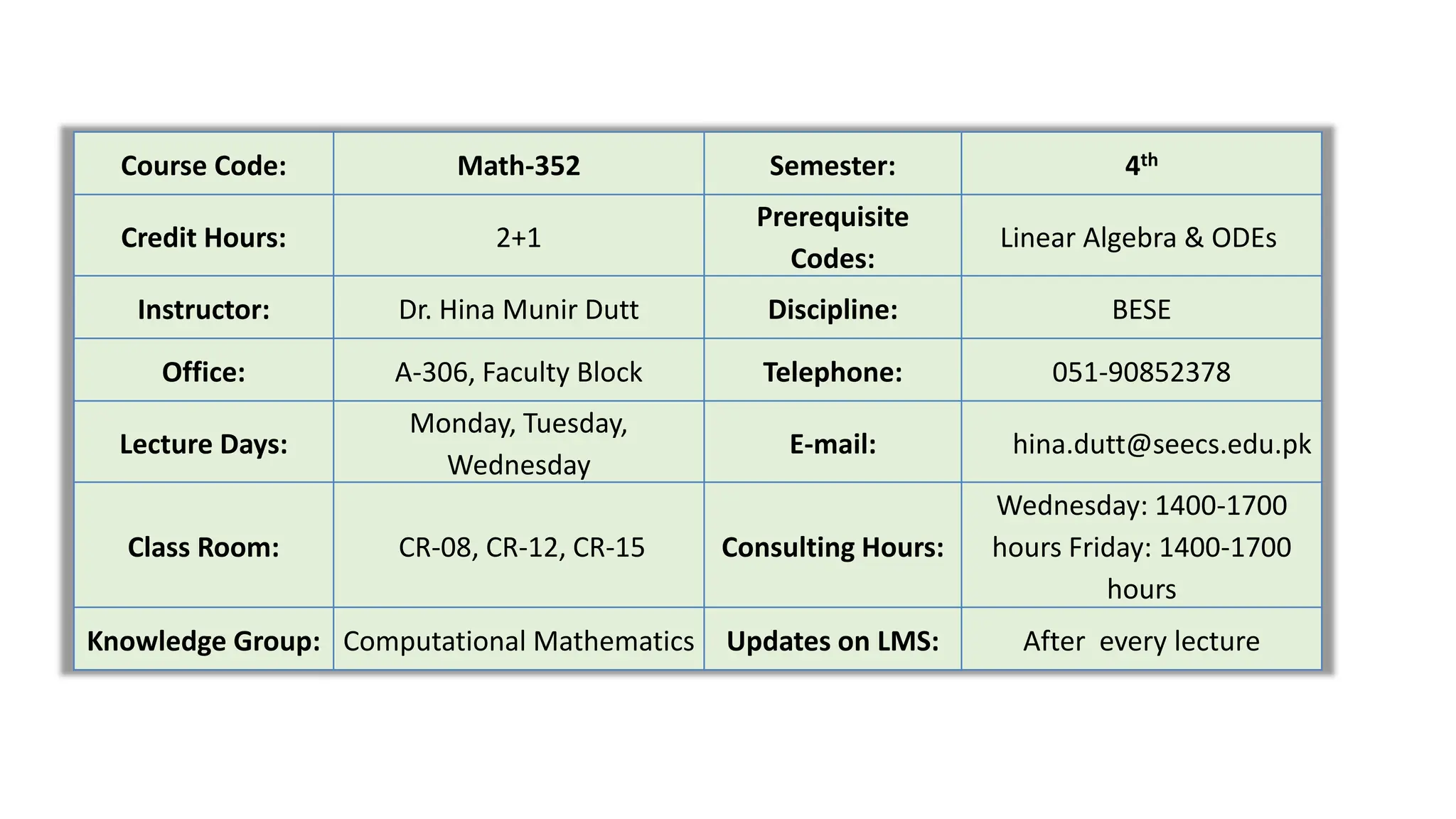
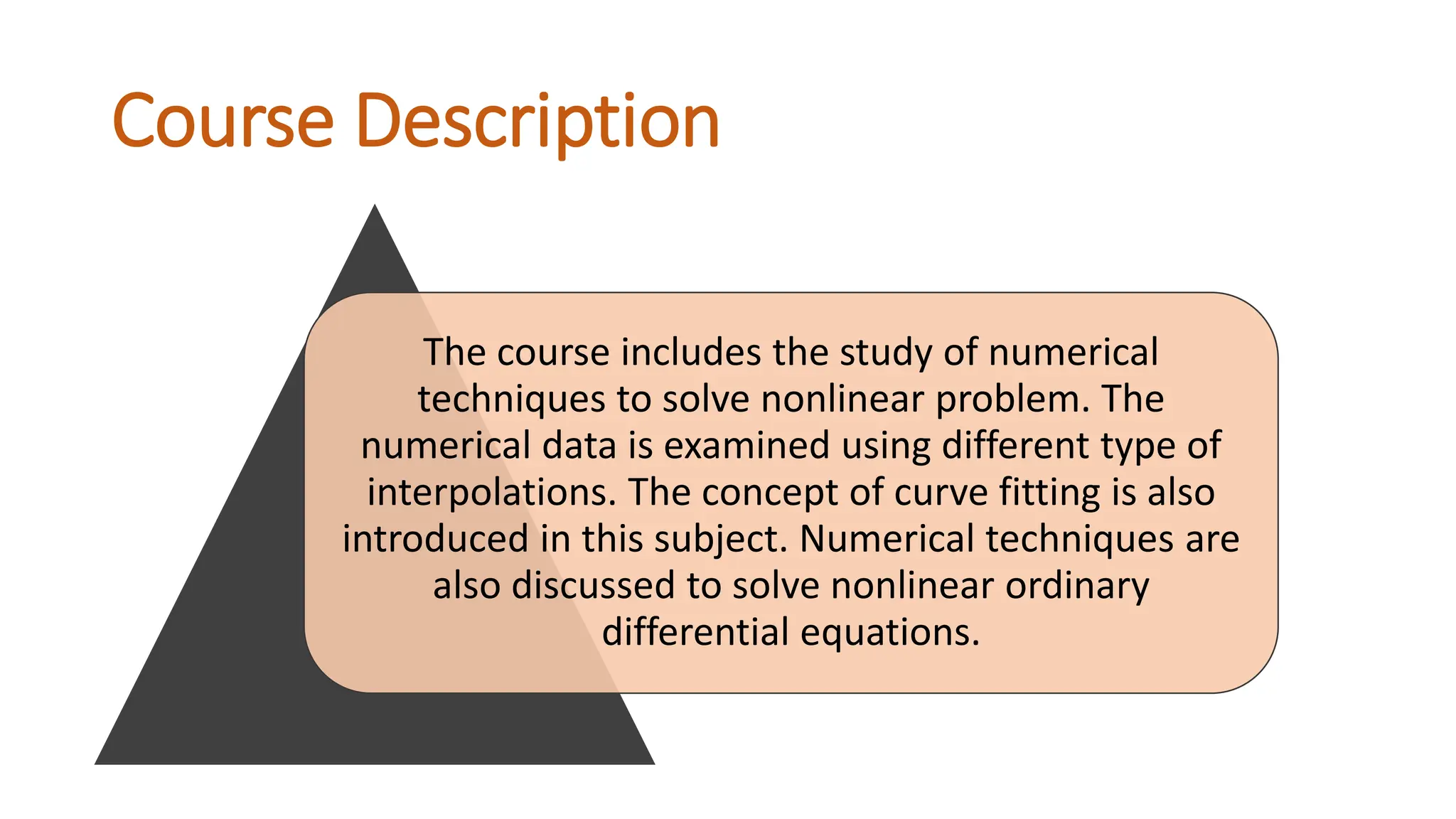
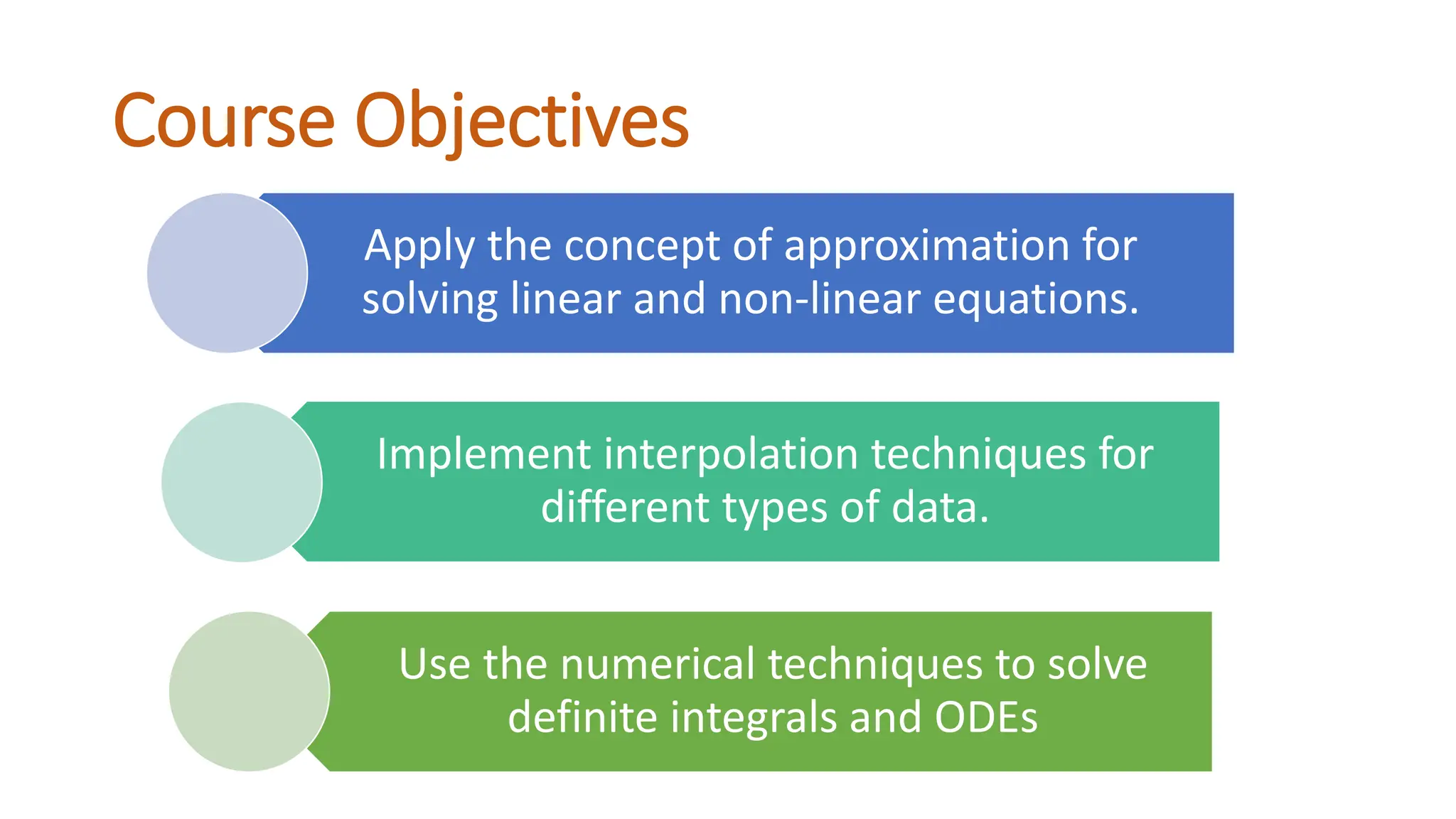
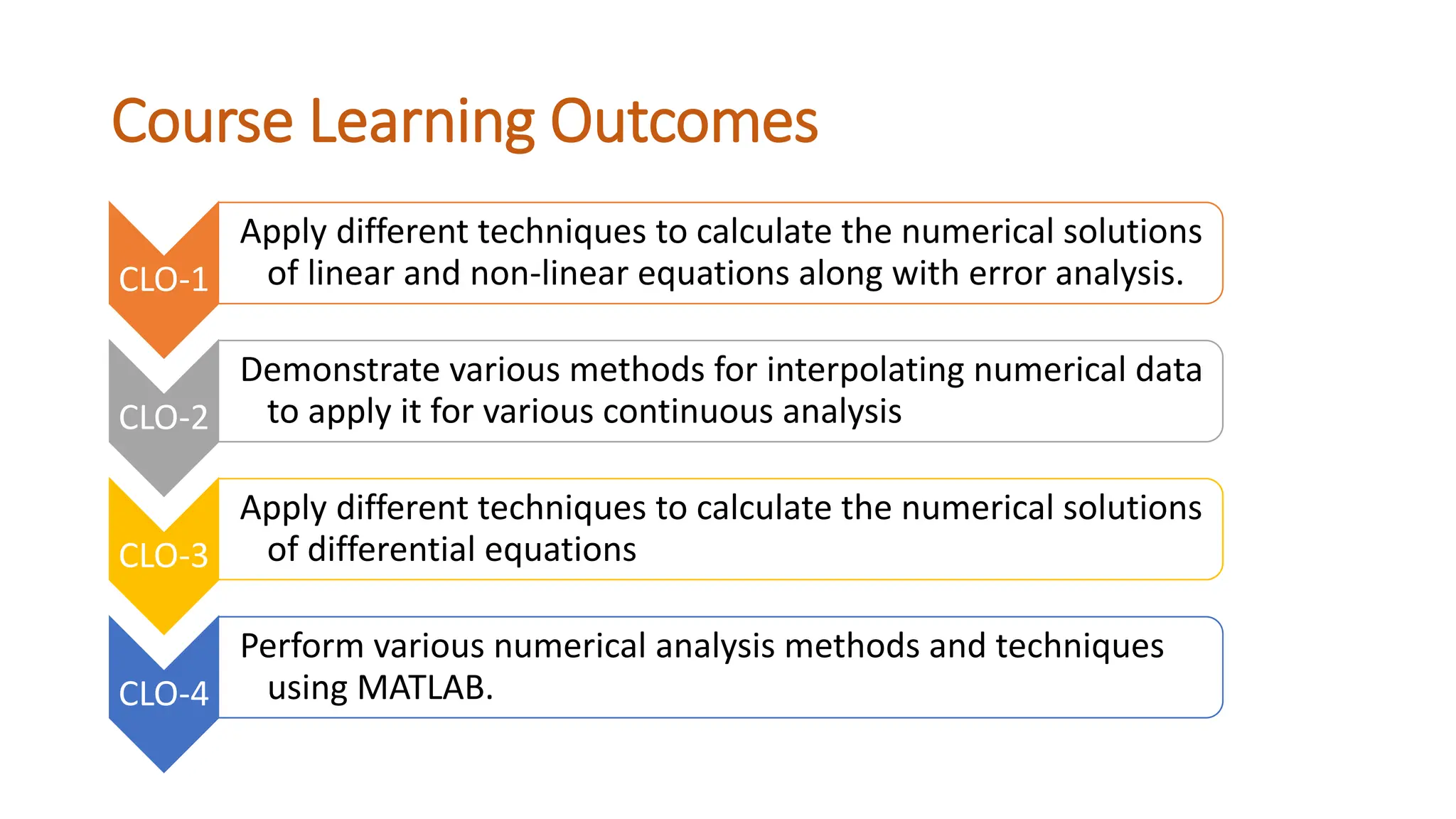
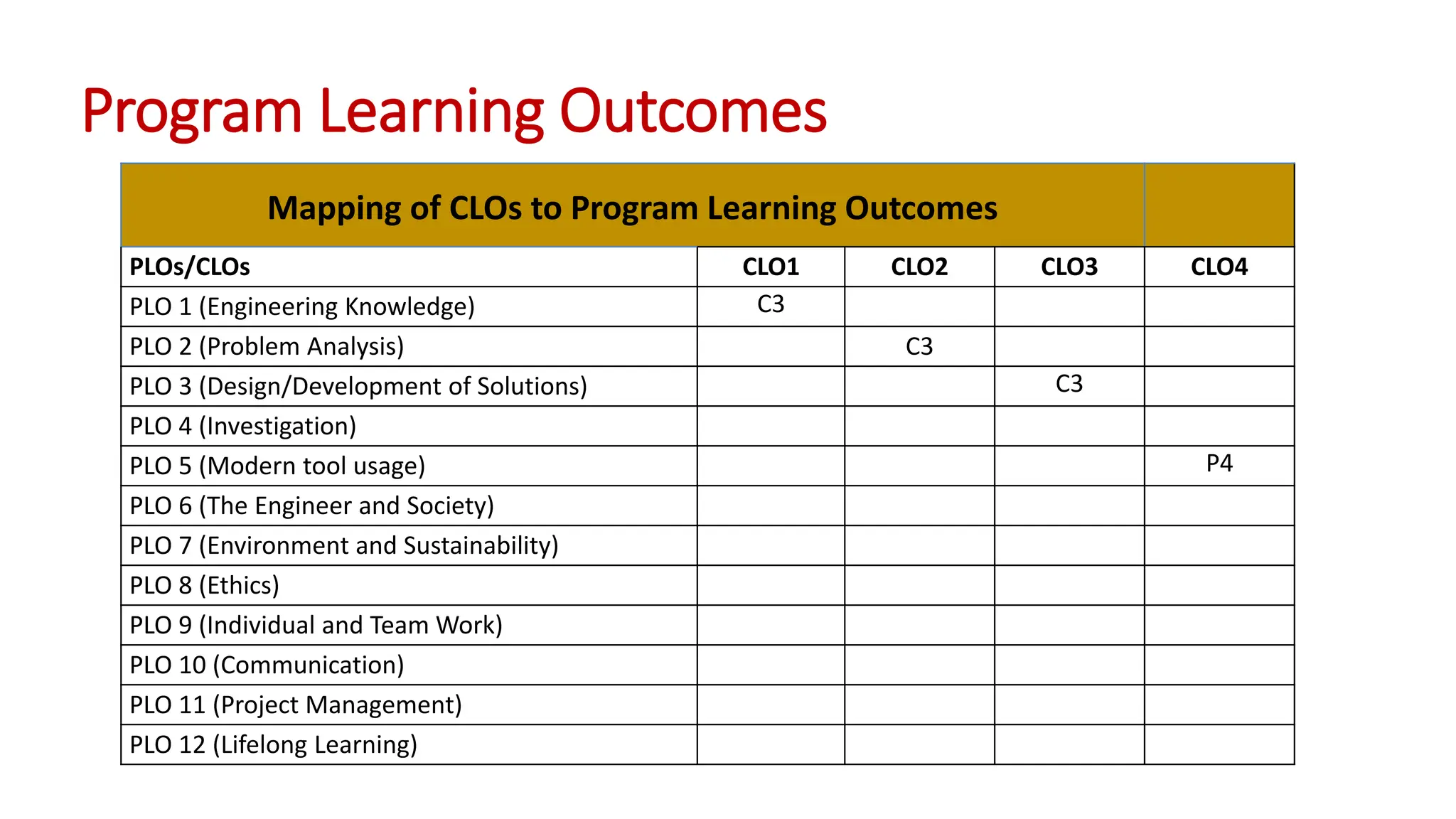
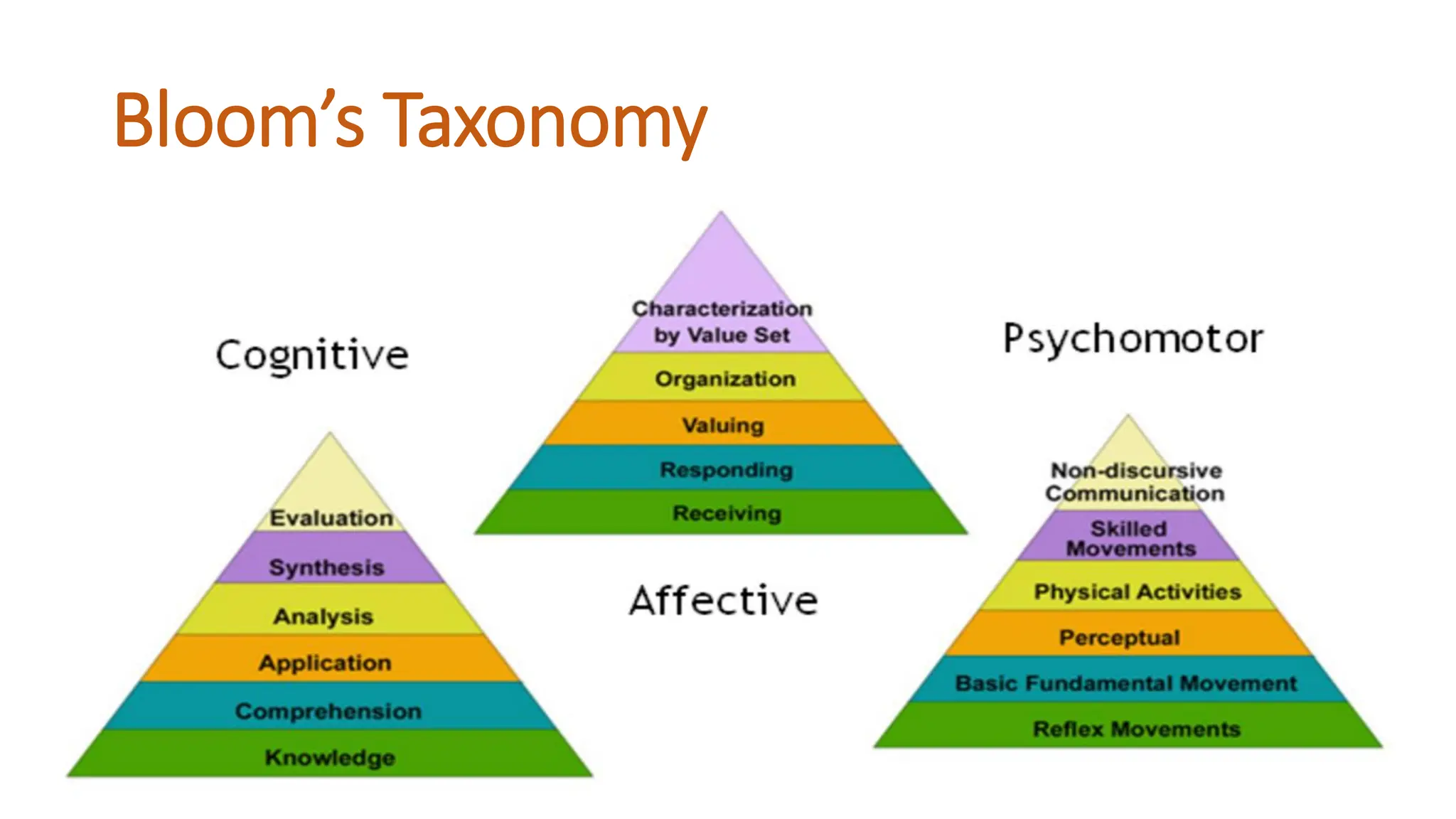
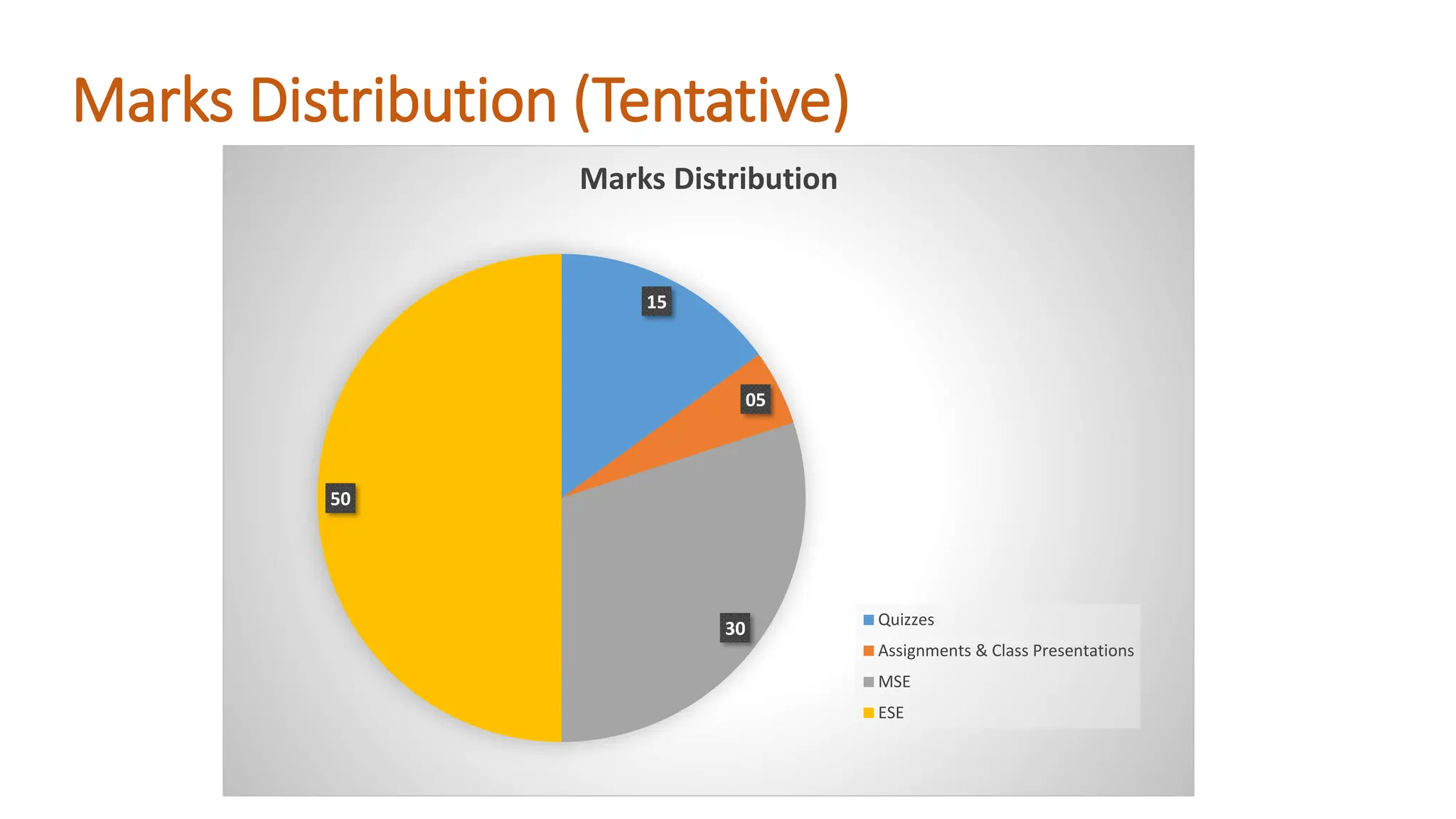
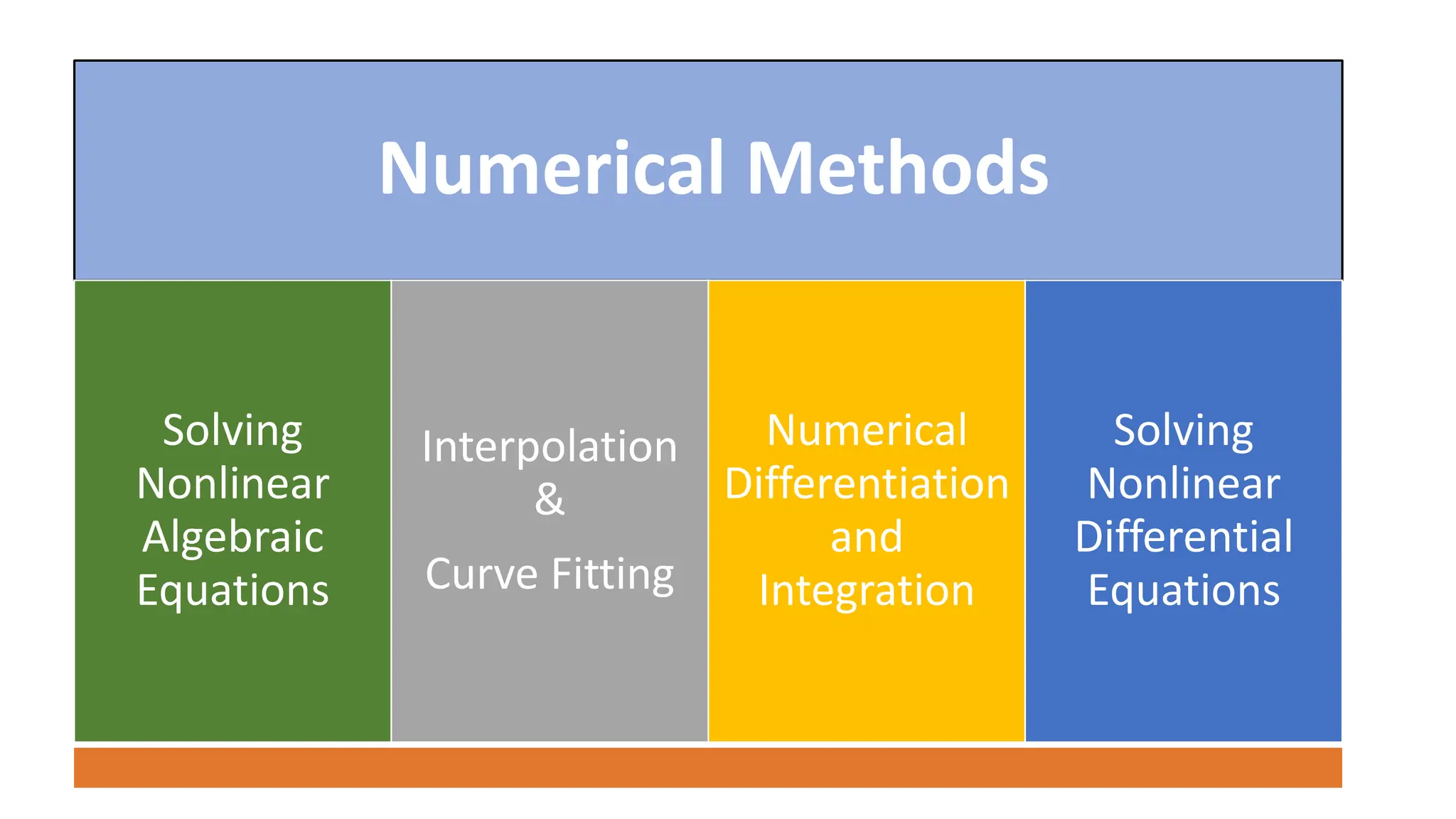
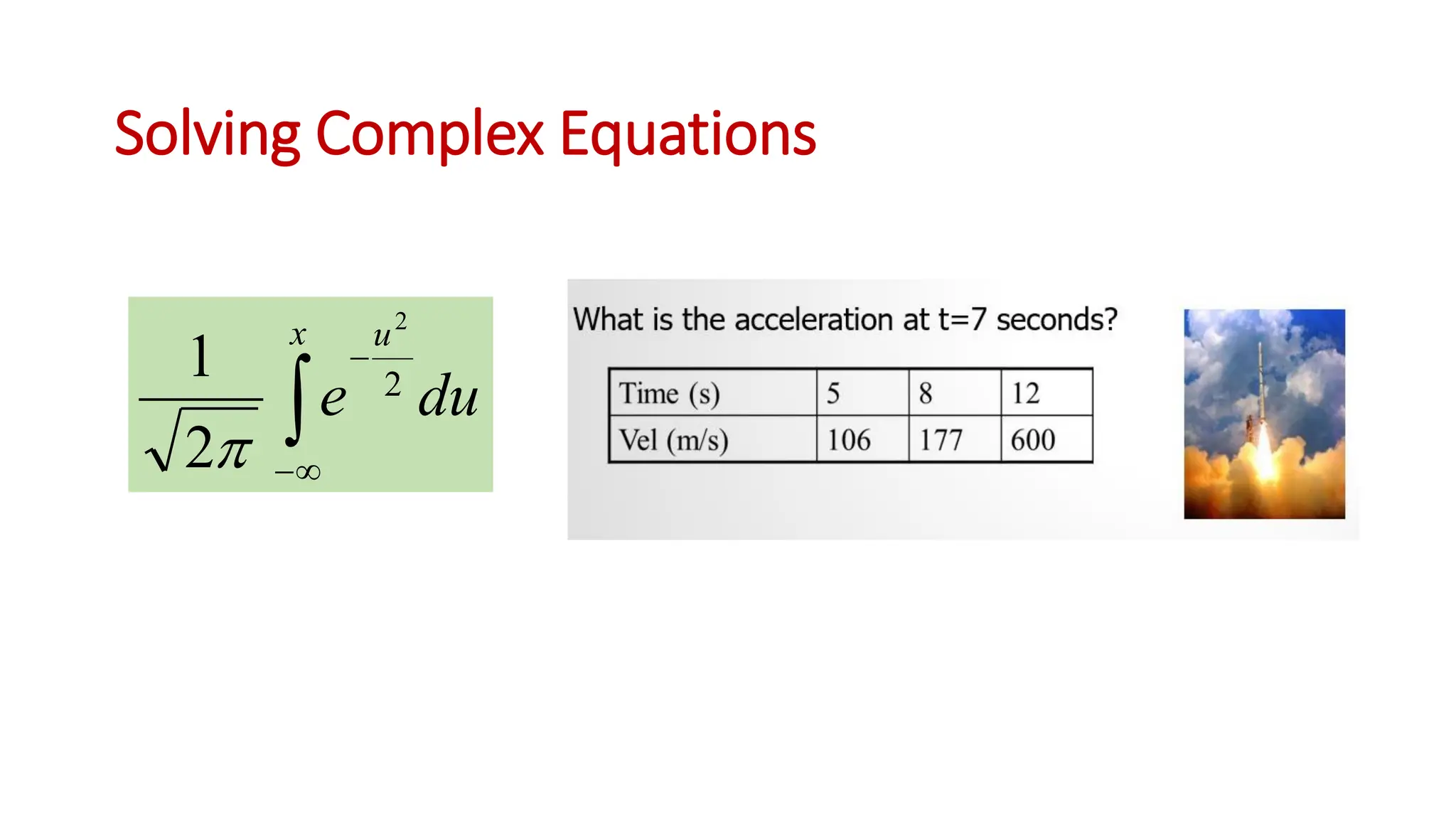
The document outlines the Numerical Methods course (MATH-352) taught by Dr. Hina Dutt, covering topics such as approximation techniques, interpolation, and solutions to differential equations. Key objectives include applying numerical methods for data analysis and performing computations using MATLAB. The course incorporates various assessments and aligns with program learning outcomes related to engineering knowledge and problem-solving.