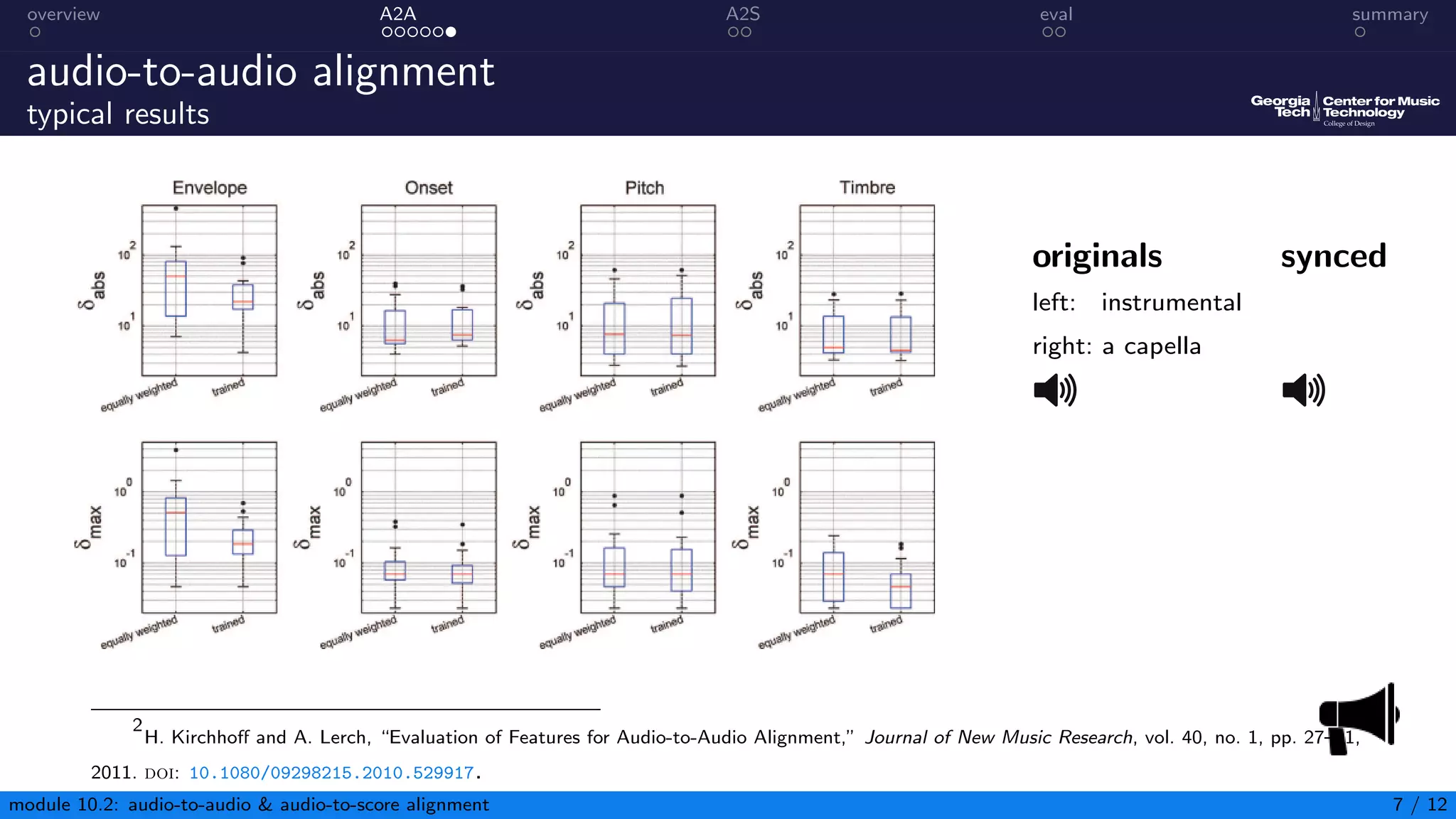
This document summarizes an introduction to audio content analysis module on audio-to-audio and audio-to-score alignment. It discusses using audio feature extraction and dynamic time warping to align two audio sequences or an audio sequence to a musical score. Key steps include extracting features from the audio, computing a distance matrix using measures like Euclidean distance, and finding the optimal alignment path. Evaluation of alignment accuracy can be challenging due to differences in the domains of audio and scores.