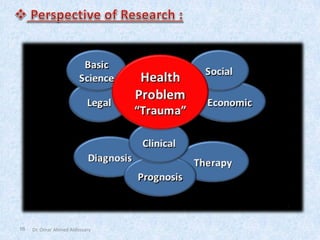
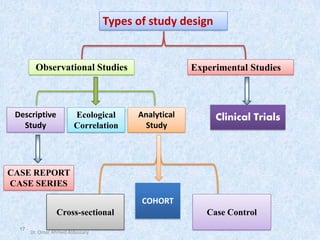
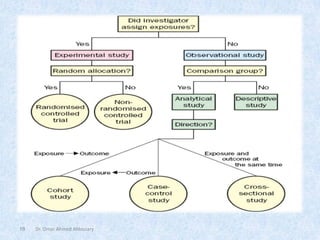
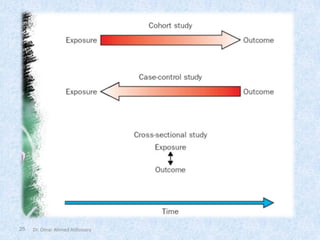
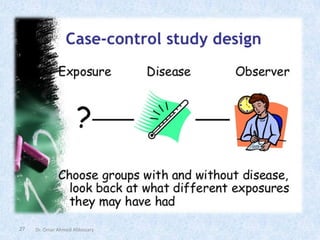
The document outlines the definition and importance of research, emphasizing its systematic approach and integrative role in health sciences, particularly dentistry. It categorizes research types based on application, objectives, and processes, detailing methodologies such as observational and experimental studies. Additionally, it discusses ethical considerations in research involving human subjects and the necessity of teamwork and planning in conducting effective research.