The document summarizes the key functions and characteristics of the body's fluid compartments. It discusses:
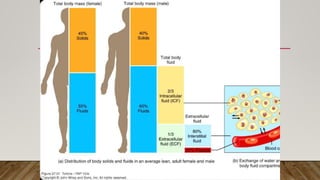
- Body fluids facilitate transport of nutrients, waste removal, and cellular metabolism. Total body water is 60% of weight, with two-thirds being intracellular fluid and one-third extracellular fluid.
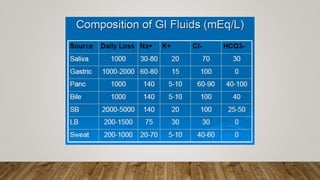
- Extracellular fluid contains sodium as the main cation while intracellular fluid contains potassium. Both fluids contain bicarbonate, chloride, and proteins as main anions.
- Transport of molecules across cell membranes can occur passively via diffusion or actively via carrier proteins and active transport pumps requiring ATP. Endocytosis and exocytosis allow transport of larger particles into and out of cells.

![INTRODUCTION
FUNCTIONS OF BODY FLUIDS
• Facilitate in the transport [nutrients, hormones, proteins,& others]
• Aid in removal of cellular metabolic wastes
• Provide medium for cellular metabolism
• Regulate body temperature
• Provide lubrication of musculoskeletal jts. and all
• body cavities [parietal, pleural fluids]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1bodyfluids-230125213325-c0087396/85/1-BODY-FLUIDS-pptx-2-320.jpg)










![TRANSPORT ACROSS CELL MEMBRANE
• Transport across cell membrane
• [I] Transport of small molecules (Micromolecules):
• A) Passive transport (diffusion):
• 1- Simple diffusion.
• 2- Facilitated diffusion.
• B) Active transport:
• 1- Primary active transport.
• 2- Secondary active transport.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1bodyfluids-230125213325-c0087396/85/1-BODY-FLUIDS-pptx-15-320.jpg)
![• [II] Transport of large molecules (macromolecules):
• “Vesicular Transport”
• Endocytosis.
• Exocytosis.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1bodyfluids-230125213325-c0087396/85/1-BODY-FLUIDS-pptx-16-320.jpg)








