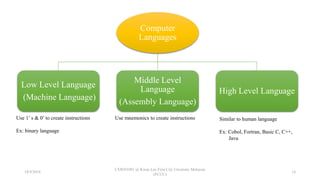
The document provides an introduction to computer systems and programming, discussing key concepts such as hardware, software, input-process-output operations, and programming languages. It outlines the program development cycle, including steps like requirement gathering, coding, testing, and maintenance, as well as the use of pseudocode and flowcharts for logic planning. Additionally, it mentions the evolution of programming models, particularly procedural and object-oriented programming.