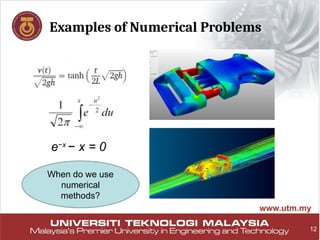
The document outlines a course on Applied Numerical Methods at Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, detailing the syllabus, learning outcomes, and assessment requirements. Students must attend at least 80% of lectures and can utilize various programming tools such as Fortran, C, and MATLAB for numerical problem-solving. The course aims to equip students with skills to model complex physical systems and solve governing equations using numerical methods.